| 53. Schiller, from the Theosophical Standpoint (Schiller Festival)
04 May 1905, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The question of freedom faces Schiller's soul, as deeply as it was never possibly put and treated in the whole German cultural life. Kant had also brought up this question shortly before. Schiller has never been a Kantian, at least he overcame Kantianism soon. During the wording of these letters he was no longer on Kant's point of view. Kant speaks of the duty so that the duty becomes a moral imperative. “Duty, you lofty and great name. You have nothing popular or mellifluous in yourself but you request submission, … you establish a law... in front of it all propensities fall silent if they counteract secretly against it...” Kant demands submission to the categorical imperative. However, Schiller renounced this Kantian view of duty. |
| 53. Schiller, from the Theosophical Standpoint (Schiller Festival)
04 May 1905, Berlin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
I have often emphasised here that the theosophical movement cannot disabuse us of the immediate reality, of the duties and tasks that the day imposes on us in this time. Now it must become apparent whether this theosophical movement finds the right words if it concerns to give us an understanding of the great spiritual heroes who are, in the end, the creators of our culture and education. During these days, everybody who counts himself among the German education directs his thoughts upon one of our greatest spiritual heroes, on our Friedrich Schiller (1759–1805). Hundred years separate us from his earthly decease. The last big celebration of Schiller, which was committed not only within Germany, but also in England, in America, in Austria, in Russia, was in 1859, on his hundredth birthday. It was interlinked with jamborees, with devoted words to the highest idealism of Schiller. These were words that were spoken over whole regions of the earth. There will be again jamborees which are celebrated during these days to honour of our great spiritual hero. However, as intimate and sincere and honest as the sounds were, which were spoken in those days in 1859, so intimate and devoted and completely spoken from the heart the words will not be that are spoken about Schiller today. Education and the national view about Schiller has substantially changed during the last fifty years. In the first half of the 19th century, Schiller's great ideals, the great portrayals of his dramas settled down, slowly and gradually It was an echo of that which Schiller himself had planted, an echo of that which he had sunk in the hearts and souls which flowed in enthusiastic words from the lips of the best of the German nation in those days. The most excellent men of this time have exerted their best to say what they had to say. There the brothers Ernst and Georg Curtius, the aesthete Vischer, the linguist Jacob Grimm, Karl Gutzkow and many others united. They joined in the big choir of Schiller celebrations and everywhere it sounded in such a way, as if one heard anything from Schiller himself, anything of that which Schiller himself had planted. We have to acknowledge to ourselves that this changed in the last decades. The immediate interest in Schiller has decreased because Schiller's great ideals do no longer speak so familiarly and intimately to our contemporaries. Hence, it may be a substitute that we bear in mind clearly and vividly what Schiller can still be for our present and future. It behoves the theosophist above all to take the big theosophical basic questions up and to ask himself whether Schiller has to do anything with these theosophical basic questions. I hope that the course of this evening shows that it is not pure invention if we bring together Schiller and the theosophical movement, if we theosophists feel called in certain way to care for the remembrance of Schiller. What is our basic question, what do we long for, what do we want to investigate and fathom? It is the big question to find the way to that which surrounds us as sense-perceptible objects and to that which is beyond the sensuous, as the spiritual, the super-sensible that lives in us and above us. This was also an early question which moved our Schiller. I cannot get involved in details. But I would like to show one thing, nevertheless, that Schiller's life and work was penetrated by this basic question: how is the physical with the psycho-spiritual, the super-sensible connected? Schiller wanted to solve this problem from the beginning of his life up to the heights of his work, even through his whole work, which is the artistic and philosophical expression of this question. At that time, he wrote a treatise after he had completed his study of medicine. This treatise, a kind of thesis, which he wrote with the departure from the Karlsschule (elite military academy) addresses the question: which is the interrelation between the sensuous nature of the human being and his spiritual nature? Schiller treats in this work emphatically and nicely how the spirit is connected with the physical nature of the human being. Our time has already outdistanced what Schiller answers to this question; but that does not matter with such a great genius like Schiller. It matters how he engrossed his mind and how he put up with such things. Schiller understood this in such a way that there no conflict may be permitted between the sensuous and the spiritual. Thus he tried to subtly show how the spirit, how the soul of the human being works on the physical, that the physical is only an expression of the spirit living in the human beings. Any gesture, any form and any verbal utterance is an expression of it. He investigates at first how the soul enjoys life in the body; then he investigates how the physical condition works on the mind. Briefly, the harmony between body and soul is the sense of this treatise. The end of the treatise is brilliant. There Schiller speaks of death in such a way, as if this is no completion of life, but only an event like other events of life. Death is no completion. He says already there: life causes death once; but life is not finished with it; the soul goes, after it has experienced the event of death, into other spheres to look at life from the other side. However, has the human being already sucked out all experience from life really at this moment? Schiller thinks that it might very well be possible that the life of the soul within the body appears as if we read in a book which we peruse, put aside and take in hand again after some time to understand it better. Then we put it aside again, after some time we take it in hand et etcetera to understand it better and better. He says to us with it: the soul lives not only once in the body, but like the human being takes a book in hand again and again, the soul returns repeatedly to a body to make new experiences in this world. It is the great idea of reincarnation, which Lessing had touched shortly before in his Education of the Human Race like in his literary will, and which Schiller also expresses now where he writes about the interrelation of the sensuous nature with the spiritual nature of the human being. At the very beginning, Schiller starts considering life from the highest point of view. Schiller's first dramas have an intense effect on somebody who has a feeling heart for what is great in them. If we ask ourselves why Schiller's great thoughts flow into our hearts, then we get the answer that Schiller touches matters in his dramas which belong to the highest of humanity. The human being does not always need to understand and realise in the abstract what takes place in the poet's soul if he lonely forms the figures of imagination. But what lives there in the breast of the poet when he forms his figures, which move there on the stage, we see this already as young people in the theatre, or if we read the dramas. There flows in us what lives in the poet's soul. What lived in Schiller's soul at that time when he out-poured his young soul in his Robbers, in Fiesco, in Intrigue and Love. We must take him from the spiritual currents of the 18th century if we want to completely understand him. Two spiritual currents existed which influenced the spiritual horizon of Europe at that time. A term of the French materialism calls one current. If we want to understand it, we have to see deeper into the development of the nations. What seethed in Schiller's soul has taken its origin in the striving and thinking of centuries. Approximately around the turn of the 15-th to the 16-th century the time begins when the human beings looked up at the stars in a new way. Copernicus, Kepler, Galilei, they are those who bring up a new age, an age in which one looks at the world differently than before. Something new crept into the human souls relying on the external senses. Who wants to compare the difference of the old world view of the12th, 13th centuries with that which arose around the turn of the 16th century with Copernicus and later with Kepler must compare what plays in Dante's Divine Comedy with the world view of the 17th, 18th centuries. One may argue against the medieval world view as much as one likes. It can no longer be ours. But it had what the 18th century did no longer have: it arranged the world as a big harmony, and the human being was arranged in this divine world order as its centre, he himself belonged to this big harmony. All things were the outflow of the divine, of the creativity which was revered in faith, in particular that of Christianity. The superior was an object of faith. It had to hold and bear. And this had an effect down to the plants and minerals. The whole world was enclosed in a big harmony, and the human being felt existing in this harmony. He felt that he can be released growing together and being interwoven with this divine harmony. He rested in that which he felt as the world permeated by God, and he felt contented. This changed and had to change in the time when the new world view got entrance in the minds when the world was permeated with the modern spirit of research. There one had gained an overview about the material. By means of philosophical and physiological research one had received an insight into the sensory world. One could not harmonise what one thought of the sensuous world with faith this way. Other concepts and other views took place. However, the human beings could not harmonise their new achievements with that which they thought and felt about the spirit. One could not harmonise it with that which one had to believe about the sources of life according to the ancient traditions. Thus something came up in the French Revolution that one can express with the sentence:”the human being is a machine.” One had understood the substances, but one had lost the connection with the spirit. One felt the spiritual in oneself. However, one did not feel how the world is connected with it; one did no longer have this. The materialists created a new world view in which actually nothing but substances existed. Goethe was repelled by such views like Holbach's Systeme de la nature, he found it empty and dull. But this world view of Holbach (1723–1789) was got out of the scientific view. It mirrors the external truth. How should the human being face up to it now who has lost the spirit? He has lost the connection, he has lost the harmony which the medieval human being felt, the harmony between the soul and the material. Thus the best spirits of that time had to strive to find the connection again or were forced to choose between the spiritual and the sensuous. This was, as we have seen, Schiller's basic question in his youth, this interrelation between ideal and reality, nature and spirit. But the trend had torn up a deep abyss between the spiritual and the sensuous, it pressed like a nightmare on his soul. How can one reconcile ideal and reality, nature and spirit? This was the question. This abyss had been still torn open by another trend, which issued from Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712–1778). Rousseau had rejected the culture modern at that time up to a certain degree. He had found that the human being alienated himself by this culture, that he has torn out himself from nature. He had alienated himself from nature not only by the world view; he also could no longer find the connection with the spring of life. Therefore, he had to long for the return to nature, and thus Rousseau establishes the principle that basically the culture diverts the human beings from the true harmonies of life, that it is a product of decline. At that time, the question of the spiritual, of the ideal had faced up the greatest of the contemporaries in new form: why should it not be there if they looked at life? In the time in which one felt the ideal of life so much, one had to feel the conflict twice if one looked at the real life as it had developed, and then at that which there was in the human society. Schiller's teens were in this time. All that towered up; and Schiller had to feel that as disharmony. His youth dramas originated from this mood. Back to the ideal! Which is the right social existence which is decreed to us in a divine world order? These are the feelings which lived in Schiller's youth, which he expressed then in his dramas, in the Robbers, in particular, however, also in the court dramas; we feel them if we take in the great drama Don Carlos. We have seen how the young doctor Schiller put the basic question of the interrelation between the sensuous and the spirit, and that he put it as a poet before his contemporaries. After the hard trials which he was exposed to on account of his youth dramas he was invited by the father of the freedom poet Körner (Christian Gottfried K., 1756–1831) who did everything to support the cultural life. Körner's fine philosophical education brought Schiller to philosophy, and now the question arose philosophically before Schiller's mind anew: how can the interrelation of the sensuous with the spirit be found again? What was spoken in those days in Dresden between Schiller and Körner (1785–1787) and which great ideas were exchanged is reflected in Schiller's philosophical letters. Indeed, these may be somewhat immature compared with Schiller's later works. What is immature, however, for Schiller, is still very ripe for many other people and is important for us because it can show us how Schiller has struggled up to the highest heights of thinking and imagination. These philosophical letters, The Theosophy of Julius, represent the correspondence between Julius and Raphael; Schiller as Julius, Körner as Raphael. The world of the 18-th century faces us there. Nice sentences are in this philosophy, sentences like those which Paracelsus expressed as his world view. In the sense of Paracelsus that of the whole outside world is shown to us which the divine creativity accomplished in the most different realms of nature: minerals, plants, animals with capacities of the most varied kind are spread out over nature. The human being is like a big summary, like a world like an encyclopaedia repeats everything once again in itself that is otherwise scattered. A microcosm, a little world in a macrocosm, a big world! Like hieroglyphics, Schiller says, is that which is contained in the different realms of nature. The human being stands there as the summit of the whole nature, so that he combines in himself and expresses on a higher level what is poured out in the whole nature. Paracelsus expressed the same thought largely and nicely: all beings of nature are like the letters of a word, and, if we read them, nature represents her being, a word results which presents itself in the human being. Schiller expresses this lively and emotionally in his philosophical letters. It is so lively to him that the hieroglyphics speak vividly for themselves in nature. I see, Schiller says, the chrysalises outside in nature which change to the butterflies. The chrysalis does not perish, it shows a metamorphosis; this is a guarantee to me that also the human soul changes in similar way. Thus the butterfly is a guarantee of human immortality to me. In the most marvellous way the thoughts of the mind associate themselves in nature with the thought which Schiller studies as that which lives in the human soul. Then he struggles up to the view that the force of love lives not only in the human being, but finds expression in certain stages all over the world, in the mineral, in the plant, in the animal, and in the human being. Love expresses itself in the forces of nature and most purely in the human being. Schiller phrases that in a way which reminds of the great mystics of the Middle Ages. He calls what he pronounced that way the Theosophy of Julius. At it he developed up to his later approaches to life. His whole lifestyle, his whole striving is nothing else than a big self-education, and in this sense Schiller is a practical theosophist. Theosophy is basically nothing else than self-education of the soul, perpetual work on the soul and its further development to the higher levels of existence. The theosophist is convinced that he can behold higher and higher things the higher he develops. Who accustoms himself only to sensuality can see the sensuous only; who is trained for the psycho-spiritual sees soul and spirit around himself. We have to become spirit and divine first, then we can recognise something divine. The Pythagoreans already said this in their secret schools that way, and Goethe also said it in accordance with an old mystic:
But we must develop the forces and capacities which are in us. Thus Schiller tries to educate himself throughout his whole life. A new stage of his self-development is his aesthetic letters, About the Aesthetic Education of Man in a Series of Letters. They are a jewel in our German cultural life. Only somebody can feel what mysteriously pours out between and from the words also from Schiller's later dramas who knows these aesthetic letters; they are like a heart- balm. Who has concerned himself a little with the lofty spiritual, educational ideal, which lives in his aesthetic letters, has to say: we have to call these aesthetic letters a book for the people. Only when in our schools not only Plato, not only Cicero, but Schiller's aesthetic letters are equally studied by the young people, one will recognise that something distinct and ingenious lives in them. What lives in the aesthetic letters becomes productive first if the teachers of our secondary schools are permeated with this spiritual life, if they let pour in something of that which Schiller wanted to bring up giving us this marvellous work. In the modern philosophical works you do not find any reference to these aesthetic letters. However, they are more significant than a lot that has been performed by the pundits of philosophy, because they appeal to the core of the human being and want to raise this core a stage higher. Again, it is the big question which faces Schiller in the beginning of the nineties of the 18th century. He puts the question now in such a way: the human being is subjected, on one side, to the sensuous hardships, the sensuous desires and passions. He is subjected to their necessities, he follows them, he is a slave of the impulses, desires and passions. The logical necessity stands on the other side: you have to think in a certain way. The moral necessity stands on the other side, too: you must submit to certain duties. The intellectual education is logically necessary. The moral necessity demands something else that exceeds the modern view. Logic gives us no freedom, we must submit to it; also the duty gives us no freedom, we must submit to it. The human being is put between logical necessity and the needs of nature. If he follows the one or the other, he is not free, a slave. But he should become free. The question of freedom faces Schiller's soul, as deeply as it was never possibly put and treated in the whole German cultural life. Kant had also brought up this question shortly before. Schiller has never been a Kantian, at least he overcame Kantianism soon. During the wording of these letters he was no longer on Kant's point of view. Kant speaks of the duty so that the duty becomes a moral imperative. “Duty, you lofty and great name. You have nothing popular or mellifluous in yourself but you request submission, … you establish a law... in front of it all propensities fall silent if they counteract secretly against it...” Kant demands submission to the categorical imperative. However, Schiller renounced this Kantian view of duty. He says: “with pleasure I serve the friends, however, I do it, unfortunately, with propensity” and not with that which kills propensity which even kills love. Kant demands that we act from duty, from the categorical imperative. Schiller wants harmony between both, a harmony between propensity and passion on the one hand and duty and logic on the other side. He finds it at first in the view of beauty. The working of beauty becomes a big universal music and he expressed this: ”Only through beauty's morning gate you enter the land of knowing.” If we have a piece of art, the spiritual shines through it. The piece of art does not appear to us as an iron necessity, but as a semblance that expresses the ideal, the spiritual to us. Spirit and sensuality are balanced in beauty. As to Schiller, spirit and sensuality must also be balanced in the human being. Where the human being is between these two conditions, where he depends neither on the natural necessity nor on the logic one, but where he lives in the condition which Schiller calls the aesthetic one, passion is overcome. He got down the spirit to himself, he purified sensuality with beauty; and thus the human being has the impulse and the desire to do voluntarily what the categorical imperative has demanded. Then morality is something in the human being that has become flesh and blood in him, so that the impulses and desires themselves show the spiritual. Spirit and sensuality have penetrated the aesthetic human being that way, spirit and sensuality have interpenetrated in the human being because he likes what he has to do. What slumbers in the human being has to be awakened. This is Schiller's ideal. Also concerning the society, the human beings are forced by the natural needs or by the rational state to live together according to external laws. The aesthetic society is in between where love accomplishes what every human being longs for and what is imposed on him by his innermost propensity. In the aesthetic society, the human beings freely co-operate, there they do not need the external laws. They themselves are the expression of the laws according to which the human beings have to live together. Schiller describes this society where the human beings live together in love and in mutual propensity and do voluntarily what they should and have to do. I could only outline the thoughts of Schiller's aesthetic letters in a few words. But they have an effect only if they are not read and studied, but if they accompany the human being like a meditation book through the whole life, so that he wants to become as Schiller wanted to become. At that time, the time had not yet come. It has come today where one can notice the large extent of a society which founds the interrelation of human beings on love as its first principle. At that time, Schiller tried to penetrate such a knowledge and such a living together. Schiller wanted to educate the human beings with his art at least, so that they become ripe once because his time was not ripe to create the free human beings in a free society. It is sad how little just these most intimate thoughts and feelings of Schiller have found entrance in the educational life which would have to be filled completely with them, which should be a summary of them. In my talks on Schiller, which I have held in the “Free College,” I have explained how we have to understand Schiller concerning the present. I tried there to show the thoughts in coherent and comprehensive way. You can read up there in detail what I can only indicate today. In any Schiller's biography you can find basically only little of these intimacies of Schiller. But once a pedagogue, a sensitive, dear pedagogue concerned himself with the content of Schiller's aesthetic letters in nice letters. Deinhardt (Heinrich D., 1805-1867) was his name. I do not believe that you can still buy the book. All teachers, in particular of our secondary schools, had to purchase it. However, I believe, it was pulped. The man, who wrote it, could hardly achieve a poor tutor's place. He had the mishap to pick up a leg fracture; the consulted doctors said that the leg fracture could be cured, however, the man were too badly nourished. Thus he died as a result of this accident. After Schiller had advanced to this point of his life that way, something very important occurred to him: an event took place that intervened deeply in his life and also in the life of our whole nation. It is an event which is very important generally for the whole modern spiritual life. This is the friendship between Schiller and Goethe. It was founded peculiarly. It was at a meeting of the “Society of Naturalists” in Jena. Schiller and Goethe visited a talk of a significant scientist, Batsch (Johann Karl B., 1761-1802, botanist). It happened that both went together out of the hall. Schiller said to Goethe: this is such a fragmented way to look at the natural beings; the spirit that lives in the whole nature is absent everywhere. Thus Schiller put his basic question again to Goethe. Goethe answered: there may probably be another way to look at nature. Goethe had also pointed in his Faust to that where he says that somebody who searches in such a way expels the spirit, then he has the parts in his hands “however, unfortunately, the spirit band is absent.” Goethe had seen something in all plants that he calls the archetypal plant (Urpflanze), in the animals what he calls the archetypal animal. He saw what we call the etheric body and he drew this etheric body with a few characteristic lines before Schiller. He realised that something really living expresses itself in every plant. Schiller argued: “yes, however, this is no experience, this is an idea!” Goethe responded: “this can be very dear to me that I have ideas without knowing it, and even see them with my eyes.” Goethe was clear in his mind that it was nothing else than the being of the plant itself. Schiller had now the task to attain the great and comprehensive view of Goethe. It is a fine letter, which I have mentioned already once; it contains the deepest psychology which generally exists and with which Schiller makes friends with Goethe. “For a long time and with always renewed admiration I have already observed the course of your mind although from considerable distance and the way, which you have marked for yourself. You search for the necessary of nature, but you search for it in the most difficult way, for any weaker strength will probably take good care not do that. You summarise the whole nature to get light about the single; you try to explain the individual in all its appearances. From the simple organisation you ascend step by step to the more intricate one to build, finally, the most intricate one of all, the human being, genetically from the materials of the whole nature. Because you recreate him in nature as it were, you try to penetrate his concealed techniques. A great and really heroic idea which shows well enough how much your mind holds together the whole wealth of its ideas in an admirable unity. You can never have hoped that your life will suffice to such a goal, but even to take such a way is more worth than to finish any other and you have chosen like Achilles in the Iliad between Phthia and immortality. If you had been born as a Greek, or just as an Italian, and a choice nature and an idealising art had surrounded you already from the cradle, your way would be endlessly shortened, would maybe rendered quite superfluous. Then already in the first observation of the things you would have comprehended the form of the necessary, and with your first experiences the great style would have developed in you. Now, because you are born as a German, because your Greek mind was thrown into this northern creation, no other choice remained to you to become either a northern artist, or to give your imagination what reality refused to it to substitute with the help of mental capacity and to bear a Greece as it were from within on a rational way.” This is something that continued having an effect on Schiller as we will see immediately. Schiller now returns again to poetry. What had a lasting effect faces us in his dramas. Greatly and comprehensively life faces us in Wallenstein. You do not need to believe that you find the thoughts which I develop now, if you read Schiller's dramas. But deeply inside they lie in his dramas, as well as the blood in our veins pulsates, without us seeing this blood in the veins. They pulsate in Schiller's dramas as blood of life. Something impersonal is mixed in the personal. Schiller said to himself: there must be something more comprehensive that goes beyond birth and death. He tried to understand which role the great transpersonal destiny plays in the personal. We have often mentioned this principle as the karma principle. In Wallenstein he describes the big destiny which crushes or raises the human being. Wallenstein tries to fathom it in the stars. Then, however, he realises again that he is drawn by the threads of destiny, that in our own breasts the stars of our destinies are shining. Schiller tries to poetically master the personal, the sensuous nature in connection with the divine in Wallenstein. It would be inartistic if we wanted to enjoy the drama with these thoughts. But the big impulse flows unconsciously into us which originates from this connection. We are raised and carried to that which pulsates through this drama. In each of the next dramas, Schiller tries to reach a higher level to educate himself and to raise the others with him. In The Maid of Orleans transpersonal forces play a role in the personal. In The Bride of Messina he tries to embody something similar going back to the old Greek drama. He attempts to bring in a choir and a lyrical element there. Not in the usual colloquial language, but in sublime language he wanted to show destinies, which rise above the only personal. Why Schiller tied in with the Greek drama? We must visualise the origin of the Greek drama itself. If we look back to the Greek drama behind Sophocles and Aeschylus, we come to the Greek mystery drama, to the original drama whose later development stages are those of Aeschylus, Sophocles and Euripides. In his book The Birth of the Tragedy from the Spirit of Music (1872) Nietzsche (1844–1900) tries to explore the origin of the drama. In the Homeric time, something was annually brought forward to the Greeks in great dramatic paintings that was at the same time religion, art and science truth, devoutness and beauty. What did this original drama thereby become? This original drama was not a drama which shows human destinies. It should show the godhead himself as the representative of humanity Dionysus. The god, who has descended from higher spheres, who embodies himself in the material substances, who ascends through the realms of nature to the human being to celebrate his redemption and resurrection in the human being. This path of the divine in the world was shaped most beautifully in the descent, in the resurrection and the ascension of the divine. This original drama took place in manifold figures before the eyes of the Greek spectators. The Greek saw what he wanted to know about the world, what he should know as truth about the world, the triumph of the spiritual over the natural. Science was to him what was shown in these dramas, and it was shown to him in such a way that this presentation was associated with devoutness and could be a model of the human lifestyle. Art, religion and wisdom was that which happened before the spectators. The single actors spoke not in usual language, but in sublime language about the descent, the suffering and overcoming, about the resurrection and ascension of the spiritual. The choir reflected what happened there. It rendered what took place as a divine drama in the simple music of the past. From this homogeneous spring flows out what we know as art, as science, which became physical, and as religion, which emerged from these mysteries. Thus we look back at something that links art with truth and religious devoutness. The great re-thinker of the Greek original drama, the French author Edouard Schuré (1841–1929), attempted in our time to rebuild this drama. You can read up this really ingenious rebuilding in The Holy Drama of Eleusis (Le drame sacré d'Eleusis). Engrossing his mind in this drama he got to the idea that it is a task of our time to renew the theatre of the soul and the self. In The Children of Lucifer (Les Enfants de Lucifer) he tries to create a modern work that connects self-observation and beauty, dramatic strength and truth content with each other. If you want to know anything about the drama of the future, you can get an idea of it in these pictures of The Children of Lucifer. The whole Wagner circle strives for nothing else than to show something transpersonal in the dramas. In Richard Wagner's dramas, we have the course from the personal to the transpersonal, to the mythical. Hence, Nietzsche also found the way to Wagner when he sought the birth of the tragedy in the original drama. Schiller had already tried in his Bride of Messina what the 19th century aimed at. In this drama, the spiritual is represented in sublime language, and the choir echoes the divine actions before us. He says in his exceptionally witty preface of the writing About the Use of the Choir in the Tragedy from which depths he wanted to bear a Greece in those days. This writing is again a pearl of German literature and aesthetics. Schiller attempted the same that the 19th century wanted to enter the land of knowing through beauty's morning gate and to be a missionary of truth. With the drama Demetrius which he could not finish because death tore him away, with this drama he tried to understand the problems of the human self, with a clearness and so greatly and intensely that none of those who tried it could finish Demetrius because the great wealth of Schiller's ideas is not to be found with them. How deeply he understands the self that lives in the human being! Demetrius thinks of himself because of certain signs that he is the real Russian successor to the throne. He does everything to attain what is due to him. At the moment when he is near to arrive at his goal everything collapses that had filled his self. He has now to be what he has made of himself merely by the strength of his inside. This self which was given to him does no longer exist; a self which should be his own action should arise. Demetrius should act out of it. The problem of the human personality is grasped grandiloquently like by no other dramatist of the world. Schiller had such a great thing in mind when death tore him away. In this drama, something lies that with those who could not put it in clear words will now find more response. What was built in the human hearts and in the depths of human souls gushed out again in 1859. 1859 caused a change in the whole modern education. Four works appeared by chance round this time. They influenced the basic attitude of our education. One of them is Darwin's On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life that brought a materialistic movement with it. The second work was also typical, in particular concerning Schiller if we remember his words which he called out to the astronomers: “do not chat to me so much about nebulas and suns! Is nature only great, because she gives you something to count? Admittedly, your object is the loftiest in space; but, friends, the elated does not live in space.” But it became possible to understand just this elated in space by a work about the spectral analysis which Kirchhoff (Robert K., 1824–1887, physicist) and Bunsen (Robert Wilhelm B., 1811–1899, physicist) published. The third work was again in a certain opposition to Schiller. Gustav Theodor Fechner (1801–1887) wrote in idealistic spirit: The Preliminaries of Aesthetics (1876). An aesthetics should be created “from below.” Schiller had started it stupendously “from above.” Fechner took the simple sensation as his starting point. The fourth work carried materialism into the social life. What Schiller wanted to found as society was moved under the point of view of the crassest materialism in the work by Karl Marx (1818–1883) A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy (1859). All that crept in. These are things which were far from the immediate-intimate which Schiller poured in the hearts, honestly and sincerely. And now those who are exposed to the modern literature can no longer look at Schiller in such an idealistic way. Recently, in the last decade of the 19-th century, a man wrote a biography on Schiller who had grown together thoroughly with the aesthetic culture. The first word in it was: “I hated Schiller in my youth!” And only by his scholarly activity he was able to acknowledge Schiller's greatness. Who can listen only a little to what floods in our time sees that there a certain internal coercion prevails. Time has changed. Nevertheless, perhaps some great, enthusiastic words and some nice festivity will be also connected with Schiller. But somebody who has a good ear will not hear anything that still moved through the minds and souls before half a century when we revered Schiller. We must understand it; we do not reproach those who have no connection with Schiller today. But with the immense dimension of Schiller's oeuvre we have to concede to us: he has to become a component of our cultural education again. The immediate present has to follow Schiller again. Why should a society striving for spiritual deepening like the Theosophical Society not take Schiller up? He is still the first pre-school of self-education if we want to reach the heights of spirit. We get to knowledge differently, if we experience him. We come to the spiritual, if we experience his Aesthetic Letters. We understand the Theosophical Society as an association of human beings, without taking into consideration nation, gender, origin and the like, as an association merely on the basis of pure human love. In the course of his life, Schiller strove for the heights of spiritual being, and his dramas are basically nothing else than what wants to penetrate artistically into the highest fields of this spiritual being. What he sought was nothing else than to develop something everlasting and imperishable in the human soul. If we remember Goethe quite briefly again: with the word “entelechy“ he termed what lives in the soul as the imperishable what the human being develops in himself, acquires experiencing reality, and what he sends up as his eternal. Schiller calls this the forming figure. As to Schiller, this is the everlasting that lives in the soul that the soul develops constantly in itself, increases in itself and leads to the imperishable realms. It is a victory which the figure gains over the transient corporeality in which the figure only acts. Schiller calls it the everlasting in the soul-life, and we are allowed, like Goethe, after Schiller had deceased, to stamp the words: “he was ours.” If we understand Schiller with living mind, we are allowed to imbue ourselves with that which lived in him with which he lives in the other world, which took up his best friendly and affectionately. We are also allowed as theosophists to celebrate that mysterious connection with him which we can celebrate as a Schiller festival. As well as the mystic unites with the spiritual of the world the human being unites with the great spiritual heroes of humanity. Everybody who strives for a spiritual world view should celebrate such a festival, a “unio mystica,” for himself, still beside the big Schiller jamborees. Nothing should be argued against these big festivals. However, only somebody who celebrates this intimate festival in his heart connecting him with Schiller intimately finds Schiller's work. Aspiring to spirit we find the way best if we make it like Schiller who educated himself all his life. He expressed it, and it sounds like a motto of the theosophical world view:
|
| 136. Spiritual Beings in the Heavenly Bodies and in the Kingdoms of Nature: Lecture VI
08 Apr 1912, Helsinki Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| How often are children told at school—at least I do not know whether it is done here, but in Central Europe they are always told—that according to the Kant-Laplace system of the origin of the world a mass of original matter was in rotation from which then the separate planets split off. |
| The essential condition in the origin of this planetary system is however that the teacher should stand there and make it revolve, otherwise the whole system could not originate! The Kant-Laplace theory would thus only be possible if those who believe in it could at the same time supply a gigantic teacher in cosmic space, who would revolve the whole etheric mass. |
| This should be the answer to those who would believe that the ordinary materialistic theory as expressed in Kant-Laplace, or in later hypotheses, is sufficient to explain the cosmic system, and that it is not necessary to consider anything else, as do the occultists. |
| 136. Spiritual Beings in the Heavenly Bodies and in the Kingdoms of Nature: Lecture VI
08 Apr 1912, Helsinki Tr. Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In our last lecture we tried to consider a planetary system in its dependence on the various spiritual beings of the three hierarchies, ranged, as it were, one above the other; and which we tried to describe in the previous lectures. We gained an idea of all that participates in forming a planet, and we have seen how a planet receives its form, its enclosed form, as a result of the activity of the Spirits of Form. We saw further that the inner life, the inner mobility of the planet, is the result of the activity of the Spirits of Motion. What we may call the lowest consciousness of the planet, which can be compared with the consciousness present in man in his astral body, we have to allot to the Spirits of Wisdom. That impulse through which the planet, instead of remaining stationary changes its place in space, we have to allot to the Spirits of Will, or Thrones. The organizing of the planet in such a way that it does not follow an isolated course in space but so moves that its impulses of motion are in harmony with the whole planetary system to which it belongs, the regulating of the individual movements of the planet in harmony with the whole system, that is an activity of the Cherubim. Finally we ascribe to the Seraphim what we may call the inner soul-life of the planet, whereby the planet comes as it were, into connection with the other heavenly bodies, as a man by means of his speech enters into relation with other men. So that we must observe a sort of coherence in the planet; and in this, what comes from the Spirits of Form is but a sort of kernel. On the other hand every planet has something like a spiritual atmosphere, we might even say something like an aura, in which work the spirits belonging to those two higher hierarchies which are higher than the Spirits of Form. Now if we want to understand all this aright, we must make ourselves acquainted with yet other concepts than those I have just recalled to you—concepts to which we shall most easily attain if we begin with the beings of that hierarchy which stands, so to speak, nearest to humanity in the spiritual world, namely the beings of the Third Hierarchy. We have said that characteristic of the beings of the Third Hierarchy is the fact that what is perception in man is in them manifestation, and that what in man is inner life, in them is being filled with spirit. Even in those beings who start immediately above man in the cosmic order, the Angels or Angeloi, we already find this peculiarity, that they are actually conscious of that which they manifest from out of themselves. When they return to their inner being, they have nothing independent, nothing self-enclosed, like the inner life of man; but they then feel shining and springing forth in their inner being, the forces and beings of the higher hierarchies above them. In short they feel themselves filled and inspired by the spirit and its beings, immediately above them. Thus what we men call our independent inner life, really does not exist in them. If they wish to develop their own being, if they wish to feel, think and will somewhat as a man does, all that is immediately manifested externally; not as in man, who can shut up within himself his thoughts and feelings, and allow the impulses of his will to remain unfulfilled. What lives as thought in these beings, in so far as they themselves bring forth these thoughts, is at the same time also externally revealed. If they do not wish to manifest externally they have no other means of returning into their inner being, but by once again filling themselves with the world above them. Thus, in the inner life of these beings dwells the world above them, and when they live a life of their own, they project themselves externally, objectively. Thus, as we have seen, these beings could hide nothing within them as the product of their own thought and feeling, for whatever they bring about in their inner being must show itself externally. As we mentioned in one of the former lectures, they cannot lie, they cannot be untrue to their nature so that their thoughts and feelings did not harmonize with the external world; they cannot have an idea within them which does not agree with the external world; for any ideas which they have in their inner being, are perceived by them in their manifestation. But now let us just suppose that these beings had a desire to be untrue to their own nature, what would be the result? Well, in the beings we have designated as Angels, Archangels, and Spirits of the Age or Archai, we find throughout that everything which reveals itself to them, everything which they can perceive is, so to speak, their own being. If they were to wish to be untrue, they would be obliged to develop something in their inner being which would not be consistent with their own nature. Every untruth would be a denial of their nature. That would mean nothing less than a deadening, a damping-down of their own being. Now suppose that nevertheless these beings had the desire to experience something in their inner nature which they did not manifest externally; to do so they would have to take on another nature. What I have just described as the denial of their own nature by beings of the Third Hierarchy, the taking on of another nature, did actually take place; it did occur in the course of the ages. We shall see, as these lectures go on, why this had to happen; but to begin with we will confine our attention to the fact that it did happen; that, as a matter of fact, among the beings of the Third Hierarchy there were some possessed with this desire to have experiences in their inner nature which they need not manifest externally. That is, they had the wish to deny their own nature. What did this bring about in these beings? Something entered, which the other beings, those of the Third Hierarchy which retained their own nature, cannot have. The beings of the Third Hierarchy can have no inner independence such as man has. If they wish to live in their inner being, they must immediately be filled with the spirit-world above them. A certain number of the beings of the Third Hierarchy had the desire to develop something within their inner being which they would not immediately encounter in the external world as perception, or revelation of their own being. Hence the necessity arose of denying their own nature and taking on another nature. To develop an inner life of their own, to attain inner independence, a number of beings of the Third Hierarchy had to give up their own nature, to deny it. They had, so to speak, to bring about in themselves the power not to manifest certain inner experiences externally. Now let us ask:—What then were the reasons which moved these beings of the Third Hierarchy to develop such a desire within them? If we fix our attention upon the nature of the beings of the Third Hierarchy, with their manifestation and enfilling with spirit, we see that these beings are in reality wholly at the service of the beings of the higher hierarchies. Angels have no life of their own; their own life is manifestation, which is for the whole world; as soon as they do not manifest themselves there radiates into their inner being the life of the higher hierarchies. That which induced a number of them to deny their nature was a feeling of power, of independence and freedom. At a certain time a number of beings of the Third Hierarchy had an impulse, an urge, not merely to be dependent upon the beings of the higher hierarchies, but to develop within themselves an inner life of their own. The result of this was very far-reaching for the whole evolution of the planetary system to which we belong; for these beings whom we may call the rebels of the Third Hierarchy, brought about nothing less than the actual independence of man—making it possible for him to develop an independent life of his own, which does not immediately manifest externally, but can be independent of external manifestation. I am intentionally using many words to describe this circumstance, because it is extremely important to grasp accurately what is here in question, namely, that an impulse arose in a number of the Third Hierarchy to develop an inner life of their own. Everything else was simply the result, the consequence of this impulse. What then was this result? It was in fact a terrible one, namely, the betrayal of their own nature; untruth, falsehood. You see, it is important that you should understand that the spirits of the Third Hierarchy which had this impulse, did not do what they did for the sake of lying, but in order to develop an independent life of their own; but in so doing they had to take the consequence, they had to become Spirits of Untruth—spirits which betrayed their own being—in other words, Spirits of Lies. It is as though someone were to take a journey on foot—and he meets with a wet day; he must of necessity make the best of it and put up with getting wet, which he did not at all intend:—in the same way the spirits of which we are speaking, had no intention of doing something in order to sink into untruth. Their action arose from their wish to develop an inner life, an inner activity; but the result, the consequence was, that they at the same time became Spirits of Untruth. Now all the spiritual beings which in this way, through betraying their own nature, arose as a second category beside the spirits of the Third Hierarchy, are called in occultism, Luciferic Spirits. The concept of the Luciferic Spirits consists essentially in the fact that these beings wish to develop an inner life. Now the question is—What have these spirits to do, to attain their goal? We have already seen what they had to develop as a result; and we shall now inquire further what they had to do in order to attain this goal of an inner independent life. What did these spirits wish to surmount? They wished to prevent themselves from being filled wholly with the substance of the higher hierarchies; they wished to be filled, not only with the beings of the higher hierarchies, but with their own being. They could only accomplish this in the following way: Instead of filling themselves with the spirit of the higher hierarchies, and, as it were, leaving themselves open to the free outlook towards the higher hierarchies, they cut themselves off, detached themselves from them, in order in this way to create substance of their own from the substance of the higher hierarchies. We can gain a correct idea of what is here in question if we think of the beings of the Third Hierarchy in the following way. We think of them represented symbolically, graphically, in such a way that they manifest their own being outwardly, as it were, as though it were their skin; so that each time they developed inner thought or feeling, a manifestation arises, like a shining-forth of their own being. The moment they do not manifest themselves, they take up the light of the higher hierarchies which flows into them; they fill themselves with the spirit of the higher hierarchies and, as it were, open their whole being to them. 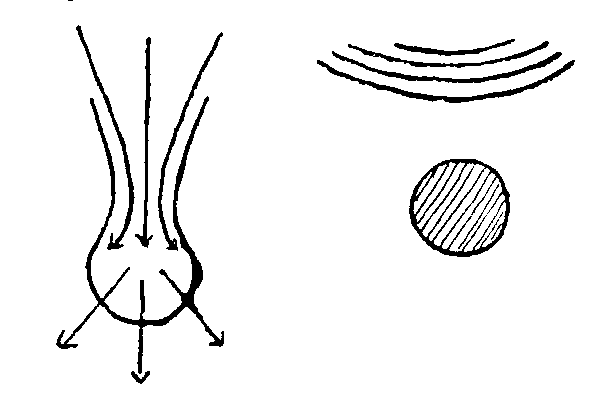 Those spiritual beings of the Third Hierarchy of which we have just spoken did not wish to be filled with the spirit nor to be connected with the spiritual substance of the hierarchies. They wanted an independent spiritual life, they therefore cut themselves off, they detached themselves, so that the being of the higher hierarchies was above them; they cut the connection and detached themselves as independent beings, retaining the actual light in their inner being. Thus they, as it were, stole what should only have filled them, and then returned to the higher hierarchies. They stole it for themselves, filled their own inner being with it, and by that means developed an independent side to their nature. This concept can provide an explanation of events in the cosmos, without which we should be quite unable to grasp a stellar system, the constitution of the stars in general as we know them with our human physical consciousness. Without these concepts one cannot possibly grasp the life of the stars, the life of the heavenly bodies. I have now tried to indicate to you how certain beings of the Third Hierarchy have become quite different beings—Luciferic Spirits. That which took place in these beings of the Third Hierarchy cannot, of course, take place in the same way in the beings of the other hierarchies but something similar takes place even with these. If we apply that which takes place in the beings of the other hierarchies to a consideration of the Spirits of Form, it will give us an idea of how a planetary system is actually formed. At the conclusion of the last lecture it was said that what our vision first perceives in the planets, proceeds from the Spirits of Form; but it is not quite accurate to represent it thus. If you consider the planets—Mars, Saturn or Jupiter for instance—which are outside in cosmic space; as you see them with your physical eyes, or with the telescope, you have in the form revealed to you, not merely the Spirits of Form. Let us take, for example, the planet which for a long period of time, has been reckoned as the outermost one in our system; Uranus and Neptune were added later, as we shall see; but to begin with we will consider Saturn as the outermost. If we look at Saturn with physical vision we find him outside in cosmic space, a sort of luminous globe (leaving his rings out of the question). To the occultist who follows the spiritual events in the cosmos, this globe which is seen out there is not what the occultist calls Saturn; to him Saturn is that which fills the whole space bounded by the apparently elliptical orbit of Saturn. 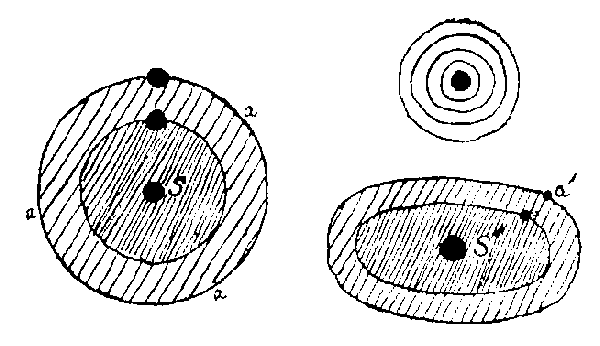 You know that astronomy describes an orbit of Saturn which it interprets as the path of Saturn round the Sun. We will not at present discuss the accuracy of that statement, but if you take this accepted concept and here in the center imagine the Sun (S), and the outer circle as the orbit of Saturn, as astronomy conceives it, then everything which is within this orbit of Saturn, within the ellipse of Saturn, is to the occultist Saturn. For to him not only is that which the external eye sees as the most external physical matter, Saturn; not only that which gleams in the heavens, for the occultist knows, occult vision teaches him that, as a matter of fact, a sort of accumulation exists which extends from the Sun to the orbit of Saturn (a,a,a, in the diagram). So that if with occult vision we regard this orbit of Saturn, we have a sort of etheric filling in of the whole space: (the wide crosslines). That which lies within this orbit we must think of as filled with matter, not however in the form of a globe, for we have to do with a very flattened ball, a lens. Looked at from the side, we should if we had the Sun at (S1) have to draw the Saturn of the occultist thus:—as a much flattened ball, and at (a1), would be that which is designated the physical Saturn. We shall understand still better what is in question if we add an idea which we can gain in a similar manner from occult science with regard to Jupiter. External physical astronomy knows as Jupiter that shining body which revolves round the Sun as the second planet (the inner circle). That to the occultist, is not Jupiter: to him, Jupiter is all that lies within the orbit of Jupiter (narrow sloping lines). Looked at from the side, we should have to draw Jupiter so that if we put wide sloping lines for Saturn, we can put narrow sloping lines for Jupiter. That which astronomy describes is only a body (bl) which is, so to speak, on the outermost limits of the true occult Jupiter. What I am here saying is not a mere theoretical idea or fancy, the fact actually is, that matter, not coarse physical matter but fine etheric matter, fills the space within the orbit of Saturn in its lenticular, flattened, ball-like form, as drawn here. It is just as much a fact that the second smaller space for Jupiter is filled with a different etheric substance which permeates the first; so that there is simple etheric substance only between the two orbits; within, the two etheric substances permeate one another, mutually permeate one another. Now let us ask: What is the task of the Spirits of Form in this whole disposition? That Spirit of Form which forms the basis of Saturn, sets a boundary, gives form to this etheric substance which in an occult sense we call Saturn. Thus the outermost line in the formation of Saturn has been shaped by the Spirit of Saturn, which is also a Spirit of Form. In the same way the line of Jupiter was formed by the Spirit of Form allotted to Jupiter; the line of Mars by the Spirit of Mars, which is a Spirit of Form. Now we may ask: Where then actually dwells the Spirit of Form which corresponds to Saturn, or Jupiter, or Mars? If we can speak of a place in which these beings are, where is this place? In the ordinary sense of the word we cannot so do; we can only say:—The spiritual beings which we call the Spirits of Form work as forces within the etheric substance I have just mentioned; but they all have a common center, and this is none other than the Sun. Thus if we seek for the actual place whence the Spirits of Form work, the Spirits of Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, etc., as also the Spirit of Form belonging to our Earth—if we seek for the center, the starting point from which the Spirits of Form work—we find it in the Sun. That means that the Spirits of Form corresponding to our planets, comprise, as it were, a synod or council of Spirits, having its seat in the Sun, and from there sets boundaries to certain etheric substances, certain masses of ether, so that what we call occult Saturn, occult Jupiter, comes into being. Now let us ask: How would it be if the Spirits of Form alone were to work? From the whole significance of these studies you will gather that those physical planets would not be in existence if only the Spirits of Form were to work. They would indeed have, as it were, their abode in the Sun, where they form a sort of college; and we should have around us the planetary spheres as far as the orbit of Saturn, for there would be, so to speak, concentric globes, flattened balls in existence as occult planets; the most external of these flattened globes being of the finest etheric matter, the next somewhat denser and the innermost of the densest etheric matter. Thus the physical planets would not be in existence if these Spirits of Form alone were to work, but there would be globe-shaped, accumulated masses bounded by what the physical astronomy of to-day calls the orbits of the planets. But within the cosmos there are certain spiritual beings corresponding to the Spirits of Form, but who, as it were, are rebels against those of their own class. Just as we find Luciferic Spirits among the beings of the Third Hierarchy, which in order to set up their own independent life, cut themselves off from the spiritual substance of the higher hierarchies, so do we also find within the category of the Spirits of Form that some separated and would not go through the usual development of a Spirit of Form, but went through an evolution of their own. These oppose the normal Spirits of Form, are in opposition to them. What then happens is as follows. Let us suppose that we had at point S the centre-point of the spiritual Council of the Spirits of Form; the Spirit of Form working upon Saturn would call forth this etheric globe, so that by the agency of this Spirit of Form a flattened globe would arise, as in the diagram. At an outermost point of this etheric globe, in opposition to the Spirit of Form working from the centre of the Sun works the rebel, the Luciferic Spirit of Form. He works from without inwards; opposingly. Thus we have the normal Spirit of Form working outwards from the Sun, centrifugally; he brings about the occult Saturn, which is then to be seen as a mighty etheric globe with its centre-point in the Sun. At the periphery, working inwards from cosmic space, is an abnormal Spirit of Form who has cut himself off from the normal evolution of the others; and at point (a) through the combined working of the forces working inwards from cosmic space, and those others working outwards from the sun, there occurs an “inturning,” which finally becomes detached, and that is the physical planet Saturn. Thus we have to imagine that where our physical eyes ace the planet Saturn, there are two forces working together; the one, the, normal force of the Spirit of Form working outward from the Sun; and at a definite point in opposition works the detached Spirit of Form. This produces an “in-turned” structure; the ether is notched, and this notch appears to the physical eye as the physical planet Saturn. Just the same occurs with the physical Jupiter, and with the physical Mars. Hence, by this example you see how in individual cases there actually arises what we call “maya,” the great illusion. Where physical astronomy places a planet, there is in truth a combined working of two forces; and only because, in truth, a great and mighty etheric heavenly body is there, which, through the contact of these opposing forces, is dented in and has a notch formed in one place, does the appearance of the physical planet arise. For in truth here we have actually to do with a turning in, and to be really accurate the matter must in the first place be described as: 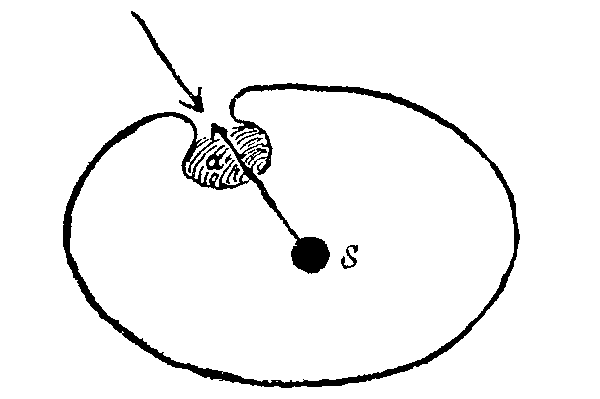 The Spirits of form working from the Sun extended the etheric substance to a certain distance; there worked the abnormal Spirits of Form in opposition, and caved the substance in, so that in reality a hollow was made in the etheric substance. As regards the original etheric substance of the planet, where the physical eye believes it sees the planet—there is really nothing; the actual planet is where the physical eye sees nothing. That is the peculiarity of “maya.” Where the physical planet is seen, there is a hollow. It may perhaps be said: “It is a very strange idea that where the physical planet is to be seen, there is a hollow,” for you will ask about our Earth. In the sense of what has been expounded, our Earth must also be a sort of flattened ball having its central point in the Sun, and it must also be such a notch, such a sort of hollow on the outermost rim. “A fine thing that!” you can say, “We know quite well that we are walking on firm, solid earth. In like manner we might take for granted that where Saturn, Jupiter or Mars are, there would naturally have to be solid filling, not hollow. And nevertheless where you walk about on our Earth—where, in the sense of Maya-perception you believe yourselves to be walking on solid, firm ground—even then, in reality, you are walking about on a hollow. Our Earth itself, in so far as it is an accumulation of matter, is a hollow in cosmic space, something bored into cosmic space. All physical matter comes into being through the meeting together of forces coming from the Spirits of Form. In this case we have the meeting of the forces of the normal Spirits of Form and those of the abnormal Spirits of Form. They collide with one another and in reality an indentation is produced and consequently at this point a simultaneous breaking up of the form, but only of the form. The form breaks up and this hollow space is bored. Now broken spiritual form, crushed form, is in reality matter. In a physical sense matter only exists when spiritual forms are broken up. Thus the planets out there are also broken-up forms. In our planetary system the Spirits of Form have helpers, as has been made evident by our previous considerations. They themselves determine the boundaries, as we have described:—but above the Spirits of Form stand the Spirits of Motion, above these the Spirits of Wisdom, above these the Spirits of Will, above them the Cherubim, the Seraphim. In all ranks of these spiritual beings there are those who can be likened to what we have described as Luciferic Spirits. So that wherever a planet is formed, on its outermost border not merely do the Spirits of Form cooperate, but that which goes out from the Sun, from the activities of the normal hierarchies, working from within outwards, is always being opposed by the forces coming from the abnormal, the rebellious hierarchies. The Cherubim and Seraphim are those hierarchies which just as much take part in the whole working of the forces, as do the Spirits of Form. They have the task of bearing the power of light outwards from the center-point of the planetary system, from the center of the Sun. Inasmuch as the beings of the higher hierarchies, the Seraphim and Cherubim, become the bearers of light, they have now the same relation to the light as the forces of the Spirits of Form to the etheric substance. Just as the forces of the normal Spirits of Form pass outwards and encounter the forces of the abnormal spirits working in opposition, and by that means a notch is hollowed out, so also do the forces work which carry the light, filling the whole etheric space; but in opposition to them work the abnormal forces (See Figure 6, point a), so that the planet arrests the light. Just as it arrests the forces of the Spirits of Form, so does it arrest the light, and throw it back; hence it appears as a reflector, as a thrower-back of the light which the spirits we call the Cherubim and Seraphim carry to it from the Sun. 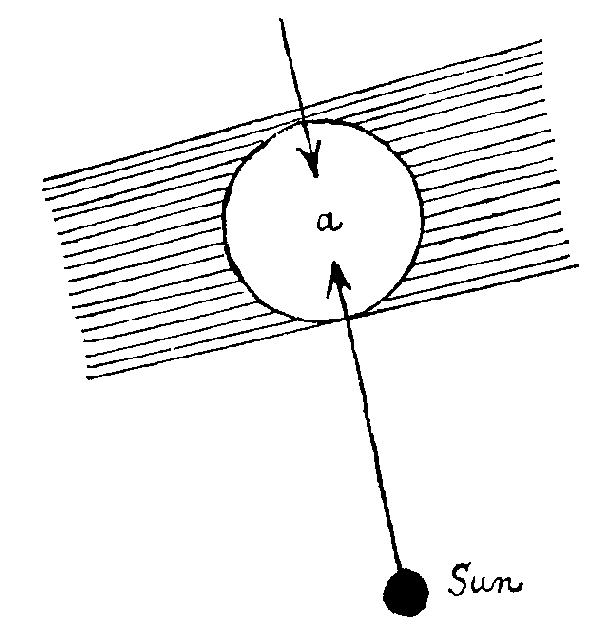 Hence the planets have no light of their own, because they claim for themselves the force of the light which would be their due as beings if they were to open themselves to the normal Cherubim and Seraphim—because they veil themselves, cut themselves from the whole. Thus every planet has a cut-off separated light. It is not correct to say that the planets only have light borrowed from the Sun; every planet has its own light; but it has cut it off, keeps it hidden within itself, and develops it for its own independent inner life of light. We shall see that each planet only shares this light with its own beings, belonging to the kingdoms of nature on the planet in question. But that light to which they ought to open themselves, which they ought to take up from outside, is brought to them from the Sun by the Cherubim and Seraphim, but to that they close themselves, and throw it back. Hence, seen in cosmic space, they are stars which have no light of their own. Thus, as it were, with the light which flows in from the Sun a notch is formed and the planet throws itself against that light flowing in from the Sun; arrests it and throws it back. Thus to occult vision what we observe in the stellar world, is absolutely different from what it appears to physical astronomy. What exists for the latter is nothing but a description of a Maya, and only behind this Maya does the truth lie; for the truth behind the material world is the spiritual world. In reality the material world does not exist at all. What is called the material world is the interplay of the forces of the spiritual world. We have tried to describe to-day how such a planetary system really arises. Very little is really known in the external world, in the world of physical science, of the origin of such a system; for though physical science imagines that a planetary system arises from a sort of massing of etheric substance, the first fundamental principle is omitted which should hold good in all natural science. How often are children told at school—at least I do not know whether it is done here, but in Central Europe they are always told—that according to the Kant-Laplace system of the origin of the world a mass of original matter was in rotation from which then the separate planets split off. (There may be some little improvement in that to-day, but the principle is the same.) And in order that this may be quite clear and comprehensible, the children are shown by means of a little experiment how easily a planetary system can be formed. A large drop of some oily substance which floats on water is taken, and a circle ingeniously made in the line of the equator which is pierced through with a card; then a needle is passed through from pole to pole, then one begins to turn, and behold, out of the drop of oil arises a pretty little planetary system. Quite in the sense of the Kant-Laplace theory of the origin of the world, little drops separate off and rotate, while in the center remains the big drop, the Sun. What is more natural than to represent this to young people as a visible proof that this was also once enacted in the great cosmic spaces. But in so doing an important error is made, one which ought never to be made in natural science. There are certain conditions that ought never to be forgotten in making experiments. A scientist who forgets conditions without which no experiment can come about does not describe it accurately even according to natural science. If you omit any essential condition you are not describing it correctly according to natural science. The essential condition in the origin of this planetary system is however that the teacher should stand there and make it revolve, otherwise the whole system could not originate! The Kant-Laplace theory would thus only be possible if those who believe in it could at the same time supply a gigantic teacher in cosmic space, who would revolve the whole etheric mass. People notice even small errors in logic—perhaps not always, but often;—but capital errors, such errors as those which in their effects extend to the whole cosmic-conception, are not remarked. Now there is no great teacher outside, making the axis of the world revolve, but there are the individual beings of the various hierarchies, who through the interplay of their forces, bring about the distribution and regulation of the movements of the different heavenly bodies. This should be the answer to those who would believe that the ordinary materialistic theory as expressed in Kant-Laplace, or in later hypotheses, is sufficient to explain the cosmic system, and that it is not necessary to consider anything else, as do the occultists. To those people who from a materialistic standpoint object to this living interplay of the hierarchies, we must again reply: with the capital error in logic which must be made by all cosmic materialistic hypotheses we cannot reach our goal; for there is no possibility of explaining a planetary system without calling to one's aid what occult vision can actually see. It is certainly abundantly proved to occult vision that what must he described with the physical senses is indeed, considered in its reality, something quite different. Thus what the eye sees is really nothing but the reflected light, which is thrown back, because, when the Seraphim and Cherubim carry the light of the Sun into cosmic space, the Luciferic Cherubim and Seraphim throw themselves against them, so to speak, and insert darkness into the substance of the sunlight; cutting off the light within, and claiming for each of the planets a light of its own. These thoughts, now given out on the basis of occult observation and occult investigation, were first expounded in the post-Atlantean period in a sublime way by the great Zarathustra to his pupils. Everything which is rayed down from the Sun into cosmic space in the way just described, by the beings of the higher hierarchies centered in the Sun, was ascribed by Zarathustra to the Spirit whom he named Ahura Mazdao, or Ormuzd. That spirit who carried the forces of his being from the center-point of the Sun into the periphery, was everywhere opposed by the abnormal spirits of the different hierarchies, which in their totality, form the kingdom of Ahriman. We shall, however, see that we must separate the kingdom of Ahriman from that of Lucifer with regard to the planetary system. We shall have more to say about this; but at the conclusion of this lecture, attention must be drawn to the fact that Zarathustra in his own way symbolically pointed out to his pupils this connection of the Light of Ahura Mazdao, or Ormuzd, streaming out from the Sun, and of the kingdom of Ahriman embedded within it. Zarathustra said: What proceeds from the Sun we represent symbolically through that which the Seraphim and Cherubim carry, i.e. through the light. That which is hurled against the light in opposition by all the abnormal spirits of the higher hierarchies, the notch thus hollowed out, we represent by what is accepted as darkness. (That is, an individual light imprisoned within, manifesting externally as darkness.) That, Zarathustra represented as a kingdom of Angramanyu, or Ahriman. Thus we see how this teaching which, having originated in Asia Minor, is in a sense, once more given to us today, was met first in the Zarathustra civilisation. What always fills us with such significant feelings with regard to the evolution of humanity, is that we ourselves come upon certain things which even if they were not traditional and not to be observed in the Akasha Chronicle, are furnished by the results of present-day occult investigations; and which we can re-discover in the great teachings of antiquity. And only when we permeate ourselves with the truth which at the present time can be found in occult investigation, and when this same truth shines towards us from the old teachers and leaders of humanity, do we acquire a right relation to these leaders of humanity. Then only do they become living to us, then only do we understand them aright. Then, too, does the evolution of humanity reveal itself to us as a mighty discourse held by the spirits, now not only resounding forth to one another in space, but interpreting one another in the successive periods of time, completing one another, and leading the stream of civilisation on into the future. |
| 320. The Light Course: Lecture X
03 Jan 1920, Stuttgart Tr. George Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Yet he spoke not untruly when he said, future generations would find it difficult to understand that there was once a world so crazy as to explain the evolution of the Earth and Solar System by the theory of Kant and Laplace. To understand such scientific madness would not be easy for a future age, thought Hermann Grimm. Yet in our modern conceptions of inorganic Nature there are many features like the theory of Kant and Laplace. And you must realize how much is yet to do for the human beings of our time to get free of the ways of Kant and Konigsberg and all their kindred. |
| (He prides himself in this very lecture that there is in him something of Kant and Konigsberg!) It was a lecture in a Baltic University, on the relation of Physics and Technics, held on the 1st of May 1918,—please mark the date! |
| 320. The Light Course: Lecture X
03 Jan 1920, Stuttgart Tr. George Adams Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
My dear Friends, I will now bring these few improvised hours of scientific study to a provisional conclusion. I want to give you a few guiding lines which may help you in developing such thoughts about Nature for yourselves, taking your start from characteristic facts which you can always make visible by experiment. In Science today—and this applies above all to the teacher—it is most important to develop a right way of thinking upon the facts and phenomena presented to us by Nature. You will remember what I was trying to shew yesterday in this connection. I shewed how since the 1890's physical science has so developed that materialism is being lifted right out of its bearings, so to speak, even by Physics itself. This is the point to remember above all in this connection. The period when Science thought that it had golden proofs of the universality of waves and undulations was followed, as we say, by a new time. It was no longer possible to hold fast to the old wave-theories. The last three decades have in fact been revolutionary. One can imagine nothing more revolutionary in any realm than this most recent period has been in Physics. Impelled by the very facts that have not emerged, Physics has suffered no less a loss than the concept of matter itself in its old form. Out of the old ways of thinking, as we have seen, the phenomena of light had been brought into a very near relation to those of electricity and magnetism. Now the phenomena produced by the passage of electricity through tubes in which the air or gas was highly rarefied, led scientists to see in the raying light itself something like radiating electricity. I do not say that they were right, but this idea arose. It came about in this way:—The electric current until then had always been hidden as it were in wires, and one had little more to go on than Ohm's Law. Now one was able, so to speak, to get a glimpse of the electricity itself, for here it leaves the wire, jumps to the distant pole, and is no longer able as it were to conceal its content in the matter through which it passes. The phenomena proved complicated. As we say yesterday, manifold types of radiation emerged. The first to be discovered were the so-called cathode rays, issuing from the negative pole of the Hittorf tube and making their way through the partial vacuum. In that they can be deflected by magnetic forces, they prove akin to what we should ordinarily feel to be material. Yet they are also evidently akin to what we see where radiations are at work. This kinship comes out most vividly when we catch the rays (or whatsoever it is that is issuing from the negative electric pole) upon a screen or other object, as we should do with light. Light throws a shadow. So do these radiations. Yet in this very experiment we are again establishing the near relation of these rays to the ordinary element of matter. For you can imagine that a bombardment is taking place from here (as we say yesterday, this is how Crookes thinks of the cathode rays). The “bombs” do not get through the screen which you put in the way; the space behind the screen is protected. This can be shewn by Crookes's experiment, interposing a screen in the way of the cathode rays. We will here generate the electric current; we pass it through this tube in which the air is rarefied. It has its cathode or negative pole here, its anode or positive pole here. Sending the electricity through the tube, we are now getting the so-called cathode rays. We catch them on a screen shaped like a St. Andrew's cross. We let the cathode rays impinge on it, and on the other side you will see something like a shadow of the St. Andrew's cross, from which you may gather that the cross stops the rays. Observe it clearly, please. Inside the tube is the St. Andrew's cross. The cathode rays go along here; here they are stopped by the cross; the shadow of the cross becomes visible upon the wall of the vessel behind it. I will now bring the shadow which is thus made visible into the field of a magnet. I beg you to observe it now. You will find the shadow influenced by the magnetic field. You see then, just as I might attract a simple bit of iron with a magnet, so too, what here emerges like a kind of shadow behaves like external matter. It behaves materially. Here then we have a type of rays which Crookes regards as “radiant matter”—as a form of matter neither solid, liquid or gaseous but even more attenuated,—revealing also that electricity itself, the current of electricity, behaves like simple matter. We have, as it were, been trying to look at the current of flowing electricity as such, and what we see seems very like the kind of effects we are accustomed to see in matter. I will now shew you, what was not possible yesterday, the rays that issue from the other pole and that are called “canal rays”. You can distinguish the rays from the cathode, going in this direction, shimmering in a violet shade of colour, and the canal rays coming to meet them, giving a greenish light. The velocity of the canal rays is much smaller. Finally I will shew you the kind of rays produced by this apparatus: they are revealed in that the glass becomes fluorescent when we send the current through. This is the kind of rays usually made visible by letting them fall upon a screen of barium platinocyanide. They have the property of making the glass intensely fluorescent. Please observe the glass. You see it shining with a very strong, greenish-yellow, fluorescent light. The rays that shew themselves in this way are the Roentgen rays or X-rays, mentioned yesterday. We observe this kind too, therefore. Now I was telling you how in the further study of these things it appeared that certain entities, regarded as material substances, emit sheaves of rays—rays of three kinds, to begin with. We distinguished them as \(\alpha\)-, \(\beta\)-, and \(\gamma\)-rays (cf. the Figure IXc). They shew distinct properties. Moreover, yet another thing emerges from these materials, known as radium etc. It is the chemical element itself which as it were gives itself up completely. In sending out its radiation, it is transmuted. It changes into helium, for example; so it becomes something quite different from what it was before. We have to do no longer with stable and enduring matter but with a complete metamorphosis of phenomena. Taking my start from these facts, I now want to unfold a point of view which may become for you an essential way, not only into these phenomena but into those of Nature generally. The Physics of the 19th century chiefly suffered from the fact that the inner activity, with which man sought to follow up the phenomena of Nature, was not sufficiently mobile in the human being himself. Above all, it was not able really to enter the facts of the outer world. In the realm of light, colours could be seen arising, but man had not enough inner activity to receive the world of colour into his forming of ideas, into his very thinking. Unable any longer to think the colours, scientists replaced the colours, which they could not think, by what they could,—namely by what was purely geometrical and kinematical—calculable waves in an unknown ether. This “ether” however, as you must see, proved a tricky fellow. Whenever you are on the point of catching it, it evades you. It will not answer the roll-call. In these experiments for instance, revealing all these different kinds of rays, the flowing electricity has become manifest to some extent, as a form of phenomenon in the outer world,—but the “ether” refuses to turn up. In fact it was not given to the 19th-century thinking to penetrate into the phenomena. But this is just what Physics will require from now on. We have to enter the phenomena themselves with human thinking. Now to this end certain ways will have to be opened up—most of all for the realm of Physics. You see, the objective powers of the World, if I may put it so,—those that come to the human being rather than from him—have been obliging human thought to become rather more mobile (albeit, in a certain sense, from the wrong angle). What men regarded as most certain and secure, that they could most rely on, was that they could explain the phenomena so beautifully by means of arithmetic and geometry—by the arrangement of lines, surfaces and bodily forms in space. But the phenomena in these Hittorf tubes are compelling us to go more into the facts. Mere calculations begin to fail us here, if we still try to apply them in the same abstract way as in the old wave-theory. Let me say something of the direction from which it first began, that we were somehow compelled to bring more movement into our geometrical and arithmetical thinking. Geometry, you know, was a very ancient science. The regularities and laws in line and triangle and quadrilateral etc.,—the way of thinking all these forms in pure Geometry—was a thing handed down from ancient time. This way of thinking was now applied to the external phenomena presented by Nature. Meanwhile however, for the thinkers of the 19th century, the Geometry itself began to grow uncertain. It happened in this way. Put yourselves back into your school days: you will remember how you were taught (and our good friends, the Waldorf teachers, will teach it too, needless to say; they cannot but do so),—you were undoubtedly taught that the three angles of a triangle (Figure Xa) together make a straight angle—an angle of 180°. Of course you know this. Now then we have to give our pupils some kind of proof, some demonstration of the fact. We do it by drawing a parallel to the base of the triangle through the vertex. We then say: the angle \(\alpha\), which we have here, shews itself here again as \(\alpha'\). \(\alpha\) and \(\alpha'\) are alternate angles and therefore equal. I can transfer this angle over here, then. Likewise this angle \(\beta\), over here; again it remains the same. 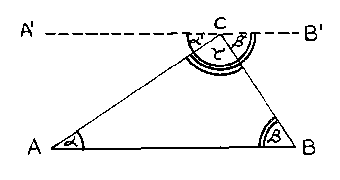 The angle \(\gamma\) stays where it is. If then I have \(\gamma = \gamma'\), \(\alpha = \alpha'\) and \(\beta=\beta'\), while \(\alpha'+\beta;' + \gamma'\) taken together give an angle of 180° as they obviously do, \(\alpha + \beta + \gamma\) will do the same. Thus I can prove it so that you actually see it. A clearer or more graphic proof can scarcely be imagined. However, what we are taking for granted is that this upper line A'B' is truly parallel to the lower line \(AB\),—for this alone enables me to carry out the proof. Now in the whole of Euclid's Geometry there is no way of proving that two lines are really parallel, i.e. that they only meet at an infinite distance, or do not meet at all. They only look parallel so long as I hold fast to a space that is merely conceived in thought. I have no guarantee that it is so in any real space. I need only assume that the two lines meet, in reality, short of an infinite distance; then my whole proof, that the three angles together make 180°, breaks down. For I should then discover: whilst in the space which I myself construct in thought—the space of ordinary Geometry—the three angles of a triangle add up to 180° exactly, it is no longer so when I envisage another and perhaps more real space. The sum of the angles will no longer be 180°, but may be larger. That is to say, besides the ordinary geometry handed down to us from Euclid other geometries are possible, for which the sum of the three angles of a triangle is by no means 180°. Nineteenth century thinking went a long way in this direction, especially since Lobachevsky, and from this starting-point the question could not but arise: Are then the processes of the real world—the world we see and examine with our senses—ever to be taken hold of in a fully valid way with geometrical ideas derived from a space of our own conceiving? We must admit: the space which we conceive in thought is only thought. Nice as it is to cherish the idea that what takes place outside us partly accords with what we figure-out about it, there is no guarantee that it really is so. There is no guarantee that what is going on in the outer world does really work in such a way that we can fully grasp it with the Euclidean Geometry which we ourselves think out. Might it not be—the facts alone can tell—might it not be that the processes outside are governed by quite another geometry, and it is only we who by our own way of thinking first translate this into Euclidean geometry and all the formulae thereof? In a word, if we only go by the resources of Natural Science as it is today, we have at first no means whatever of deciding, how our own geometrical or kinematical ideas are related to what appears to us in outer Nature. We calculate Nature's phenomena in the realm of Physics—we calculate and draw them in geometrical figures. Yet, are we only drawing on the surface after all, or are we penetrating to what is real in Nature when we do so? What is there to tell? If people once begin to reflect deeply enough in modern Science—above all in Physics—they will then see that they are getting no further. They will only emerge from the blind alley if they first take the trouble to find out what is the origin of all our phoronomical—arithmetical, geometrical and kinematical—ideas. What is the origin of these, up to and including our ideas of movement purely as movement, but not including the forces? Whence do we get these ideas? We may commonly believe that we get them on the same basis as the ideas we gain when we go into the outer facts of Nature and work upon them with our reason. We see with our eyes and hear with our ears. All that our senses thus perceive,—we work upon it with our intellect in a more primitive way to begin with, without calculating, or drawing it geometrically, or analyzing the forms of movement. We have quite other categories of thought to go on when our intellect is thus at work on the phenomena seen by the senses. But if we now go further and begin applying to what goes on in the outer world the ideas of “scientific” arithmetic and algebra, geometry and kinematics, then we are doing far more—and something radically different. For we have certainly not gained these ideas from the outer world. We are applying ideas which we have spun out of our own inner life. Where then do these ideas come from? That is the cardinal question. Where do they come from? The truth is, these ideas come not from our intelligence—not from the intelligence which we apply when working up the ideas derived from sense-perception. They come in fact from the intelligent part of our Will. We make them with our Will-system—with the volitional part of our soul. The difference is indeed immense between all the other ideas in which we live as intelligent beings and on the other hand the geometrical, arithmetical and kinematical ideas. The former we derive from our experience with the outer world; these on the other hand—the geometrical, the arithmetical ideas—rise up from the unconscious part of us, from the Will-part which has its outer organ in the metabolism. Our geometrical ideas above all spring from this realm; they come from the unconscious in the human being. And if you now apply these geometrical ideas (I will say “geometrical” henceforth to represent the arithmetical and algebraic too) to the phenomena of light or sound, then in your process of knowledge you are connecting, what arises from within you, with what you are perceiving from without. In doing so you remain utterly unconscious of the origin of the geometry you use. You unite it with the external phenomena, but you are quite unconscious of its source. So doing, you develop theories such as the wave-theory of light, or Newton's corpuscular theory,—it matters not which one it is. You develop theories by uniting what springs from the unconscious part of your being with what presents itself to you in conscious day-waking life. Yet the two things do not directly belong to one-another. They belong as little, my dear Friends, as the idea-forming faculty which you unfold when half-asleep belongs directly to the outer things which in your dreaming, half-asleep condition you perceive. In anthroposophical lectures I have often given instances of how the dream is wont to symbolize. An undergraduate dreams that at the door of the lecture-theatre he gets involved in a quarrel. The quarrel grows in violence; at last they challenge one-another to a duel. He goes on dreaming: the duel is arranged, they go out into the forest, he sees himself firing the shot,—and at the moment he wakes up. A chair has fallen over. This was the impact which projected itself forward into the dream. The idea-forming faculty has indeed somehow linked up with the outer phenomenon, but in a merely symbolizing way,—in no way consistent with the real object. So too, what in your geometrical and phoronomical thinking you fetch up from the subconscious part of your being, when you connect it with the phenomena of light. What you then do has no other value for reality than what finds expression in the dream when symbolizing an objective fact such as the fall and impact of the chair. All this elaboration of the outer world—optical, acoustic and even thermal to some extent (the phenomena of warmth)—by means of geometrical, arithmetical and kinematical thought-forms, is in point of fact a dreaming about Nature. Cool and sober as it may seem, it is a dream—a dreaming while awake. Moreover, until we recognize it for what it is, we shall not know where we are in our Natural Science, so that our Science gives us reality. What people fondly believe to be the most exact of Sciences, is modern mankind's dream of Nature. But it is different when we go down from the phenomena of light and sound, via the phenomena of warmth, into the realm we are coming into with these rays and radiations, belonging as they do to the science of electricity. For we then come into connection with what in outer Nature is truly equivalent to the Will in Man. The realm of Will in Man is equivalent to this whole realm of action of the cathode rays, canal rays, Roentgen rays. \(\alpha\)-, \(\beta\)- and \(\gamma\)-rays and so on. It is from this very realm—which, once again, is in the human being the realm of Will,—it is from this that there arises what we possess in our mathematics, in our geometry, in our ideas of movement. These therefore are the realms, in Nature and in Man, which we may truly think of as akin to one-another. However, human thinking has in our time not yet gone far enough, really to think its way into these realms. Man of today can dream quite nicely, thinking out wave-theories and the like, but he is not yet able to enter with real mathematical perception into that realm of phenomena which is akin to the realm of human Will, in which geometry and arithmetic originate. For this, our arithmetical, algebraical and geometrical thinking must in themselves become more saturated with reality. It is along these lines that physical science should now seek to go. Nowadays, if you converse with physicists who were brought up in the golden age of the old wave-theory, you will find many of them feeling a little uncanny about these new phenomena, in regard to which ordinary methods of calculation seem to break down in so many places. In recent times the physicists have had recourse to a new device. Plain-sailing arithmetical and geometrical methods proving inadequate, they now introduce a kind of statistical method. Taking their start more from the outer empirical data, they have developed numerical relations also empirical in kind. They then use the calculus of probabilities. Along these lines it is permissible to say: By all means let us calculate some law of Nature; it will hold good throughout a certain series, but then there comes a point where it no longer works. There are indeed many things like this in modern Physics,—very significant moments where they lose hold of the thought, yet in the very act of losing it get more into reality. Conceivably for instance, starting from certain rigid ideas about the nature of a gas or air under the influence of warmth and in relation to its surroundings, a scientist of the past might have proved with mathematical certainty that air could not be liquefied. Yet air was liquefied, for at a certain point it emerged that the ideas which did indeed embrace the prevailing laws of a whole series of facts, ceased to hold good at the end of this series. Many examples might be cited. Reality today—especially in Physics—often compels the human being to admit this to himself: “You with your thinking, with your forming of ideas, no longer fully penetrate into reality; you must begin again from another angle.” We must indeed; and to do this, my dear Friends, we must become aware of the kinship between all that comes from the human Will—whence come geometry and kinematics—and on the other hand what meets us outwardly in this domain that is somehow separated from us and only makes its presence known to us in the phenomena of the other pole. For in effect, all that goes on in these vacuum tubes makes itself known to us in phenomena of light, etc. Whatever is the electricity itself, flowing through there, is imperceptible in the last resort. Hence people say: If only we had a sixth sense—a sense for electricity—we should perceive it too, directly. That is of course wide of the mark. For it is only when you rise to Intuition, which has its ground in the Will, it is only then that you come into that region—even of the outer world—where electricity lives and moves. Moreover when you do so you perceive that in these latter phenomena you are in a way confronted by the very opposite than in the phenomena of sound or tone for instance. In sound or in musical tone, the very way man is placed into this world of sound and tone—as I explained in a former lecture—means that he enters into the sound or tone with his soul and only with his soul. What he then enters into with his body, is no more than what sucks-in the real essence of the sound or tone. I explained this some days ago; you will recall the analogy of the bell-jar from which the air has been pumped out. In sound or tone I am within what is most spiritual, while what the physicist observes (who of course cannot observe the spiritual nor the soul) is but the outer, so-called material concomitant, the movement of the wave. Not so in the phenomena of the realm we are now considering, my dear Friends. For as I enter into these, I have outside me not only the objective, so-called material element, but also what in the case of sound and tone is living in me—in the soul and spirit. The essence of the sound or tone is of course there in the outer world as well, but so am I. With these phenomena on the other hand, what in the case of sound could only be perceived in soul, is there in the same sphere in which—for sound—I should have no more than the material waves. I must now perceive physically, what in the case of sound or tone I can only perceive in the soul. Thus in respect of the relation of man to the external world the perceptions of sound, and the perceptions of electrical phenomena for instance, are at the very opposite poles. When you perceive a sound you are dividing yourself as it were into a human duality. You swim in the elements of wave and undulation, the real existence of which can of course be demonstrated by quite external methods. Yet as you do so you become aware; herein is something far more than the mere material element. You are obliged to kindle your own inner life—your life of soul—to apprehend the tone itself. With your ordinary body—I draw it diagrammatically (the oval in Figure Xb)—you become aware of the undulations. You draw your ether—and astral body together, so that they occupy only a portion of your space. You then enjoy, what you are to experience of the sound or tone as such, in the thus inwarded and concentrated etheric-astral part of your being. It is quite different when you as human being meet the phenomena of this other domain, my dear Friends. In the first place there is no wave or undulation or anything like that for you to dive into; but you now feel impelled to expand what in the other case you concentrated (Figure Xc). In all directions, you drive your ether—and astral body out beyond your normal surface; you make them bigger, and in so doing you perceive these electrical phenomena.   Without including the soul and spirit of the human being, it will be quite impossible to gain a true or realistic conception of the phenomena of Physics. Ever-increasingly we shall be obliged to think in this way. The phenomena of sound and tone and light are akin to the conscious element of Thought and Ideation in ourselves, while those of electricity and magnetism are akin to the sub-conscious element of Will. Warmth is between the two. Even as Feeling is intermediate between Thought and Will, so is the outer warmth in Nature intermediate between light and sound on the one hand, electricity and magnetism on the other. Increasingly therefore, this must become the inner structure of our understanding of the phenomena of Nature. It can indeed become so if we follow up all that is latent in Goethe's Theory of Colour. We shall be studying the element of light and tone on the one hand, and of the very opposite of these—electricity and magnetism—on the other. As in the spiritual realm we differentiate between the Luciferic, that is akin to the quality of light, and the Ahrimanic, akin to electricity and magnetism, so also must we understand the structure of the phenomena of Nature. Between the two lies what we meet with in the phenomena of Warmth. I have thus indicated a kind of pathway for this scientific realm,—a guiding line with which I wished provisionally to sum up the little that could be given in these few improvised hours. It had to be arranged so quickly that we have scarcely got beyond the good intentions we set before us. All I could give were a few hints and indications; I hope we shall soon be able to pursue them further. Yet, little as it is, I think what has been given may be of help to you—and notably to the Waldorf School teachers among you when imparting scientific notions to the children. You will of course not go about it in a fanatical way, for in such matters it is most essential to give the realities a chance to unfold. We must not get our children into difficulties. But this at least we can do: we can refrain from bringing into our teaching too many untenable ideas—ideas derived from the belief that the dream-picture which has been made of Nature represents actual reality. If you yourselves are imbued with the kind of scientific spirit with which these lectures—if we may take them as a fair example—have been pervaded, it will assuredly be of service to you in the whole way you speak with the children about natural phenomena. Methodically too, you may derive some benefit. I am sorry it was necessary to go through the phenomena at such breakneck speed. Yet even so, you will have seen that there is a way of uniting what we see outwardly in our experiments with a true method of evoking thoughts and ideas, so that the human being does not merely stare at the phenomena but really thinks about them. If you arrange your lessons so as to get the children to think in connection with the experiments—discussing the experiments with them intelligently—you will develop a method, notably in the Science lessons, whereby these lessons will be very fruitful for the children who are entrusted to you. Thus by the practical example of this course, I think I may have contributed to what was said in the educational lectures at the inception of the Waldorf School. I believe therefore that in arranging these scientific courses we shall also have done something for the good progress of our Waldorf School, which ought really to prosper after the good and very praiseworthy start which it has made. The School was meant as a beginning in a real work for the evolution of our humanity—a work that has its fount in new resources of the Spirit. This is the feeling we must have. So much is crumbling, of all that has developed hitherto in human evolution. Other and new developments must come in place of what is breaking down. This realization in our hearts and minds will give the consciousness we need for the Waldorf School. In Physics especially it becomes evident, how many of the prevailing ideas are in decay. More than one thinks, this is connected with the whole misery of our time. When people think sociologically, you quickly see where their thinking goes astray. Admittedly, here too most people fail to see it, but you can at least take notice of it; you know that sociological ways of thought will find their way into the social order of mankind. On the other hand, people fail to realize how deeply the ideas of Physics penetrate into the life of mankind. They do not know what havoc has in fact been wrought by the conceptions of modern Physics, terrible as these conceptions often are. In public lectures I have often quoted Hermann Grimm. Admittedly, he saw the scientific ideas of his time rather as one who looked upon them from outside. Yet he spoke not untruly when he said, future generations would find it difficult to understand that there was once a world so crazy as to explain the evolution of the Earth and Solar System by the theory of Kant and Laplace. To understand such scientific madness would not be easy for a future age, thought Hermann Grimm. Yet in our modern conceptions of inorganic Nature there are many features like the theory of Kant and Laplace. And you must realize how much is yet to do for the human beings of our time to get free of the ways of Kant and Konigsberg and all their kindred. How much will be to do in this respect, before they can advance to healthy, penetrating ways of thought! Strange things one witnesses indeed from time to time, shewing how what is wrong on one side joins up with what is wrong on another. What of a thing like this? Some days ago—as one would say, by chance—I was presented with a reprint of a lecture by a German University professor. (He prides himself in this very lecture that there is in him something of Kant and Konigsberg!) It was a lecture in a Baltic University, on the relation of Physics and Technics, held on the 1st of May 1918,—please mark the date! This learned physicist of our time in peroration voices his ideal, saying in effect: The War has clearly shewn that we have not yet made the bond between Militarism and the scientific laboratory work of our Universities nearly close enough. For human progress to go on in the proper way, a far closer link must in future be forged between the military authorities and what is being done at our Universities. Questions of mobilization in future must include all that Science can contribute, to make the mobilization still more effective. At the beginning of the War we suffered greatly because the link was not yet close enough—the link which we must have in future, leading directly from the scientific places of research into the General Staffs of our armies. Mankind, my dear Friends, must learn anew, and that in many fields. Once human beings make up their minds to learn anew in such a realm as Physics, they will be better prepared to learn anew in other fields as well. Those physicists who go on thinking in the old way, will never be so very far removed from the delightful coalition between the scientific laboratories and the General Staffs. How many things will have to alter! So may the Waldorf School be and remain a place where the new things which mankind needs can spring to life. In the expression of this hope, I will conclude our studies for the moment. |
| 217. The Younger Generation: Lecture VI
08 Oct 1922, Stuttgart Tr. René M. Querido Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| It becomes evident by contrasting the atavistic elements of the older age which play over in many ways into the present with what is living within us like the early flush of dawn. You will often have heard those fine words Kant wrote about duty: “Duty! Sublime and mighty Name, you embrace nothing that charms and require only submission”—and so forth. |
| The moral experience when he thus submits himself is that no inner satisfaction is gained from obedience to duty; only the cold statement: “I must perform my duty” remains. You know Schiller's answer to Kant's definition of duty: “Gerne dien' ich den Freunden, doch tu' ich es leider mit Neigung, Und so wurmt es mich oft, dass ich nicht tugendhaft bin.” |
| The important thing is what is necessary and possible for the evolution of humanity. We can simply not discuss whether what Kant, as a descendant of very ancient times, has said should be carried on into the future. It cannot be carried on, because humanity has developed beyond it, developed in such a way that action out of love must give mankind the impulse for the future. |
| 217. The Younger Generation: Lecture VI
08 Oct 1922, Stuttgart Tr. René M. Querido Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In the ways you want to be active during your stay here, many of you are thinking above all about the question of education. Not so much, perhaps, about education in the sense of ordinary school pedagogy but because we are living in an age when many new impulses must come into the evolution of mankind. There is a tendency to think that the attitude of the older towards the younger generation must assume a different character, and thence comes the thought of education. The fundamental character of the age is considered as having to do with education. In saying this I want to describe an impression which, I believe, may be noticed in many of you. It seems to me important that when anyone looks at his epoch, he should not only bear in mind the generation now young, entering the century in full youth, and its relation to the older generation that has, in the way I have described, carried over something from the last third of the nineteenth century, but one must also consider: What will be the attitude of this young generation towards the coming generation, to the generation which cannot, as the first, after the last third of the nineteenth century, maintain the same attitude to Nothingness that I have described? For the coming generation will not have what the present age has given to the younger generation through opposition towards their elders, namely enthusiasm—more or less indefinite, but nevertheless enthusiasm. What will further evolve will have much more the character of a longing, of an undefined yearning, than was the case among those who derived their enthusiasm from a mood of opposition against the traditional. And here we must look still more deeply into the human soul than I have done up to now. I have already shown that in the evolution in the West, consciousness of the pre-earthly existence of the soul has been lost. If we take the religious conceptions which are closest to the development of the human heart in the West during the past centuries, we can but say: For a long time existence before the descent into a physical earthly body has been lost to man's sight. Form an idea of how utterly different it is when one is permeated with the consciousness that something has come down from divine-spiritual worlds into the physical human body, has united itself with the physical human body. If nothing of this consciousness exists there is quite a different feeling, especially about the growing child. The growing child, when looked at with this consciousness, reveals from its very first breath, or even before, what is being manifested by the spiritual world. Something is revealed from day to day, from week to week, from year to year. Observed in this way, the child becomes a riddle which one approaches in quite a different way from what is possible when one thinks one is confronting a being whose existence begins with birth or conception, and who, as is said nowadays, develops from this starting point, from this point of germination. We shall understand one another still better if I call to your attention how with this there is connected the keynote of the riddle of the whole world. You know that in former days this fundamental feeling about the world-riddle was expressed in the paradigm: “Man, know thyself!” This saying, “Man, know thyself “is about the only saying which can hold its own against the objections always arising when a solution of the world-riddle is broached. Now I will say something rather paradoxical. Suppose somebody found what he might call the solution of the world-riddle. What would there remain to do after the moment when this world-riddle was solved? Man would lose all freshness of spontaneous striving; all livingness in striving would cease. It would indeed be comfortless to have to admit that the world-riddle has been solved by means of a cognitional method. All that is necessary is to look in some book or other; there the solution is given. A great many people think thus about the solution of the world-riddle. They consider the world-riddle a system of questions that must be answered by explanations or something of the kind. One feels benumbed at the thought that a solution of the world-riddle could somewhere be given in this way, that the solution could actually be studied! It is a terrible, a horrible thought; all life is frozen by it. But what lies in the words “Man, know thyself!” expresses something quite different. It really says: Man! look around you at the world; the world is full of riddles, full of mystery, and man's slightest movement points in the widest sense to cosmic mysteries.—Now one can indicate precisely where all these riddles are solved. There is quite a short formula for the indication. We can say: All the riddles of the world are solved in man—again in the very widest sense. Man himself, moving as a living being through the world—he is the solution of the world-riddle! Let him gaze at the sun and experience one of the cosmic mysteries. Let him look into his own being and know: Within thyself lies the solution of this cosmic mystery. “Man, know thyself and thou knowest the world I.” But this way of expressing the formula is an intimation that no answer is final. Man is the solution of the world-riddle but to know the human being, we have what is infinite before us and so imbued with life that we never reach an end. We know that we bear the solution of the world-riddle within ourselves. But we know too that we shall never come to an end of what there is to search for in ourselves. From such a formula we only know that we are not given out of the universe abstract questions to be answered in an abstract way, but that the whole universe is a question and the human being an answer. We know that the question of the nature of the universe has resounded from times primeval until today, that the answer to these world-questions has resounded from human hearts, but that the questioning will go on resounding endlessly, that human beings must continue on into the distant future to learn to live their answer. We are not directed in a pedantic way to what might be found in a book but to the human being himself. Yet in the sentence, “Man, know thyself!” there sounds over to us from ancient times when school, church and centers of art were all united in the Mysteries, something which points to what has not been learnt from formulae, but from that book about the world which can be deciphered, but deciphered only through endless activity. And the name of this book about the world is “Man.” If the full import of what I put before you yesterday is grasped, through such a change in the experiencing of knowledge, through the attitude we have to knowledge, the spark of life will strike into the whole nature of man. And that is what is needed. If we picture the moral evolution of man up to the time when it became problematic, up to the first third of the fifteenth century, we find that the most diverse impulses were necessary to follow what I characterized yesterday as God-given commandments. When we imagine the driving forces prevalent among various peoples in different epochs, we find a great range of inner impulses arising like instincts, depending on particular conditions of life. One could make an interesting study of how these impulses to obey the old moral intuitions originate, how they grow out of the family, out of the racial stock, out of man's inclination towards the other sex, out of the necessity to live together in communities, out of man's pursuit of his own advantage. But in the same way as we were obliged to call attention yesterday to how old moral intuitions have lived themselves out in historical evolution, so the impulses mentioned no longer contain an impelling force for the human being They cannot contain it if the self-acquired moral intuitions, of which I spoke yesterday, have to appear in man; if single individuals are challenged in the world-evolution of humanity, on the one hand, to find for themselves moral intuitions by dint of the labor of their own souls, and, on the other to acquire the inner strength to live according to these moral intuitions. And then it dawns upon us that the old moral impulses will increasingly take a different course. We see emerging in the depths of the soul, although misjudged and misunderstood today by the majority of civilized humanity, two moral impulses of supreme importance. If attempts are made to interpret them, confused ideas usually result. If people want to put them into practice, they do not know as a rule what to do with them. Nonetheless they are arising: in the inner life of man the impulse of moral love, and outwardly, in the intercourse between human beings, the moral impulse of confidence. Now the degree of strength in which moral love will be needed in the immediate future for all moral life, was not necessary in the past—not just in this form. Certainly, of former times too one could say that the words, “Joy and love are the pinions which bear man to great deeds,” are true. But if we speak truly and not in mere phrases, we must say: That joy and that love which fired human beings to do this or that were only a metamorphosis of the impulses described before. Great and pure love, working from within outwards, will have in future to give man wings to fulfil his moral intuitions. Those human beings will feel themselves weak and lacking in will, in face of moral intuitions, who do not experience the fire of love for what is moral springing from the depths of their souls, when through their moral intuitions they confront the deed to be accomplished. There you see how in our times we have a parting of the ways! It becomes evident by contrasting the atavistic elements of the older age which play over in many ways into the present with what is living within us like the early flush of dawn. You will often have heard those fine words Kant wrote about duty: “Duty! Sublime and mighty Name, you embrace nothing that charms and require only submission”—and so forth. The sternest terms in which to characterize duty! Here the content of duty stands as a moral intuition imparted from outside, and the human being confronts this moral intuition in such a way that he has to submit to it. The moral experience when he thus submits himself is that no inner satisfaction is gained from obedience to duty; only the cold statement: “I must perform my duty” remains. You know Schiller's answer to Kant's definition of duty:
Thus Schiller retorts ironically to this categorical imperative. You see, over against the so-called categorical imperative, as it comes down from former times out of old moral impulses, there stands the summons to mankind, out of the depths of his soul, evermore to unfold love for what is to become action and deed. For however often in future there may resound: “Submit to duty, to what brings you nothing that will please”—it will be of no avail. Just as little as a man of sixty can behave like a baby can we live at a later age in a way suitable to an earlier epoch. Perhaps that would please people better. But that is of no account. The important thing is what is necessary and possible for the evolution of humanity. We can simply not discuss whether what Kant, as a descendant of very ancient times, has said should be carried on into the future. It cannot be carried on, because humanity has developed beyond it, developed in such a way that action out of love must give mankind the impulse for the future. On the one hand we are led to the conception of ethical individualism, on the other, to the necessity of knowing that this ethical individualism must be borne on the love arising from perception of the deed to be accomplished. Thus it is, from man's subjective viewpoint. From the aspect of the social life, the matter presents itself differently. There are people today in whom there no longer echoes the voice of progressive evolution; because they accept all kinds of outside opinions they say: “Yes, but if you try to found morality on the individual, you will upset the social life.” But such a statement is meaningless. It is just as sensible as if someone were to say: if in Stuttgart it rains a certain number of times in three months, Nature will ruin some particular crop on the land.—If one is conscious of a certain responsibility towards knowledge one cannot imagine anything more empty. As humanity is developing in the direction of individualism, there is no sense in saying that ethical individualism upsets the community. It is rather a question of seeking those forces by which man's evolution can progress; this is necessary if man is to develop ethical individualism, which holds the community together and fills it with real life. Such a force is confidence—confidence between one human being and another. Just as in our inner being we must call upon love for an ethical future, so we must call upon confidence in relation to men's intercourse with each other. We must meet the human being so that we feel him to be a world-riddle, a walking world-riddle. Then we shall learn in the presence of every human being to unfold feelings which draw forth confidence from the depths of our soul. Confidence in an absolutely real sense, individual, unique confidence, is hardest to wring from the human soul. But without a system of education, a cultural pedagogics, which is directed towards confidence, civilization can progress no further. In future mankind will have to realize this necessity to build up confidence in social life; they will also have to experience the tragedy when this confidence cannot develop in the proper way in the human soul. Oh my dear friends, what men have ever felt in the depths of their souls when they have been disappointed by a human being on whom they had relied, all such feelings will in future be as nothing compared with the tragedy when, with an infinitely deepened feeling of trust, human beings will tragically experience disillusionment in their fellow men. It will be the bitterest thing, not because men have never been disappointed, but because the feeling of confidence and disillusionment will be infinitely deepened in future; because one will build to such a degree in the soul upon the joy of confidence and the pain of the inevitable mistrust. Ethical impulses will penetrate to depths of the soul where they spring directly from the confidence between man and man. Just as love will fire the human hand, the human arm, so that from within it draws the strength to do a deed, so from without there will flow the mood of confidence in order that the deed may find its way from the one human being to the other. The morality of the future will have to be grounded on the free moral love arising from the depths of the human soul; future social action will have to be steeped in confidence. For if one individuality is to meet another in a moral way, above all an atmosphere of confidence will be necessary. So we anticipate an ethics, a conception of morality that will speak little of the ethical intuitions of old but will emphasize how a human being must develop from childhood so that there may be awakened in him the power of moral love. Much will have to be given in the pedagogics of the future to the growing generation by teachers and educators through what educates effectively without words. In education and teaching there will have to be imparted much of that knowledge which is not an abstract indication of how man consists of this or that, but which leads us over to the other human being in such a way that we can have the proper confidence in him. Knowledge of man, but not a knowledge that makes us cold towards our fellow-men but which fills us with confidence—this must become the very fibre of future education. For we have to give weight again, but in a new way, to what once was taken seriously but is so no longer in the age of intellectualism. If you go back to Greece, you will find that the doctor in his medical art, for example, felt extraordinarily akin to the priest, and priests felt themselves akin to the doctor. Such an attitude can be seen dimly, confusedly in the personality of Paracelsus who has been, and still is, so little understood. Today we relegate to the sphere of religion the abstract instruction which leads away from real life. For in religious instruction we are told what man is without his body, and so on—in a way that is singularly foreign to life. Over against this stands the opposite pole in civilization, where everything brought forth by our own time is kept far from the realm of religion. Who today sees any trace of a religious act in healing, for instance, an act in which permeation by the spirit plays a part? Paracelsus still had a feeling for this. For him, the religious life was such that it entered into the science of healing. It was a branch of the religious life. This was so in olden times. The human being was a totality: what he had to perform in the service of mankind was permeated by religious impulses. In quite another way, for we must strive to gain moral intuitions that are not God-given but born by our own efforts,—life must again be permeated by a religious quality. But first and foremost it must be made evident in the sphere of education. Confidence between one human being and another—the great demand of the future—must permeate social life. If we ask ourselves—What is the most essential quality to be a moral human being in the future?—We can only answer: “You must have confidence in the human being.” But when a child comes into the world, that is to say, when the human being comes out of pre-earthly existence and unites with his physical body in order to use it as an instrument on earth between birth and death—when the human being confronts us as a child and reveals his soul to us, what must we bring to him in the way of confidence? Just as surely as the child, from its first movement on earth, is a human being, yet the confidence we bring him is different from the confidence we bring to an adult. When we meet the child as teacher or as a member of the older generation, this confidence is transformed in a certain respect. The child comes into earthly existence from a pre-earthly world of soul and spirit. We observe, revealing itself in a wonderful way from day to day permeating the physical out of the world of soul and spirit, what may be called in the modern sense of the word—the divine. We need again the divine which leads the human being out of pre-earthly into the present, as through his bodily nature he is led onwards in earthly existence. When we speak of confidence between men in the moral sphere, and apply it to education, we must specialize and say:—“We confront the child who has been sent down to us by the divine-spiritual Powers—and for whom we should be the solvers of all riddles—we confront the child with confidence in God.” Yes, in face of the child, confidence in man becomes confidence in God. And a future will have to come in the evolution of humanity in which what weaves even in a more neutralized form from man to man, will assume a religious coloring in relation to the child or to young people generally who have to be guided into life. There we see how through actual life, morality is transformed back into religiousness, into a religiousness that expresses itself directly in everyday life. In olden times all moral life was a special part of the religious life, for in the commandments of religion moral commandments were given at the same time. Humanity has passed through the epoch of abstraction; now, however, we must again enter the epoch of the concrete. We must feel once again how the moral becomes the religious. And in future the moral deeds of education and instruction will have to shape themselves in a modern sense into what is religious. For pedagogy, my dear friends, is not merely a technical art. Pedagogics is essentially a special chapter in the moral sphere of man. Only he who finds education within the realm of morality, within the sphere of ethics, discovers it in the right way. What I have described here as a specifically religious shade of morality, receives its right coloring if we say:—“The riddle of life stands before us as an enigma. The solution of the riddle lies in Man.”—And there indeed it does lie. But anyone who teaches has to work unceasingly, in a living way, at the solution of this riddle. When we learn to feel how in education we are working unceasingly at the solution of the world-riddle, we take our place in the world quite differently from what would have been the case had we sought for solutions merely by means of head knowledge. In regard to the feeling about Education with which you may have come here, the important thing is to carry away with you into the world this special aspect of pedagogics. This feeling will enable you to stand in the world and not only lead you to asking:—How profound is the tragedy of the young who had to follow the old?—You will also ask, looking into the future: “What living forces must I release in myself to look rightly upon those who are coming after me?” For they in turn will look back to those who were once there. A youth movement in whatever form, if it considers life in a fully responsible way, must have a Janus head; it must not only look at the demands the young make on the old, but also be able to look at the still undefined demands raging around us with tremendous power—demands which the coming youth will make upon us. Not only opposition against the old, but a creative looking forward, is the right guiding thought for a true youth movement. Opposition may, to begin with, have acted as a stimulus to enthusiasm. The power of deed will only be bestowed by the will to create, the will to do creative work within the present evolution of humanity. |
| 51. Schiller and Our Times: Schiller and Idealism (Aesthetics and Morality)
25 Mar 1905, Berlin Tr. Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| It was only a few years before Schiller's time that ideas like this could occur. We have a sort of aesthetics even in Kant's Critique of Judgment, but in him we have nothing but theory; he never had a living idea of what beauty is, and never got three miles away from his birthplace at Königsberg, and never saw any important work of art; and so could only write from the standpoint of abstract philosophy. |
| The core of his poetry is the longing to reconcile these two—the senses and morality, that morality which Kant had interpreted so rigidly that duty led men away from everything which appeared as natural inclination. |
| 51. Schiller and Our Times: Schiller and Idealism (Aesthetics and Morality)
25 Mar 1905, Berlin Tr. Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In this last lecture I want to deal with a particular question which connects up with the lecture in which I discussed Schiller's influence on the present. The problem of aesthetics in Germany comes in here because Schiller stands in close relationship to the establishment of aesthetics as a science—the science of the beautiful. We have seen what Schiller's attitude was to the beautiful at different periods of his life. Schiller saw in the beautiful something which had a peculiar cultural value. Now a science of aesthetics such as we know today is only 150 years old. It is true that Aristotle had written on Poetics, but for centuries these views remained stationary. We know that even Lessing harked back to Aristotle. No real advance was made until the Eighteenth Century when Baumgarten grew up in the Wolffian philosophy and wrote a book on the beautiful called Aesthetica in 1750. He distinguishes the beautiful from the true in that, as he says, the true contains a clear idea, while the beautiful exists in unclear and confused ideas. It was only a few years before Schiller's time that ideas like this could occur. We have a sort of aesthetics even in Kant's Critique of Judgment, but in him we have nothing but theory; he never had a living idea of what beauty is, and never got three miles away from his birthplace at Königsberg, and never saw any important work of art; and so could only write from the standpoint of abstract philosophy. Schiller, in his Aesthetic Letters, was the first to grasp the problem in any living way. What was the position at the time? Goethe looked longingly to Greece, and Winckelmann also cast a regretful glance back at the age when men copied the divine in their art. Schiller felt the same regretful longing during his second period, as we can see from his Götter Griechenlands. Again, in Greek drama, what is it but a religious feeling that lies at the back of it. It is based on the mystery, the secret of God who becomes man, who suffers as man, dies and rises again. What happened in the soul was regarded as a purification; and even through the Poetic of Aristotle there still passes a faint breath of it. The tragic was to consist in the “production of an action which aroused pity and fear and aimed at the purification of these feelings.” It was difficult to understand what was meant by that; and Lessing meditated a good deal about it. In the Nineteenth Century a vast literature grew up around the problem, and whole libraries could be filled with books dealing with Katharsis. The idea was not understood because men did not understand from what it had grown up. In Aeschylus we can still see something of this “drama of the God.” In the middle of the action stood Dionysos as the great dramatic figure, and the chorus round about him accompanied the action. This is how Edouard Schuré has recreated for us the mystery drama. The dramatic cult-action had the definite object of leading man to a higher level of existence. It was seen that man is gripped by passions, that his lower life makes him kin to them; but he can rise above them if the higher that lives in him is purified; he can raise himself by looking at the divine pattern. This type of representation was meant to bring man more easily to ennoble himself than could be achieved by teaching. As Schopenhauer said, it is easy enough to preach morality but very hard to establish it. It was only at a later age of humanity that Socrates' view grew up that virtue is teachable. But virtue is something that lives in man and is natural to him, as eating and drinking are; he can be led to it, if the divine is awoken within him, by the picture of the suffering god. This purification by the divine pattern was called Katharsis. Pity and fear were to be called forth; ordinary sympathy which is connected with the personal was to be raised to the great impersonal sympathy when the god was seen suffering for mankind. Then the dramatic action was humanised, and in the Middle Ages we can see how morality separated off and appeared independently. Thus in Christianity there was produced partially what lived incarnate in the Mysteries. The Greek looked with his own eyes on the god who rose again from humiliation. In the mysteries virtue was not merely preached but put before the eyes of men. Schiller felt very intensely the desire to give men back this knowledge to unite the sense-world and the moral. The core of his poetry is the longing to reconcile these two—the senses and morality, that morality which Kant had interpreted so rigidly that duty led men away from everything which appeared as natural inclination. Schiller, on the contrary, demanded that duty should coincide with inclination; he wanted passion to be so cleansed that it could become identical with duty. This is why he revered Goethe so much, for in him he saw a perfect union of the sense-world and the moral. He looked for this unification in the beautiful. And since Schiller possessed to an unusual degree the German quality of an aesthetic conscience, he wanted to make art a means of raising man to a higher level of existence. During the classical period there was a strong feeling that the beautiful did not exist merely to fill up idle hours but that it was the bridge between the sense-world and the divine. Schiller pushed far enough to find freedom here. Inclination is no longer to be suppressed: he remarked that a man must be very low in the scale if he has to be virtuous in opposition to his own inclinations. His inclination must be developed so far that he acts virtuously of himself. Earlier in his The Stage as a moral Institution he had preached something very like the severe Kantian morality. “In the conquest of the matter by the form lies the secret of the master.” But what is, in fact, the material of the poet? In what attitude can we find the right view of the beautiful? As long as we are interested only in a single face, we have not yet got the true artistic view; there is still a clinging to matter. (“Heed the `what' but heed more the `how'!”) As long as a poet shows that he hates a villain, as if this were a personal interest, he still clings to matter and not the form; he has not yet reached the aesthetic view. He only attains that if the villain is represented in such a way that the natural order, and not the poet, inflicts the punishment. Then the “world karma” is accomplished; world-history becomes a world-judgment. The poet disregards himself and looks at world history objectively. This means moreover that what Aristotle said is realised, that poetry is truer than history. In history we cannot always survey the whole event; it is only an extract that lies before us so that we often get an impression of injustice. In this way a work of art is truer than history. Thus was created a pure and noble conception of art; the purification, the Katharsis, stands beyond sympathy and antipathy. The spectator should stand before a work of art with a pure, almost godlike feeling, and see before him an objective, divine image of the world, and create for himself a microcosm. The dramatist shows us within a limited framework how guilt and atonement are connected, shows us in detail what the truth is, but gives this truth universal currency. Goethe means the same thing when he says that the beautiful is a manifestation of natural laws which, without the beautiful, would never find expression. Goethe and Schiller looked for a realism, but it was an idealistic realism. Nowadays we think that we can get realism by an exact copying of nature. Schiller and Goethe would have said that that is not the whole truth; the sense-world only represents a part of what is perceptible and lacks the spiritual; nor can we regard it as truth unless we bring the whole tableau of nature simultaneously into a work. The work of art is however still only an extract of the real. In that they strove for truth, they could not admit the immediate truth of nature. In this way Schiller and Goethe laboured to awaken an idealism, which had actually existed in earlier times. In Dante we have got a representation not of external reality but of what passes in the human soul. Later on, men demanded to see the spiritual in external form. Goethe showed in Grosskophta how anyone who materialises the spirit becomes subject to delusions; Schiller also occupied himself with this materialisation of the spiritual. At that time, there was a good deal of investigation along these lines; and much of what we nowadays call spiritualism engaged men's attention. In this, lies the occasion of the Geisterseher, which treats of these things. Before he had struggled upward, by the help of Kantianism and the artistic, to higher views, Schiller depicted the dangers to which anyone who seeks the spiritual in the external world instead of in himself, is subject. That is the origin of the Geisterseher. A prince whose faith has become alien to him and who is not strong enough to waken the spiritual in his own soul, is greatly excited by a strange prophecy which a mysterious stranger announces to him and which is shortly afterwards fulfilled. In this mood he falls in with some tricksters who skilfully employ certain circumstances to bring him into a state of mind in which he will be receptive for the appearance of a spirit. The business is proceeding when suddenly a stranger interrupts and unmasks the trick; but himself produces an apparition in place of that of the trickster, and this apparition makes an important pronouncement to the prince. The prince is torn by doubts, for this stranger is none other than the man who had just prophesied to him; and he soon begins to think that both parties are concerned in the plot since the trickster, though he had been locked up, soon escaped. New and inexplicable incidents make him strive for an explanation of all the secrets; as a result, he comes into complete dependence on an occult society, losing all moral stability. The novel was never finished. In it the struggles of a seeker after spirits are represented in a terrifying fashion; we see how the longing for the spiritual leads men downwards when he looks for it in the external. No one who clings to the material, even if he only seeks to find the spiritual appearing in sensible form, can penetrate to the spiritual. The spiritual has to unveil itself in the soul of man. That is the true secret of the spiritual; that is why the artist sees it first as beauty. The beautiful, conquered and permeated by the spirit, is made real in a work of art. Hence it is the worthy material of the spiritual. At first the beautiful was the only means for Schiller by which it could reveal itself. He looked with longing back to the time of the Greeks when there existed another means for the awakening of the spiritual: when man raised himself to the divine while bringing god down, making god into man and raising himself by god's means. Mankind must now rise once more to the divine by conquest over the material. Schiller in his plays was always striving higher until the physical fell away more and more until the
which Goethe cried to him after his death, became the full truth. The word “gemein” is not used here in any low, contemptuous sense; it is the common humanity, the common fashion of men that is meant, above which Schiller had raised himself. He had raised himself, as a true seer, to the vision of the spiritual. He must stand as a pattern before us. That has been the whole object of these lectures; so far as it was possible in a few hours, to trace out this struggling soul of Schiller's, as it rises to greater and greater heights of spiritual insight, and seeks to grasp the spiritual, so that he may impress it upon the sense world. In this struggle we really get to know Schiller, and in him Goethe's words are in truth fulfilled:
In this way Schiller fought his way upward, till he became the master of an etheric spirit-permeated form. |
| 32. Collected Essays on Literature 1884-1902: Goethe's World View and the Present
31 Dec 1897, Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| This doctrine still dominates contemporary philosophy, even revolutionary minds such as Baco of Verulam, Descartes and Kant, who are convinced of the necessity of faith. Goethe stands alone against them all. He emphasizes the unity of the spiritual and the sensual world. |
| 32. Collected Essays on Literature 1884-1902: Goethe's World View and the Present
31 Dec 1897, Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Presentation of a lecture held on December 19, 1897 in the "Literary Society" in Leipzig Dr. Rudolf Steiner spoke about "Goethe's world view and the present" at the "Literary Society". The topic is not new. Numerous philosophers and literary historians have dealt with it. But you can see how inexhaustible Goethe is, because there are always new sides to this topic, and Dr. Steiner's lecture in the large hall of the "Hötel de Pologne" offered an interesting picture of the intellectual life of the Weimar prince of poets. The speaker referred to Goethe's position on the dispute between the conservative Cuvier and the revolutionary Geoffroy de St.-Hilaire. Goethe suspected that this dispute would result in a whole revolution in people's views. The old way of thinking, according to which man was a being dependent on God and nature, fell, and he became the master of creation, who was alone with everything that lives and weaves around him. Goethe had already adopted this world view early on, but only a few people understood it. Our world view goes back to Parmenides. He was followed by Plato, whose doctrine of this world and the hereafter was further developed by Christianity. This doctrine still dominates contemporary philosophy, even revolutionary minds such as Baco of Verulam, Descartes and Kant, who are convinced of the necessity of faith. Goethe stands alone against them all. He emphasizes the unity of the spiritual and the sensual world. The path of nature leads from the plant through the animal world to man. Man is not gifted with anything supernatural, he is only the most highly organized product of nature. He is indeed the master of creation. In old age, however, Goethe returned to the old world view, as Part II of "Faust" shows us. Goethe's view, however, was taken up and expanded. Ludwig Feuerbach, who destroyed everything that had been valid until then, was followed by Max Stirner. It was then the great natural scientists of the modern age, namely Darwin, who rebuilt something new from the ruins and created the world view of the present. In his magnificent lecture, Redner followed on from a book he had published on the same subject. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity (1986): Moral Imagination
Tr. William Lindemann Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| In the same way the evolutionary theorists would have to picture to himself that a being could have observed the emergence of the solar system out of the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula, if he had been able to dwell freely in the realm of world ether in a suitable place during that infinitely long time. The fact that, with a picture such as this, both the nature of the proto-amniotes and also that of the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula would have to be thought of differently than the materialistic thinkers do, does not come into consideration here. |
| Just as little could the solar system be deduced from the concept from the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula. This means, in other words, that the evolutionary theorists must, if he is consistent in his thinking, maintain that out of earlier phases of development later ones result in a real way, and that, once we have bestowed the concept of less perfect and that of perfect, we can then see the connection; by no means, however, should he grant that the concept gained through the earlier is far-reaching enough to evolve the later out of it. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity (1986): Moral Imagination
Tr. William Lindemann Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] The free spirit acts according to his impulses, that is, according to intuitions chosen from the whole of his world of ideas through thinking. For the unfree spirit, the reason he isolates one particular intuition from his world of ideas in order to base an action upon it lies within the world of perceptions given to him, that means within his previous experiences. He remembers, before he comes to a decision, what someone else has done or named as a good thing to do in a case analogous to his own, or what God has dictated in such a case, and so on, and then he acts accordingly. For the free spirit these preconditions are not the only stimulus to action. He makes an absolutely primal decision. In doing so, he bothers just as little about what others have done in this case, as about what they have dictated for it. He has purely ideal reasons which move him to lift just one particular concept out of the sum total of his concepts and to translate it into action. His action will, however, belong to perceptible reality. What he brings about will therefore be identical with a quite definite perceptible content. His concept will have to realize itself in a concrete individual happening. It will not, as concept, be able to contain this individual instance. It will be able to relate itself to this only in the way that any concept at all relates itself to a perception; for example, in the way the concept “lion” relates to an individual lion. The intermediary between concept and perception is the mental picture (see pages 95–97). For the unfree spirit this intermediary is given from the start. His motives are present from the start as mental pictures in his consciousness. When he wants to carry out an action, he does it in the way he has see it done or the way he's ordered to do it in this or that case. Authority works therefore best of all through examples, that means through providing quite definite single actions for the consciousness of the unfree spirit. The Christian acts less according to the teachings than to the example of the Redeemer. Rules have less value for positive action than for leaving certain actions undone. Laws take on the generalized form of concepts only when they forbid actions; not, however, when they order something done. Laws about what he ought to do must be given to the unfree spirit in a quite concrete form: clean the sidewalk in front of your house! Pay your taxes in this amount at that tax center! And so on. Laws for preventing actions have a conceptual form: You shall not steal. You shall not commit adultery! These laws also affect the unfree spirit; however, only through reference to some concrete mental picture, for example, to that of the corresponding temporal punishment, or of the pangs of conscience, or of eternal damnation, and so on. [ 2 ] As soon as the stimulus to an action is present in the generalized form of concepts (for example: You shall do good to your neighbor! You shall live in such a way that you best promote your own welfare!), then in each individual case the concrete mental picture of the action (the relation of the concept to a perceptual content) must first be found. For the free spirit, who is not impelled by any example nor by any fear of punishment, etc., this translation of the concept into a mental picture is always necessary. [ 3 ] The human being produces concrete mental pictures out of the sum total of his ideas first of all through imagination. What the free spirit needs in order to realize his ideas, in order to make his way, is therefore moral imagination.1 It is the wellspring for the actions of the free spirit. Therefore, it is also true that only people with moral imagination are actually morally productive. Mere preachers of morality, that is, the people who spin forth moral rules without being able to condense them into concrete mental pictures, are morally unproductive. They are like the art critics who know how to expound judiciously upon the way a work of art ought to be, but who are unable themselves to create even the least little one. [ 4 ] Moral imagination, in order to realize its mental picture, must reach into a particular region of perceptions. Man's action does not create any perceptions, but rather reshapes the perceptions which are already present, imparts to them a new form. In order to be able to reshape a particular object of perception or a number of such, in accordance with a moral mental picture, one must have grasped the lawful content (its way of working until now, which one wants to shape anew or give a new direction to) of this perceptual configuration. One must furthermore find the method by which this lawfulness allows itself to be transformed into a new one. This part of one's moral activity rests upon knowledge of the phenomenal work with which one is involved. It is therefore to be sought in one branch of scientific knowledge in general. Moral action therefore presupposes, along with the faculty2 for moral ideas and along with moral imagination, the ability to transform the world of perceptions without violating their natural lawful connections. This ability is moral technique. It can be learned in the same sense that science in general can be learned. Generally, people are in fact better able to find the concepts for the already existing world, than productively, out of their imagination, to determine not yet existing future action. Hence, it is quite possible that people without moral imagination would receive moral mental pictures from others and would skillfully imprint them upon reality. The opposite case can occur also, that people with moral imagination are without technical skillfulness and must then make use of other people to realize their mental pictures. [ 5 ] Insofar as knowing the objects in our sphere of action is necessary for moral action, our action rests upon the knowing. What comes into consideration here are the laws of nature. We have to do with natural science, not with ethics. [ 6 ] Moral imagination and the capacity for moral ideas can become the object of knowing only after they have been produced by the individual. Then, however, they are no longer regulating life, but have already regulated it. They are to be grasped as operating causes like all others (they are purposes merely for the subject). We concern ourselves with them as with a natural history of moral mental pictures. [ 7 ] Besides this there can be no ethics as a science of norms. [ 8 ] People have wanted to hold to the normative character of moral laws, at least insofar as they have grasped ethics in the sense of dietetics, which extracts general laws out of the life conditions of the organism, in order then, on the basis of these laws, to influence the body in particular ways (Paulson, System of Ethics).3 This comparison is false, because our moral life cannot be compared with the life of our organism. The functioning of the organism is there without our doing; we find all its laws already there in the world, can therefore seek them, and then apply the ones we have found. Moral laws, however, are first created by us. We cannot apply them before they are created. The error arises through the fact that moral laws are not created, new in content, at every moment, but rather are handed down to others. The moral laws taken over from our ancestors then appear to be given, like the natural laws of the organism. It will definitely not, however, be as right for future generations to apply them as to apply laws of diet. For moral laws have to do with the individual and not, as is the case with a natural law, with a member of a species. As an organism I am just such a member of a species, and I will live in accordance with nature when I apply the natural laws of the species also in my particular case; as a moral being I am an individual and have laws entirely my own.4 [ 9 ] The view put forward here seems to stand in contradiction to that basic doctrine of modern natural science known as the theory of evolution. But it only seems to do so. By evolution is understood the real emerging of the later out of the earlier in ways corresponding to natural laws. By evolution in the organic world one means that the later (more perfect) organic forms are real descendants of earlier (less perfect) ones, and have emerged from them in a way corresponding to natural laws. The adherents of the theory or organic evolution would actually have to picture to themselves that there was once a period of time on earth when someone could have followed with his eyes the gradual emergence of the reptiles out of the proto-amniotes, if he could have been present as observer back then and had been endowed with sufficiently log life. In the same way the evolutionary theorists would have to picture to himself that a being could have observed the emergence of the solar system out of the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula, if he had been able to dwell freely in the realm of world ether in a suitable place during that infinitely long time. The fact that, with a picture such as this, both the nature of the proto-amniotes and also that of the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula would have to be thought of differently than the materialistic thinkers do, does not come into consideration here. But it should not occur to any evolutionary theorists to maintain that, even without ever having seen a reptile, he could draw forth from his concept of the proto-amniotes that of the reptile with all its characteristics. Just as little could the solar system be deduced from the concept from the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula. This means, in other words, that the evolutionary theorists must, if he is consistent in his thinking, maintain that out of earlier phases of development later ones result in a real way, and that, once we have bestowed the concept of less perfect and that of perfect, we can then see the connection; by no means, however, should he grant that the concept gained through the earlier is far-reaching enough to evolve the later out of it. From this it follows for the philosopher of ethics that he can in fact gain insight into the connection of later moral concepts with earlier ones; but not that even one single new moral idea can be drawn from an earlier one. As a moral being the individual produces his content. This content he produces is, for the philosopher of ethics, something given, exactly in the same way as, for the scientific researcher, the reptiles are something given. The reptiles have come forth out of the proto-amniotes; but the scientific researcher cannot draw the concept of the reptiles from that of the proto-amniotes. Later moral ideas evolve out of earlier ones; the philosopher of ethics cannot, however, draw, out of the moral concepts of an earlier cultural epoch, those of later ones. The confusion is caused through the fact that, as scientific researchers, we already have the phenomena before us and only afterward observe and know them; whereas in our moral actions we ourselves first create ht phenomena which we the afterward know. In the evolutionary process of the moral world order we do what nature does on a lower level: we transform something perceptible. The ethical norm can therefore at first not be known the way a law of nature can, but rather it must be created. Only when it is there can it become the object of our knowing. [ 10 ] But can we not then measure the new against the old? Is not each person compelled to measure what is produced through his moral imagination against the moral teachings already there from the past? For that which is to reveal itself as something morally productive, this is just as nonsensical as it would be for someone to want to measure a new natural form against an old one and then say: Because the reptiles do not match up with the proto-amniotes, they are an invalid (pathological) form. [ 11 ] Ethical individualism does not therefore stand at odds with a rightly understood theory of evolution, but rather follows directly form it. Haeckel's genealogical tree from the protozoa up to man as an organic being would have to be able to be followed, without any break in the lawfulness of nature and without any break in the unity of evolution, right up to the individual as a being who is moral in a particular sense. At no point, however, could the nature of a later species be decided form the nature of an ancestral species. But as true as it is that the moral ideas of the individual have observably come forth out of those of his ancestors, it is also just as true that he is morally barren if he himself does not have any moral ideas. [ 12 ] The same ethical individualism which I have developed on the basis of the preceding considerations could also be derived out of the theory of evolution. The final conviction would be the same; only the path upon which it is achieved would be a different one. [ 13 ] The emergence of totally new moral ideas out of our moral imagination is, for the theory of evolution, as little to be wondered at as the emergence of a new species of animal out of another. But this theory, as a monistic world view in moral life just as in the life of nature, must reject any influence from the beyond, any (metaphysical) influence which is merely inferred and not experienced in idea. This theory follows thereby the same principle which motivates it when it seeks the causes of new organic forms and in so doing does not refer to the intervention of some being, outside the world, who calls forth each new species through supernatural influence, according to new creative thought. Just as monism can have no use for any supernatural creative thoughts to explain a living being, so for monism it is al impossible to derive the moral world order from causes which do not lie within the experienceable world. Monism cannot believe that the nature of an act of will, as a moral one, has been fully explored by tracing it back to a continuing supernatural influence upon one's moral life (divine world-rule from outside), or to a particular revelation in time (the giving of the ten commandments), or to the appearance of God (of Christ) on earth. What occurs in and with the human being through al this becomes something moral only when within his human experience, it becomes something individually his own. For monism the moral processes are produced by the world like everything else that exists, and their causes must be sought in the world, that means in man, because he is the bearer of morality. [ 14 ] Ethical individualism is therefore the crowning feature of that edifice which Darwin and Haeckel have striven to build for natural science. Ethical individualism is spiritualized evolutionary teaching carried over into moral life. [ 15 ] Someone who from the beginning, in a narrow-hearted way, restricts his concept of nature to an arbitrarily limited sphere, can easily come to the point of finding no place in nature for free individual action. The evolutionary theorist who proceeds consequently cannot fall into any such narrowness of heart. He cannot terminate natural evolution at the ape and attribute to man a supernatural origin; he must, even when seeking the natural ancestors of man already seek the spirit in nature; he can also not stop short at the organic functions of man and find only these to be of nature, but rather he must also regard his morally free life as a spiritual continuation of organic life. [ 16 ] According to his basic principles, the evolutionary theorist can only maintain that the moral actions of the present emerge out of other kinds of world happening; his determining of the character of an action, that is whether it is free, he must leave up to his direct observation of the action. He maintains, after all, only that human beings have evolved out of ancestors that were not yet human. How human beings are constituted must be determined through observation of human beings themselves. The results of this observation cannot come into contradiction with a rightly viewed evolutionary history. Only the assertion that the results are such as to exclude a natural world order could not be brought into agreement with the present direction of natural science.5 [ 17 ] Ethical individualism has nothing to fear from a natural science that understands itself: observation shows inner freedom to be the characteristic of the perfect form of human action. This freedom must be attributed to human willing, insofar as this willing realizes purely ideal intuitions. For these are not the results of some necessity working upon them from outside, but rather are something based upon themselves. If a person finds that an action is the image of such an ideal intuition, he experiences it as a free one. In this characteristic of an action lies inner freedom. [ 18 ] How do matters stand now, from this point of view, with the distinction already made above (page 9f. and 4–5) between the two statements: that to be free means to be able to do what one wants to, and the other as to whether being at liberty to be able to desire and not to desire is the real proposition involved in the dogma of free will.—Hamerling in fact bases his view about free will upon this distinction, in that he declares the first statement to be correct and the second to be an absurd tautology. He says that I can do what I want to. But to say that I can want what I want to is an empty tautology.—Whether I can do, that means, can translate into reality, what I want to, what I have therefore put before me as the idea of my doing, this depends upon outer circumstances and upon my technical skill (see page 180f.) To be free means to be able, out of oneself, through moral imagination, to determine which mental pictures (stimuli to action) are to underlie one's actions. Inner freedom is impossible if something outside of me (a mechanical process or a merely inferred God outside the world) determines my moral mental pictures. I am therefore free only when I myself produce these mental pictures, not when I am able to carry out the stimuli to action which another being has instilled in me. A free being is one that can want what he himself considers to be right. Whoever does something other than he wants to, has to be driven to this other thing by motives which do not lie within him. Such a person acts unfreely. To be at liberty to be able to want what one considers to be right or wrong, means therefore to be at liberty to be able to be free or unfree. That is of course just as absurd as to see freedom in the ability to be able to do what one must want. But this last, however, is just what Hamerling maintains when he says that it is perfectly true that the will is always determined by stimuli to action, but that it is absurd to say that the will is therefore unfree; for no greater freedom could either be wished or imagined for it than the freedom to realize itself in proportion to its own strength and determination.—Yes! A greater freedom can indeed by wished for, and only that is the true one; namely, the freedom to determine for oneself the grounds for one's willing. [ 19 ] Under certain circumstances a person may let himself be motivated to refrain from carrying out what he wants to do. To let be prescribed what he ought to do, that is, to want what someone else and not he considers to be right, to this he can succumb only insofar as he does not feel himself to be free. [ 20 ] External powers can hinder me from doing what I want. They then simply condemn me to doing nothing or to being unfree. Only when they enslave my mind and spirit and drive my own impulses to action from my head and want to replace them with theirs, do they then intend my inner unfreedom. This is why the church, therefore, works not merely against my doing, but especially against my impure thoughts, that is against the impulses of my actions. The church makes me unfree if all impulses to action which it does not decree appear impure to it. A church or another community creates inner unfreedom when its priests or teachers make themselves into the ones who dictate conscience, that is, when the faithful must draw the impulses for their actions from them (in the confessional). Addendum to the Revised Edition, 1918 [ 21 ] In these considerations of human willing there is presented what the human being can experience with respect to his actions, in order through this experience to come to the consciousness: my willing if free. It is of particular significance that the justification for designating a willing as free is established through the experience that in the willing an ideal intuition realizes itself. This can only be the result of observation, but is so in the sense in which human willing observes itself in a stream of development whose goal lies in reaching just such a potential of willing that is carried by purely ideal intuitions. This potential can be reached because nothing is at work within ideal intuition other than its own being, which is founded upon itself. If such an intuition is present in human consciousness, then it has not developed out of the processes of the organism (p. 133ff.), but rather the organic activity has drawn back, in order to make room for the ideal activity. If I observe a willing that is the image of intuition, then the organically necessary activity has also drawn back out of this willing. The willing is free. A person will not be able to observe this freedom of willing who cannot see how free willing consists in the fact, that first, through the intuitive element, the necessary working of the human organism is paralyzed, forced back, and that the spiritual activity6 of will filled with ideas is set in its place. Only someone who cannot make this observation of the twofold nature of a free willing believes in the unfreedom of every willing. Whoever can make it struggles through to the insight that the human being, insofar as he cannot fully accomplish the process of damming up organic activity, is unfree; but that this unfreedom is striving toward freedom, and this freedom is in no way an abstract ideal, but rather is a power of direction lying within the human being. Man is free to the extent that he is able in his willing to realize the same mood of soul which lives in him when he is conscious of giving shape to purely ideal (spiritual) intuitions.
|
| 4. The Philosophy of Freedom (1964): Moral Imagination
Tr. Michael Wilson Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Similarly, evolutionists ought to picture to themselves that a being could have watched the development of the solar system out of the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula, had he been able to remain in a suitable spot out in the cosmic world ether during that infinitely long time. That with such mental pictures, the nature of both the proto-amniotes and the Kant-Laplace cosmic nebula would have to be thought of differently from the way the materialist thinkers do, is here irrelevant. |
| Just as little would it be possible to derive the solar system from the concept of the Kant-Laplace nebula, if this concept of a primordial nebula is thought of as being directly determined only by the percept of the primordial nebula. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Freedom (1964): Moral Imagination
Tr. Michael Wilson Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] A free spirit acts according to his impulses, that is, according to intuitions selected from the totality of his world of ideas by thinking. For an unfree spirit, the reason why he singles out a particular intuition from his world of ideas in order to make it the basis of an action, lies in the world of percepts given to him, that is, in his past experiences. He recalls, before coming to a decision, what someone else has done or recommended as suitable in a comparable case, or what God has commanded to be done in such a case, and so on, and he acts accordingly. For a free spirit, these prior conditions are not the only impulses to action. He makes a completely first-hand decision. What others have done in such a case worries him as little as what they have decreed. He has purely ideal reasons which lead him to select from the sum of his concepts just one in particular, and then to translate it into action. But his action will belong to perceptible reality. What he achieves will thus be identical with a quite definite content of perception. The concept will have to realize itself in a single concrete occurrence. As a concept it will not be able to contain this particular event. It will refer to the event only in the same way as a concept is in general related to a percept, for example, the concept of the lion to a particular lion. The link between concept and percept is the mental picture (see Chapter 6). For the unfree spirit, this link is given from the outset. Motives are present in his consciousness from the outset in the form of mental pictures. Whenever there is something he wants to carry out, he does it as he has seen it done, or as he has been told to do it in the particular case. Hence authority works best through examples, that is, through providing quite definite particular actions for the consciousness of the unfree spirit. A Christian acts not so much according to the teaching as according to the example of the Saviour. Rules have less value for acting positively than for refraining from certain actions. Laws take on the form of general concepts only when they forbid actions, but not when they prescribe them. Laws concerning what he ought to do must be given to the unfree spirit in quite concrete form: Clean the street in front of your door! Pay your taxes, amounting to the sum here given, to the Tax Office at X! and so on. Conceptual form belongs to laws for inhibiting actions: Thou shalt not steal! Thou shalt not commit adultery! These laws, too, influence the unfree spirit only by means of a concrete mental picture, for example, that of the appropriate secular punishment, or the pangs of conscience, or eternal damnation, and so on. [ 2 ] Whenever the impulse for an action is present in a general conceptual form (for example, Thou shalt do good to thy fellow men! Thou shalt live so that thou best promotest thy welfare!) then for each particular case the concrete mental picture of the action (the relation of the concept to a content of perception) must first be found. For the free spirit who is impelled by no example, nor fear of punishment or the like, this translation of the concept into a mental picture is always necessary. [ 3 ] Man produces concrete mental pictures from the sum of his ideas chiefly by means of the imagination. Therefore what the free spirit needs in order to realize his ideas, in order to be effective, is moral imagination. This is the source of the free spirit's action. Therefore it is only men with moral imagination who are, strictly speaking, morally productive. Those who merely preach morality, that is, people who merely spin out moral rules without being able to condense them into concrete mental pictures, are morally unproductive. They are like those critics who can explain very intelligibly what a work of art ought to be like, but who are themselves incapable of even the slightest productive effort. [ 4 ] Moral imagination, in order to realize its mental picture, must set to work in a definite sphere of percepts. Human action does not create percepts, but transforms already existing percepts and gives them a new form. In order to be able to transform a definite object of perception, or a sum of such objects, in accordance with a moral mental picture, one must have grasped the principle at work within the percept picture, that is, the way it has hitherto worked, to which one wants to give a new form or a new direction. Further, it is necessary to discover the procedure by which it is possible to change the given principle into a new one. This part of effective moral activity depends on knowledge of the particular world of phenomena with which one is concerned. We shall, therefore, look for it in some branch of learning in general. Moral action, then, presupposes, in addition to the faculty of having moral ideas (moral intuition) and moral imagination, the ability to transform the world of percepts without violating the natural laws by which these are connected.1 This ability is moral technique. It can be learnt in the same sense in which any kind of knowledge can be learnt. Generally speaking, men are better able to find concepts for the existing world than to evolve productively, out of their imagination, the not-yet-existing actions of the future. Hence it is perfectly possible for men without moral imagination to receive such mental pictures from others, and to embody them skillfully into the actual world. Conversely, it may happen that men with moral imagination lack technical skill, and must make use of other men for the realization of their mental pictures. [ 5 ] In so far as knowledge of the objects within our sphere of action is necessary for acting morally, our action depends upon such knowledge. What we are concerned with here are laws of nature. We are dealing with natural science, not ethics. [ 6 ] Moral imagination and the faculty of having moral ideas can become objects of knowledge only after they have been produced by the individual. By then, however, they no longer regulate life, for they have already regulated it. They must now be regarded as effective causes, like all others (they are purposes only for the subject). We therefore deal with them as with a natural history of moral ideas. [ 7 ] Ethics as a science that sets standards, in addition to this, cannot exist. [ 8 ] Some people have wanted to maintain the standard-setting character of moral laws, at least in so far as they have understood ethics in the sense of dietetics, which deduces general rules from the organism's requirements in life as a basis for influencing the body in a particular way (e.g., Paulsen, in his System der Ethik). This comparison is false, because our moral life is not comparable with the life of the organism. The functioning of the organism occurs without any action on our part; we come upon its laws in the world ready-made and can therefore seek them and apply them when found. Moral laws, on the other hand, are first created by us. We cannot apply them until we have created them. The error arises through the fact that, as regards their content, moral laws are not newly created at every moment, but are inherited. Those that we have taken over from our ancestors appear to be given, like the natural laws of the organism. But a later generation will certainly not be justified in applying them as if they were dietetic rules. For they apply to individuals and not, as natural laws do, to specimens of a general type. Considered as an organism, I am such a generic specimen and I shall live in accordance with nature if I apply the natural laws of my general type to my particular case; as a moral being, I am an individual and have laws of my very own.2 [ 9 ] This view appears to contradict the fundamental doctrine of modern natural science known as the theory of evolution. But it only appears to do so. Evolution is understood to mean the real development of the later out of the earlier in accordance with natural law. In the organic world, evolution is understood to mean that the later (more perfect) organic forms are real descendants of the earlier (imperfect) forms, and have developed from them in accordance with natural laws. The adherents of the theory of organic evolution ought really to picture to themselves that there was once a time on our earth when a being could have followed with his own eyes the gradual development of reptiles out of proto-amniotes, had he been able to be there at the time as an observer, endowed with a sufficiently long span of life. Similarly, evolutionists ought to picture to themselves that a being could have watched the development of the solar system out of the Kant-Laplace primordial nebula, had he been able to remain in a suitable spot out in the cosmic world ether during that infinitely long time. That with such mental pictures, the nature of both the proto-amniotes and the Kant-Laplace cosmic nebula would have to be thought of differently from the way the materialist thinkers do, is here irrelevant. But no evolutionist should ever dream of maintaining that he could get the concept of the reptile, with all its characteristics, out of his concept of the proto-amniotic animal, if he had never seen a reptile. Just as little would it be possible to derive the solar system from the concept of the Kant-Laplace nebula, if this concept of a primordial nebula is thought of as being directly determined only by the percept of the primordial nebula. In other words, if the evolutionist is to think consistently, he is bound to maintain that later phases of evolution do actually result from earlier ones, and that once we have been given the concept of the imperfect and that of the perfect, we can see the connection; but on no account should he agree that the concept attained from the earlier is, in itself, sufficient for evolving the later out of it. From this it follows for ethics that, though we can certainly see the connection between later moral concepts and earlier, we cannot get even a single new moral idea out of the earlier ones. As a moral being, the individual produces his own content. For the student of ethics, the content thus produced is just as much a given thing as reptiles are a given thing for the scientist. Reptiles have developed out of proto-amniotes, but the scientist cannot get the concept of reptiles out of the concept of the proto-amniotes. Later moral ideas evolve out of earlier, but the student of ethics cannot get the moral concepts of a later civilization out of those of an earlier one. The confusion arises because, as scientists, we start with the facts before us, and then get to know them, whereas in moral action we ourselves first create the facts which we then get to know. In the process of evolution of the moral world order we accomplish something that, at a lower level, is accomplished by nature: we alter something perceptible. The ethical standard thus cannot start, like a law of nature, by being known, but only by being created. Only when it is there, can it become an object of knowledge. [ 10 ] But can we not then make the old a measure for the new? Is not every man compelled to measure the products of his moral imagination by the standard of traditional moral doctrines? For something that should reveal itself as morally productive, this would be just as absurd as to want to measure a new form in nature by an old one and say that, because reptiles do not conform to the proto-amniotes, they are an unjustifiable (pathological) form. [ 11 ] Ethical individualism, then, is not in opposition to a rightly understood theory of evolution, but follows directly from it. Haeckel's genealogical tree, from protozoa up to man as an organic being, ought to be capable of being continued without an interruption of natural law and without a break in the uniformity of evolution, up to the individual as a being that is moral in a definite sense. But on no account could the nature of a descendant species be deduced from the nature of an ancestral one. However true it is that the moral ideas of the individual have perceptibly developed out of those of his ancestors, it is equally true that the individual is morally barren unless he has moral ideas of his own. [ 12 ] The same ethical individualism that I have developed on the basis of views already given could also be derived from the theory of evolution. The final conviction would be the same; only the path by which it was reached would be different. [ 13 ] The appearance of completely new moral ideas through moral imagination is, for the theory of evolution, no more miraculous than the development of a new animal species out of an old one ; only, as a monistic view of the world, this theory must reject, in morality as in science, every transcendental (metaphysical) influence, every influence that is merely inferred and cannot be experienced ideally. In doing so, the theory follows the same principle that guides it when it seeks the causes of new organic forms without invoking the interference of an extra-mundane Being who produces every new species, in accordance with a new creative thought, by supernatural influence. Just as monism has no use for supernatural creative thoughts in explaining living organisms, so it is equally impossible for it to derive the moral world order from causes which do not lie within the experienceable world. It cannot admit that the moral nature of will is completely accounted for by being traced back to a continuous supernatural influence upon moral life (divine government of the world from the outside), or to an act of revelation at a particular moment in history (giving of the ten commandments), or to God's appearance on the earth (as Christ). What happens to man, and in man, through all this, becomes a moral element only when, in human experience, it becomes an individual's own. For monism, moral processes are products of the world like everything else that exists, and their causes must be sought in the world, that is, in man, since man is the bearer of morality. [ 14 ] Ethical individualism, then, is the crowning feature of the edifice that Darwin and Haeckel have striven to build for natural science. It is spiritualized theory of evolution carried over into moral life. [ 15 ] Anyone who, in a narrow-minded way, restricts the concept of the natural from the outset to an arbitrarily limited sphere may easily conclude that there is no room in it for free individual action. The consistent evolutionist cannot fall a prey to such narrow-mindedness. He cannot let the natural course of evolution terminate with the ape, and allow man to have a “supernatural” origin; in his very search for the natural progenitors of man, he is bound to seek spirit in nature; again, he cannot stop short at the organic functions of man, and take only these as natural, but must go on to regard the free moral life as the spiritual continuation of organic life. [ 16 ] If he is to keep to his fundamental principles, the evolutionist can state only that the present form of moral action evolves from other forms of activity in the world; the characterizing of an action, that is, whether it is a free one, he must leave to the immediate observation of the action. In fact, he maintains only that men have developed out of ancestors that were not yet human. What men are actually like must be determined by observation of men themselves. The results of this observation cannot contradict the properly understood history of evolution. Only the assertion that the results are such as to exclude a natural ordering of the world would contradict recent trends in the natural sciences.3 [ 17 ] Ethical individualism has nothing to fear from a natural science that understands itself: for observation shows that the perfect form of human action has freedom as its characteristic quality. This freedom must be allowed to the human will, in so far as the will realizes purely ideal intuitions. For these intuitions are not the results of a necessity acting upon them from without, but are due only to themselves. If a man finds that an action is the image of such an ideal intuition, then he feels it to be free. In this characteristic of an action lies its freedom. [ 18 ] What are we to say, from this standpoint, about the distinction mentioned earlier (see Chapter 1) between the two propositions, “To be free means to be able to do as one wills” and, “To be at liberty to desire or not to desire is the real proposition involved in the dogma of freewill”? Hamerling bases his view of free will precisely on this distinction, by declaring the first statement to be correct but the second to be an absurd tautology. He says, “I can do as I will. But to say I can want as I will is an empty tautology.” Whether I am able to do, that is, to translate into reality, what I will, that is, what I have set before myself as my idea of action, depends on external circumstances and on my technical skill (ee above). To be free means to be able of one's own accord to determine by moral imagination those mental pictures (motives) which underlie the action. Freedom is impossible if anything other then myself (mechanical process or merely inferred extra-mundane God) determines my moral ideas. In other words, I am free only when I myself produce these mental pictures, not when I am merely able to carry out the motives which another being has implanted in me. A free being is one who can want what he himself considers right. Whoever does anything other than what he wants must be impelled to it by motives which do not lie within him. Such a man is unfree in his action. To be at liberty to want what one considers right or what one considers wrong, would therefore mean to be at liberty to be free or unfree. This is, of course, just as absurd as to see freedom in the ability to do what one is compelled to will. But this last is just what Hamerling maintains when he says, “It is perfectly true that the will is always determined by motives, but it is absurd to say that on this account it is unfree; for a greater freedom can neither be desired nor conceived than the freedom to realize oneself in proportion to one's own strength and determination.” In deed it can! It is certainly possible to desire a greater freedom, and this for the first time the true one: namely, to decide for oneself the motives for one's will. [ 19 ] Under certain conditions a man may be induced to abandon the execution of his will. To allow others to prescribe to him what he ought to do—in other words, to want what another, and not he himself, considers right—to this a man will submit only to the extent that he does not feel free. [ 20 ] External powers may prevent me from doing as I will. Then they simply condemn me to do nothing or to be unfree. Not until they would enslave my spirit, drive my motives out of my head, and put their own motives in the place of mine, do they really aim at making me unfree. For this reason the Church sets itself not only against the mere doing, but especially against the impure thoughts, that is, the motives of my action. The Church makes me unfree if, for her, all those motives she has not herself enunciated seem impure. A Church or other community produces unfreedom when its priests or teachers make themselves into keepers of consciences, that is, when the faithful are obliged to go to them (to the confessional) for the motives of their actions. Author's addition, 1918[ 21 ] In these chapters on the human will I have shown what man can experience in his actions so that, through this experience, he comes to be aware: My will is free. It is particularly significant that the right to call an act of will free arises from the experience that an ideal intuition comes to realization in the act of will. This experience can only be the result of an observation, and is so, in the sense that we observe our will on a path of development towards the goal where it becomes possible for an act of will to be sustained by purely ideal intuition. This goal can be reached, because in ideal intuition nothing else is at work but its own self-sustaining essence. When such an intuition is present in human consciousness, then it has not been developed out of the processes of the organism, but rather the organic activity has withdrawn to make room for the ideal activity (see Chapter 9). When I observe an act of will that is an image of an intuition, then from this act of will too all organically necessary activity has withdrawn. The act of will is free. This freedom of the will cannot be observed by anyone who is unable to see how the free act of will consists in the fact that, firstly, through the intuitive element, the activity that is necessary for the human organism is checked and repressed, and then replaced by the spiritual activity of the idea-filled will. Only those who cannot make this observation of the twofold nature of a free act of will, believe that every act of will is unfree. Those who can make this observation win through to the recognition that man is unfree in so far as he cannot complete the process of suppressing the organic activity; but that this unfreedom tends towards freedom, and that this freedom is by no means an abstract ideal but is a directive force inherent in human nature. Man is free to the extent that he is able to realize in his acts of will the same mood of soul that lives in him when he becomes aware of the forming of purely ideal (spiritual) Intuitions.
|
| 4. The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity (1949): Moral Imagination (Darwinism and Morality)
Tr. Hermann Poppelbaum Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Similarly, Evolutionists ought to suppose that a being could have watched the development of the solar system out of the primordial nebula of the Kant-Laplace hypothesis, if he could have occupied a suitable spot in the world-ether during that infinitely long period. [That on this supposition, the nature of both the proto-amniotes and of the primordial nebula of the Kant-Laplace hypothesis would have to be conceived differently from the Materialist's conception of it, is here irrelevant.] |
| Just as little would it be possible to derive the solar system from the concept of the Kant-Laplace nebula, if this concept of an original nebula had been formed only from the percept of the nebula. |
| 4. The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity (1949): Moral Imagination (Darwinism and Morality)
Tr. Hermann Poppelbaum Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
[ 1 ] A free spirit acts according to his impulses, i.e., intuitions, which his thinking has selected out of the whole world of his Ideas. For an unfree spirit, the reason why he singles out a particular intuition from his world of Ideas, in order to make it the basis of an action, lies in the perceptual world which is given to him, i.e., in his past experiences. He recalls, before making a decision, what someone else has done, or recommended as proper in an analogous case, or what God has commanded to be done in such a case, etc., and he acts on these recollections. For a free spirit these preliminary conditions are not the only impulses to action. He takes an absolutely original decision. He cares as little what others have done in such a case as what commands they had laid down. He has purely ideal reasons which determine him to select a particular concept out of the sum of his concepts, and to realize it in action. But his action will belong to perceptible reality. Consequently, what he achieves will be identical with a definite content of perception. The concept will have to realize itself in a concrete particular event. As a concept it will not contain this particular event. It will refer to the event only in the same way as, in general, a concept is related to a percept, e.g., the concept lion to a particular lion. The link between concept and percept is the representation.1 To the unfree spirit this intermediate link is given from the outset. Motives exist in his consciousness from the first in the form of representations. Whenever he intends to do anything he acts as he has seen others act, or as he is ordered to do in each separate case. Hence authority is most effective in the form of examples, i.e., in the form of quite definite particular actions handed down for the consciousness of the unfree spirit. A Christian models his conduct less on the teaching than on the model of the Saviour. Rules have less value for telling men positively what to do than for telling them what to leave undone. Laws take on the form of general concepts only when they forbid actions, not when they prescribe actions. Laws concerning what we ought to do must be given to the unfree spirit in wholly concrete form. Clean the street in front of your door! Pay your taxes to such and such an amount to the tax-collector! etc. Conceptual form belongs to laws which inhibit actions. Thou shalt not steal! Thou shalt not commit adultery! These laws, too, influence the unfree spirit only by means of a concrete representation, e.g., that of the punishments attached by human authority, or of the pangs of conscience, or of eternal damnation, etc. [ 2 ] When the motive to an action exists in general conceptual form (e.g., Thou shalt do good to thy fellow-men! Thou shalt live so that thou promotest best thy welfare!) there must first be found, in the particular case, the concrete representation of the action (the relation of the concept to a content of perception). For a free spirit who is not compelled by any model nor by fear of punishment, etc., this translation of the concept into a representation is always necessary. [ 3 ] Now man produces concrete representations from out of the sum of his Ideas by means of the imagination. Hence what the free spirit needs in order to realize his Ideas, in order to assert himself in the world, is moral imagination. This is the source of the free spirit's action. Only those men, therefore, who are endowed with moral imagination are, properly speaking, morally productive. Those who merely preach morality, i.e., those who merely excogitate moral rules without being able to condense them into concrete representations, are morally unproductive. They are like those critics who can explain very reasonably how a work of art ought to be made, but who are themselves incapable of the smallest artistic production. [ 4 ] Moral imagination, in order to realize its representation, must set to work upon a determinate sphere of percepts. Human action does not create percepts, but transforms already existing percepts and gives them a new form. In order to be able to transform a definite object of perception, or a sum of such objects, in accordance with a moral representation, one must have grasped the law-abiding content of the percept-picture (its hitherto existing mode of working to which one wants to give a new form or a new direction). Further, it is necessary to discover the procedure by which it is possible to change the given law into the new one. This part of effective moral activity depends on knowledge of the particular world of phenomena with which one has got to deal. We shall, therefore, find it in some branch of scientific knowledge in general. Moral action, then, presupposes, in addition to the faculty of moral Ideation 2 and of moral imagination, the ability to transform the world of percepts without breaking the natural laws by which they are connected. This ability is moral technique. It may be learnt in the same sense in which science in general may be learnt. For, in general, men are better able to find concepts for the ready-made world than productively to originate out of their imagination future, and as yet non-existing, actions. Hence, it is very well possible for men without moral imagination to receive moral representations from others, and to engrave them skillfully into the actual world. Vice versa, it may happen that men with moral imagination lack technical skill, and are dependent on the service of other men for the realization of their representations. [ 5 ] In so far as we require for moral action knowledge of the objects upon which we are about to act, our action depends upon such knowledge. What we need to know here are laws of nature. These belong to the Natural Sciences, not to Ethics. [ 6 ] Moral imagination and the faculty of moral Ideation can become objects of knowledge only after they have first been produced by the individual. But, then, they no longer regulate life, but have already regulated it. They must now be treated as efficient causes, like all other causes (they are purposes only for the subject). The study of them is, as it were, the Natural Science of moral representations. [ 7 ] Ethics as a Normative Science, over and above this science, cannot exist. [ 8 ] Some would maintain the normative character of moral laws at least in the sense that Ethics is to be taken as a kind of dietetic which from the conditions of the organism's life, deduces general rules, on the basis of which it hopes to give detailed directions to the body. (Paulsen, System der Ethik.) This comparison is mistaken, because our moral life cannot be compared with the life of the organism. The function of the organism occurs without any volition on our part. We find its laws ready-made in the world; hence we can discover them and apply them when discovered. Moral laws, on the other hand, do not exist until we create them. We cannot apply them until we have created them. The error is due to the fact that moral laws are not, in their content, at every moment new creations, but are handed down by tradition. Those which we take over from our ancestors appear to be given like the natural laws of the organism. But it does not follow that a later generation has the right to apply them in the same way as dietetic rules. For they apply to individuals, and not, like natural laws, to specimens of a genus. Considered as an organism I am such a generic specimen, and I shall live in accordance with nature if I apply the laws of my genus to my particular case. As a moral being I am an individual and have laws which are wholly my own.3 [ 9 ] The view here upheld appears to contradict that fundamental doctrine of modern Natural Science which is known as the Theory of Evolution. But it only appears to do so. By evolution we mean the real development of the later out of the earlier in accordance with natural law. In the organic world, evolution means that the later (more perfect) organic forms are real descendants of the earlier (imperfect) forms, and have grown out of them in accordance with natural laws. The upholders of the theory of organic evolution ought really to believe that there was once a time on our earth, when a being could have observed with his own eyes the gradual evolution of reptiles out of proto-amniotes, supposing that he could have been present as an observer, and had been endowed with a sufficiently long span of life. Similarly, Evolutionists ought to suppose that a being could have watched the development of the solar system out of the primordial nebula of the Kant-Laplace hypothesis, if he could have occupied a suitable spot in the world-ether during that infinitely long period. [That on this supposition, the nature of both the proto-amniotes and of the primordial nebula of the Kant-Laplace hypothesis would have to be conceived differently from the Materialist's conception of it, is here irrelevant.] But no Evolutionist should ever dream of maintaining that he could from his concept of the proto-amniote deduce that of the reptile with all its qualities, if he had never seen a reptile. Just as little would it be possible to derive the solar system from the concept of the Kant-Laplace nebula, if this concept of an original nebula had been formed only from the percept of the nebula. In other words, if the Evolutionist is to think consistently, he is bound to maintain that out of earlier phases of evolution later ones really develop; that once the concept of the imperfect and that of the perfect have been given, we can understand the connection. But in no case should he admit that the concept formed from the earlier phases is, in itself, sufficient for deducing from it the later phases. From this it follows for Ethics that, whilst we can understand the connection of later moral concepts with earlier ones, it is not possible to deduce a single new moral Idea from earlier ones. The individual, as a moral being, produces his own content. This content, thus produced, is for Ethics a datum, as much as reptiles are a datum for Natural Science. Reptiles have evolved out of proto-amniotes, but the scientist cannot manufacture the concept of reptiles out of the concept of the proto-amniotes. Later moral Ideas evolve out of the earlier ones, but Ethics cannot manufacture out of the moral principles of an earlier culture those of a later one. The confusion is due to the fact that, as scientists, we start with the facts before us, and then make them objects of knowledge, whereas in moral action we first produce the facts ourselves, and then gain knowledge of them. In the evolution of the moral world-order we accomplish what, at a lower level, nature accomplishes: we alter some part of the perceptual world. Hence the ethical norm cannot straightway be made an object of knowledge, like a law of nature, for it must first be created. Only when that has been done can the norm become an object of knowledge. [ 10 ] But is it not possible to make the old a measure for the new? Is not every man compelled to measure the products of his moral imagination by the standard of traditional moral doctrines? If he would be truly productive in morality, such measuring is as much an absurdity as it would be an absurdity if one were to measure a new species in nature by an old one and say that reptiles, because they do not agree with the proto-amniotes, are an illegitimate (degenerate) species. [ 11 ] Ethical Individualism, then, so far from being in opposition to the theory of evolution rightly understood, is a direct consequence of it. Haeckel's genealogical tree, from protozoa up to man as an organic being, ought to be capable of being worked out without a breach of natural law, and without a gap in its uniform evolution, up to the individual as a moral being in a definite sense. But in no case could we deduce the nature of a later species from the nature of an ancestral species. However true it is that the moral Ideas of the individual have perceptibly grown out of those of his ancestors, it is also true that the individual is morally barren, unless he has moral Ideas of his own. [ 12 ] The same Ethical Individualism, which I have developed on the basis of the preceding conceptions, might be equally well developed on the basis of the theory of evolution. The final result would be the same; only the path by which it was reached would be different. [ 13 ] That absolutely new moral Ideas should be developed by the moral imagination is for the theory of evolution no more miraculous than the development of one animal species out of another, provided only that this theory, as a Monistic world-view, rejects, in morality as in science, every transcendent (metaphysical) influence which cannot be ideally experienced. In doing so, it follows the same principle by which it is guided in seeking the causes of new organic forms without referring to the interference of an extra-mundane Being, who produces every new species in accordance with a new creative thought through supernatural influence. Just as Monism has no use for supernatural creative thoughts in explaining living organisms, so it is equally impossible for it to derive the moral world-order from causes which do not lie within the world of our experience. It cannot admit that the nature of moral will is exhausted by being traced back to a continuous supernatural influence upon moral life (divine government of the world from the outside), or a particular act of revelation at a particular moment in history (giving of the ten commandments), or through God's appearance on the earth (as Christ). All that happens in this way to and in man becomes a moral element only when it enters into human experience and becomes an individual's own. Moral processes are, for Monism, products of the world like everything else that exists, and their causes must be looked for in the world, i.e., in man, because man is the bearer of morality. [ 14 ] Ethical Individualism, then, is the crown of the edifice that Darwin and Haeckel have striven for Natural Science. It is Spiritualized Evolutionism applied to the moral life. [ 15 ] Anyone who restricts the concept of the natural from the outset to an arbitrarily narrowed sphere, is easily tempted not to find any room within it for free individual action. The consistent Evolutionist does not easily fall a prey to such a narrow-minded view. He cannot let the natural process of evolution terminate with the ape, and acknowledge for man a “supernatural” origin. He is bound, in his very search for the natural progenitors of man to seek Spirit even in nature. Again, he cannot stop short at the organic functions of man, and regard only these as natural. He is bound to look on the life of moral self-determination as the spiritual continuation of organic life. [ 16 ] The Evolutionist, then, in accordance with his fundamental principles, can maintain only that the present form of moral action evolves out of other kinds of world-happenings. He must leave the characterization of action, i.e., its determination as a free action, to the immediate observation of each action. All that he maintains is only that men have developed out of non-human ancestors. What the nature of men actually is must be determined by observation of men themselves. The results of this observation cannot possibly contradict the true history of evolution. Only the assertion that the results are such as to exclude their being due to a natural world-order would contradict recent developments in the Natural Sciences.4 [ 17 ] Ethical Individualism, then, has nothing to fear from a Natural Science which understands itself. Observation yields spiritual activity (freedom) as the characteristic quality of the perfect form of human action. Freedom must be attributed to the human will, in so far as the will realizes purely ideal intuitions. For these are not the results of a necessity acting upon them from without, but are grounded in themselves. When we find that an action embodies such an ideal intuition, we feel it to be free. Freedom consists in this character of an action. [ 18 ] What, then, from this standpoint are we to say of the distinction, already mentioned above (p. 7) between the two statements “To be free means to be able to do what you will,” and “To be able, as you please, to desire or not to desire is the real meaning of the dogma of freewill”? Hamerling bases his theory of freewill precisely on this distinction, by declaring the first statement to be correct but the second to be an absurd tautology. He says, “I can do what I will, but to say I can will what I will is an empty tautology.” Whether I am able to do, i.e., to make real, what I will, i.e., what I have set before myself as my Idea of action, that depends on external circumstances and on my technical skill (cp. p. 156). To be free means to be able to determine by moral imagination out of oneself those representations (motives) which lie at the basis of the action. Freedom is impossible if anything other than I myself (whether a mechanical process or extra-mundane God whose existence is only inferred) determines my moral representations. In other words, I am free only when I myself produce these representations, but not when I am merely able to realize the motives which another being has implanted in me. A free being is one who can will what he regards as right. Whoever does anything other than what he wills must be impelled to it by motives which do not lie in himself. Such a man is unfree in his action. Accordingly, to be able to will, as you please, what you consider right or what you consider wrong would mean to be free or unfree as you please. This is, of course, just as absurd as to identify freedom with the ability to do what one is compelled to will. But this is just what Hamerling maintains when he says, “It is perfectly true that the will is always determined by motives, but it is absurd to say that on this ground it is unfree; for a greater freedom can neither be desired nor conceived than the freedom to realize oneself in proportion to one's own power and strength of decision.” On the contrary, it is well possible to desire a greater freedom and that a true freedom, viz., the freedom to determine for oneself the reasons for one's volitions. [ 19 ] Under certain conditions a man may be induced to abandon the execution of his will; but to allow others to prescribe to him what he ought to do—in other words, to will what another and not what he himself regards as right—to this a man will submit only when he does not feel free. [ 20 ] External powers may prevent me from doing what I will, but that is only to condemn me to do nothing or to be unfree. Not until they enslave my spirit, drive my motives out of my head, and put their own motives in the place of mine, do they really aim at making me unfree. That is the reason why the church attacks not only the mere doing, but especially the impure thoughts, i.e., motives of my action. The church makes me unfree if she calls impure all those motives which she has not enunciated. A church or other community produces unfreedom when its priests or teachers turn themselves into rulers of consciences, i.e., when the faithful are compelled to go to them (to the confessional) for the motives of their actions. Addition to the Revised Edition, 1918 [ 21 ] In the preceding chapters on human willing I have pointed out what man can experience in his actions, so as, through this experience, to become conscious that his willing is free. It is especially important to recognize that we derive the right to call an act of will free from the experiment of an ideal intuition realizing itself in the act. This can be nothing but a result of observation, in the sense that we observe the development of human volition in the direction towards the goal of attaining the possibility of just-such volition sustained by purely ideal intuition. This attainment is possible because the ideal intuition is effective through nothing but its own self-dependent essence. Where such an intuition is present in human consciousness, it has not developed itself out of the processes in the organism (cp. p. 111 ff.), but the organic activity has retired to make room for the ideal activity. Observation of an act of will which is an image of an intuition shows that out of it, likewise, all organically necessary activity has retired. The act of will is free. No one can observe this freedom of will who is unable to see how free will consists in this, that, first, the intuitive element lames and represses the necessary activity of the human organism and then puts in its place the spiritual activity of a will permeated by the Idea. Only those who are unable to observe these two factors in the free act of will believe that every act of will is unfree. Those who are able to observe them win through to the recognition that man is unfree in so far as he cannot carry through the repressing of the organic activity, but that this unfreedom is tending towards freedom, and that this freedom, so far from being an abstract ideal, is a directive force inherent in human nature. Man is free in proportion as he succeeds in realizing in his acts of will the same mood of soul which pervades him when he is conscious in himself of the formation of purely ideal (spiritual) intuitions.
|
| 69d. Death and Immortality in the Light of Spiritual Science: The Origin of Man in the Light of Spiritual Science
26 Feb 1912, Munich Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The spiritual researcher recognizes that objections have recently been raised against this so-called Kant-Laplace theory, but in the broadest circles it still prevails. It is believed that the whole solar system itself emanated from a kind of primeval nebula that was in rotation, and it is also imagined that the planets, including our Earth, were separated by the forces that were at work in this rotation. |
| Now, if one were to undertake the usual presentations of the Kant-Laplacean theory and the associated operations, one could say that it is possible to derive what our body is and the shaping of physical and mental structures from the rotation in the primeval nebula. If we want to make the assumption that some kind of giant teacher is out there and sets the whole thing in motion, then we can speak, if need be, of the formation of the earth having emerged from the Kant-Laplacean primeval nebula. But then we come to a critical point again, and this has been seen not only by spiritual researchers, but also by thoughtful natural scientists. |
| 69d. Death and Immortality in the Light of Spiritual Science: The Origin of Man in the Light of Spiritual Science
26 Feb 1912, Munich Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The previous lecture, which is followed by today's lecture, was about the hidden depths of the soul's life and explained that the soul's life is not absolutely bound to matter, that it is not only separable from the physical, but also from the ideas that are gained from it through the senses and the mind. The possibility of the separation of soul experiences from physical ideas was demonstrated by the difference between memories and dreams. Those [memories] arise without the original power of the soul's compassion, these [dreams] with the original accompanying phenomena of the emotional life of joy, suffering and the like. There - in memory - the soul life detaches itself from the life of imagination, which is gained in the outside world, and withdraws into the hidden depths of the soul, where it works and works, where it exercises its power by working on the entire human organism. While the life of imagination often proves powerless – for we know not what goes on in the depths of the sea when the surface ripples – the hidden life of the soul proves itself to be a power. We see this in dreams, in the trance of mediums, in the work of art and in the knowledge of the spiritual researcher. For man can penetrate into it by training his mind, so that he learns to consciously draw from the sources of truly real life, into which he not only gazes without control like the dreamer and fantasist and thereby becomes a dreamer, hallucinist or even a liar, not like the one with atavistic gifted with atavistic clairvoyance, becomes the plaything of the spirits of such a soul or astral world in his dreams, nor alone, as the true artist draws from the spirit and shapes it in beauty, but as a knower, consciously seeing, can distinguish what is vision from what is true and self-willed. [...] This knowledge of the hidden can only lead to the right spiritual research if it is gained, firstly, through self-knowledge, through descending into one's own inner being. With this self-knowledge, secondly, knowledge of the spiritual environment arises and grows. The greater the self-knowledge, the broader the spiritual horizon, the power to penetrate into the realities of the environment, into the hidden world spirit. l..] Dear attendees! When approaching the subject of today's consideration, then one comes, starting from the points of view that are represented here, in a basically quite strange situation compared to everything that has been thought and researched in our age for decades about the important question of the origin of man. The reason why one finds oneself in a strange position is that, over the past few decades, the origin of man has been presented primarily in the form in which one believes one should think about the origin of man in the present day: in terms of the results of modern science. And who could deny that the great and tremendous advances in natural science in recent times have every right to have a say at the moment when this important question is put to man. Most of the people present who are dealing with the question from the point of view of natural science must understandably have the impression that anything that can be said here from the point of view of spiritual science about this question is basically directly opposed to what natural science has to say about the point – understandably, dear attendees, and I ask you to bear in mind that this is being said. For it is precisely with such questions that what should emerge on the occasion of the two lectures of my last visit, which dealt with how to refute theosophy on the one hand and how to defend it on the other, always hovers in the background. Especially with questions like today's, the spiritual scientist must be completely clear that much, much can be brought forward from the ideas of the present, seemingly with good reason, against his assertions. Therefore, it must be understood that a lecture such as this evening's can provide some suggestions, but is far from quickly convincing someone who is still unfamiliar with the theosophical views. This is said as an introduction to characterize the attitude from which such a lecture is given. What have we experienced in recent decades [in relation to our topic today]? More and more, those [scientists] who believe they have a judgment in this area have come to the conclusion that man in the totality of his being has its origin from creatures that, in the sense of a systematic arrangement of living beings, actually belong to the sphere of what today's man calls his education, his culture, in fact, the sphere of his human activities. The extraordinarily fruitful principle of development has led to the belief that in the past, development would have progressed in such a way that from simple, primitive life forms, to which today's primitive life forms still resemble, through slow development - as a result of the “struggle for existence,” through adaptation - gradually more and more complicated forms of life have formed, up to the higher animals, and that in such a progressive development, man has risen, as it were, from the lower realms. So man's ancestors are sought in animal life, and there is such a conviction in [wide] circles on this point that anyone who wants to put forward something that does not agree with it is actually thought of as a retarded mind. Now, first of all, the natural scientists – not so much the natural scientists who remain in the realm of facts, but rather the natural scientists who have felt called upon to link worldviews, world mysteries to their research – they have felt compelled to present, so to speak, the outer form and the outer physical conditions of human life as a first as complications that arose from the forces that come from the realms that stand below the human, so that one would only have more complicated living conditions than in the case of animals, especially those that stand one step lower than humans, but that one must still derive the forces from what is already found in the lower living beings. Those natural scientists who wanted to tie an outlook on life to the facts of natural science have strengthened this belief. But not only has this belief become established, but it has also become established that the higher intellectual powers, what we call man's aesthetic perception, his moral impulses, are also only higher forms of the spiritual, of the soul, that one finds in the animal kingdom, that one can also look for the more primitive forms more primitive forms of moral behavior in animals that can be grasped in terms of moral concepts in relation to humans, so that one is often convinced that man has emerged as an intellectual, moral, and aesthetic being only through complication from the living beings below him. It must be conceded that in the face of the magnificent results of modern natural science, it is extremely difficult to come up with any other attitude, any other view. And it must be readily admitted that as a spiritual scientist one often finds oneself in a strange position when, on the one hand, one allows the achievements of natural science to take effect and, on the other hand, one has to deal with what certain more or less amateurish spiritual scientists believe they have to extract from the scientific results. When one compares the conscientiousness of the two presentations, it is the case that, in terms of conscientiousness, one would actually prefer to side with the natural scientist than with some amateur spiritual researchers. Now the point is that spiritual research in this field is also in a very special position because, basically, it only comes into disharmony with the thoughts, ideas and hypotheses that have emerged from the results of natural science , while it becomes ever clearer to the spiritual researcher that the actual results of natural science virtually force human thinking to gradually take a perspective as it is given by spiritual science. Actually, the dichotomy between spiritual science and natural science is not that great, because the facts of natural science correspond more to spiritual science than to the monistic and materialistic [interpretations]. So, as a spiritual researcher, one feels in harmony with the facts as one progresses, and only comes into conflict with the hypotheses that are drawn from the facts from some quarters. If one observes man in his development and wants to trace him back to his origin, it seems only natural that the views about him must be in line with the views one has about the course of the earth's development, [this going back] was indeed [previously] held entirely in the materialistic sense in which the biological theory of evolution, the theory of the development of living beings, is [carried out]. When one reflects on the course of the Earth's development, then as a rule one only considers what the external, inanimate forces, the forces of physics, chemistry, geology, can achieve, and one follows the Earth in a state in which it looked different from what it looks like today, in which it was perhaps in a state that, compared to our present-day Earth formation, resembles a gaseous ball. We know that this is a widespread hypothesis, that it is assumed that the Earth condensed from a gaseous state. It is known that if you trace this back even further into the distant past, you come to see the whole solar system in a gaseous state. The spiritual researcher recognizes that objections have recently been raised against this so-called Kant-Laplace theory, but in the broadest circles it still prevails. It is believed that the whole solar system itself emanated from a kind of primeval nebula that was in rotation, and it is also imagined that the planets, including our Earth, were separated by the forces that were at work in this rotation. I have often pointed out how the so-called [Plateau's] experiment is carried out in schools to illustrate this Kant-Laplacean theory. You take a large drop of a substance that can float on water, let a sheet of card penetrate at the point of the equator, pierce it at the point of the axis with a needle and make the drop rotate, thus showing that small drops do indeed come off and move around the center. What could be simpler than to prove in this way how a planetary system could have formed in such a way? But in an experiment, it is important to take into account everything that needs to be logically included, and it turns out that something is forgotten in this experiment: one forgets oneself, forgets that one is standing there and turning, and that you only have the logical right to put forward the hypothesis [and to transfer the experiment to the solar system] if you assume that there is a giant teacher out there in the universe who has caused all this movement with a giant needle. If you do not make this addition in this experiment, then you are on completely unjustified ground. Of course, spiritual science does not place a professor out in space, but it does say that nowhere is there a formless matter like this cosmic fog; that matter is permeated or at least directed by spiritual powers and forces everywhere, [without us falling into anthropomorphism in the process]. Therefore, for spiritual science it is clear: Even if it is justified in terms of material formation that such a primeval nebula is there, then a spiritual event underlies this outer event, just as the activity of the spiritual soul underlies the events in the human body. Spiritual science does not start from an analogy, but from spiritual research. In the specifically concrete, spiritual science seeks the spiritual events, the spiritual forces and the spiritual entities that underlie them, so that instead of external, materialistic hypotheses, it sees the spirit in them. Now, if one were to undertake the usual presentations of the Kant-Laplacean theory and the associated operations, one could say that it is possible to derive what our body is and the shaping of physical and mental structures from the rotation in the primeval nebula. If we want to make the assumption that some kind of giant teacher is out there and sets the whole thing in motion, then we can speak, if need be, of the formation of the earth having emerged from the Kant-Laplacean primeval nebula. But then we come to a critical point again, and this has been seen not only by spiritual researchers, but also by thoughtful natural scientists. This point concerns the origin of life in general on our earth body. One can, of course, if one does not take certain conditions into account, perhaps indulge in the belief that living things could once have come into being through the spontaneous generation of certain substances. It would be a very long way indeed if one wanted to explain all the philosophical and other reasons that demonstrate the impossibility of deriving life from conditions that are purely physical. It is much more important that this impossibility has become clear to deep-thinking natures such as Gustav Fechner and Wilhelm Preyer, the brilliant biographer of Darwin, that they found no way to come to terms with it in their thoughts, to see life emerging from a spiritless, [inanimate] earth. So these researchers have resorted to the assumption that our Earth, at the beginning of its formation, was by no means just any physical or physical-chemical body, but they assumed that, even if it is true for the present that the Earth body that we have under our feet, presents itself as a lifeless one to mineralogists, and that the living beings on it reproduce in their own realms through inheritance, this does not apply to ancient times, but Preyer and Fechner were forced to think of the earth in the distant past as a living being, as a large organism, so that in the sense of these naturalists the earth was originally a large living organism in the universe. Then the time would have come when certain substances and components of this earth crystallized out of this so-called living substance, and what crystallized out is our present body, containing chemical and physical forces. While originally the earth had a life of its own, it now gives its life, in its own way, to individual earth creatures, so that the origin of living beings could be thought of as the emergence of a living being from a living earth body. It makes a strange impression when Darwin's biographer directs his thoughts to this primeval form of the earth and creates an image out of his thinking. When we read in Preyer that the earth organism was originally to be imagined as being alive, that its bloodstreams were glowing iron vapors, that the breath of this earth body was incoming world vapors from the environment and the nutrition of the earth body was matter that flowed to it from the universe - a strange mixture of natural physical ideas [with life processes]! He cannot completely free himself from his physical conceptions, but he must admit that something like nutrition, breathing and blood circulation can be assumed in the incoming vapors. We do not think of glowing iron as performing these functions when it comes to nutrition. But Preyer shows us one thing: that even natural scientists can feel compelled to recognize the earth as an organism. They meet spiritual science halfway; they admit that if you go backwards, you come to a starting point where the earth [was a large living organism], that the earth, as something dead, in the further course [of development], has set the living [...] aside, [specialized] into [the most diverse] beings, into [plants], animals, humans. They think of remote pasts imbued with full life. But there is still something missing, which spiritual science must ascribe from these prerequisites to this earth body: [The thought is missing] that the earthly body must in truth not only have a living starting point, but that it must be thought of as having a soul and a spirit, so that when we look at the origin of the earth, we are not only dealing with a living organism, but we have to imagine the earth as a soul-inspired, spirit-inspired organism. Yes, now one could say: What is being done here, other than what is to be explained first, is being placed into what was originally assumed? Instead of developing the spirit, one assumes the spirit as originally existing. But that is what one must do, ladies and gentlemen, according to all the possible prerequisites of a science of knowledge, because it is nowhere possible, even conceivable, that the higher natural kingdoms develop from subordinate natural kingdoms; nowhere in the course of experience are we given a stepping out of the spiritual-soul from a merely physical, of a living being from a merely [physical-] chemical. What we encounter, especially in ourselves, is that we see the spiritual-soul working on the material; and anyone who has followed the lectures given here and has heard what has been said about this spiritual-soul will know how right it is to say that, especially in the case of human beings, the spiritual-soul works on the external physical-material. We follow the person in us, let us say, in the time from that moment until we remember back in normal [human life], and see our experiences emerging from the depths of our consciousness in our memory. We see at the center of these events of consciousness becoming more and more alive that to which we apply the word “I”. It would be absurd to assume that this 'I' only began at the moment up to which we can remember. It must also have been there in the dream-like, dusky consciousness, when the child does not yet say 'I' to itself. The 'I' must have been there. How was it present in connection with the other soul forces? If we consider the ordinary life of the human soul, we can say that what emerges as consciousness in this stage is something special, something personal. We see how we work the special life energies, which are individual to us, into it. Therefore, we are compelled to think of what we see working within our consciousness later in life as the actual agent of our whole organism. We have to think that we inherit the general structure of this organism from our ancestors, but that the energies that make up our organism have to be worked into it, [right down to the finest plastic formations of the brain]. When we recognize this, then we are no longer far from being able to trace this individuality back to a previous life on earth. There we see the spiritual and soul forces at work on our inner physical and material being, and we can then say to ourselves that, as today, as in our earthly present, our ego with its soul forces is still working on our body in early childhood. This work is not inherited from our ancestors; rather, there is still a certain scope left in what we have become through the forces of heredity, in which we can work our spiritual and soul nature. We see this, for example, in the fact that we develop from a crawling creature into a walking one. We see how the spiritual-soul element lifts us up, we see the spiritual-soul element working on the physical. Only when we progress to what was mentioned in the last lecture - about the hidden depths of the soul life - to the spiritual training through which one gains insight into the spiritual world behind the physical, then we can consider what has already been described here. If you apply the methods that you will find in my writing “How to Know Higher Worlds” to yourself, you will gradually come to a point where you, as a human being, are no longer dependent on living in the soul in such a way that you have to use physical tools. Spiritual science shows that man can apply methods of meditation and concentration to himself, through which he can acquire a spiritual essence, independent of the physical, so that he has experiences and knows that he did not have them with the help of the senses; but knows: Now you are experiencing something in your original spiritual-soul nature, you become aware of what you are beyond this physical being. And it is particularly interesting that when you ascend to such a training, you have the feeling from the very beginning: Yes, you are now experiencing something supernatural. But at the same time, at the beginning you are not able to express what you experience in the same way in concepts and ideas and words. Why not? Because when you express ideas and concepts in words, you need the instrument of the brain. The ideas and concepts that people form are taken from the world, so that a gap opens up between what one experiences and what one can express. Only when one practices patience and perseverance and continues the exercises does the time come when one is able to truly express the experiences one brings down from the spiritual world in terms of concepts and ideas taken from the outer life. Before this possibility arises, one knows that one feels the brain as something that offers a great deal of resistance. One feels that in the further course of training, one must do the work of shaping the brain plastically, in a way similar to the way the child must shape the still clumsy brain plastically for life. The aim is to work such fine shapes into the brain that they cannot be recognized by natural scientists with external instruments. The work of the soul-spiritual being on the material substance of the body can, however, only be followed inwardly. Thus, we see again in the spiritual-soul realm the actual origin of what is becoming. It is no longer an unjustified claim to say that, as things currently stand on our earth, the spiritual and soul life of man, as it was before the first material atom of our body came into being, is only able to use the scope that is limited in the general structure of our physical body. While this scope, over which the conditions of heredity have no power, shapes the soul and spirit, we see that the physical, the general human form, can only be preserved by human beings of a similar nature. Thus, under today's living conditions, the soul and spirit are only able to shape certain things within a body received through heredity. If this is the case today – and if we assume that the earth has undergone an evolution, which even natural science admits – it is not to be said that in the distant past the spiritual-mental was only able to work within a certain scope. Take it for the moment as a hypothesis; it need not be dismissed out of hand as absurd, when spiritual science says: The further we go back into primeval conditions, the more powerfully the spiritual-soul [of man] is effective. In the remote past, this spiritual-soul was so significant, so powerful that it could also shape that which today can only be shaped within heredity. Just as we see today that the spiritual soul forms only a small part of the material human being, so we see that in ancient times it formed the entire organism, so that the human soul was present in the ensouled earth organism, and the earthly body was once able to yield such a substance that could be formed directly from the soul into a full human being by the spiritual-soul worlds. Thus we look back into the ancient past, where conditions were not yet as they are today, where within the total soul of the earth organism the human souls were contained, that is, the earth organism also had organic substance that was different from the present one, which can only be classified according to the forces of inheritance in the human body. So we come back to an earth configuration - in contrast to the earth formation in which we stand - in which there was no such reproduction as in our time; we do not find such a connection between generations, between male and female. In the place of the interaction between male and female, we find the interaction between the spiritual soul and the living substance of the earth body. The spiritual-soul aspect had a fertilizing effect on the earthly substance and allowed that to emerge which the human being was at the origin of his earthly existence: a creature formed and developed purely out of the spiritual-soul core of his being. If we look at present-day conditions with an open mind, this may seem like a daring hypothesis, but it is certainly not something absurd. So we see that our earthly body is formed, as it were, out of living substance. Just as it is surrounded by air today, so it was surrounded by a soul-spirit shell in those days, and just as it rains from the air shells today and the soil is fertilized by seeds, so spiritual-soul [seeds] once fertilized the living substance, causing the fertilized earth to produce man. It is quite understandable that people who are grounded in science are turned off by such ideas, and this is perfectly understandable to the spiritual researcher.Something else must be said, which is also true. When the spiritual researcher refers back to epochs of the earth when it made no sense to speak of male and female, but when the heavenly and earthly fertilized each other, the views of the natural scientists get in the way, but not the facts of natural science that have emerged in recent decades. These facts have led natural scientists to particular assumptions. We see how, in recent times, which began with Ernst Haeckel's belief that he had to give a materialistic interpretation of human origin in his conception of the Darwinian theory at the [Stettin] Natural History Society [in 1863]; we see how the naturalists who hold this older point of view felt compelled to draw a straight line of development [from the monera] to man, and how they are always obliged to say that, before man came upon the earth, there lived a creature similar to the present-day ape. [But more recent research has] corrected this view. Everywhere we see that attempts have been made to bring man's ancestor closer to a physical, animal-like being, which, through the perfection of its physical organization, also produced the height of the spiritual organization. We can no longer accept such things, that man had an ancestor who was somehow similar to a present-day animal form. We see the necessity for this. Naturalists say that there were once human ancestors that resembled today's apes. That which now lives as the animal world has arisen from decadence, so that what we have as apes is a being that has arisen from a declining formation of a higher form on the one hand, and on the other hand we have man. We see monkeys and humans as two branches leading back to a being that no longer exists, that was only in very distant geological times. This common ancestor of animal-kind and humanity, to which the facts lead the natural science worldview people, is [hypothetical], a being that is purely imagined. Now, certain naturalists have been forced by careful results to move this being further and further up, so that many are already forced to say that even higher mammals do not resemble this hypothetical being, we would have to go back even further to a being from which the very first mammalian forms descended, and this being would have developed a branch at the same time that was always superior to animality and that finally developed into man. When one sees a monkey, one must always trace it back to an earlier stage of animal existence and then assume a purely hypothetical, purely imagined entity that developed a branch that became reptiles, while another branch was formed that became human. So we see the naturalist going to something that formed humans and animals from the same being. How far removed are such scholars from what we have expounded from spiritual science? No further than that their habits of thought compel them to shape the conditions of the earth's development in such a way that they can only conceive of the origin of present-day life forms in a physical way, whereas the spiritual researchers put something in this place that emerged under completely different earthly conditions and from completely different conditions: the fertilization of the earthly substance by the spiritual soul. We also find the possibility of thinking of the further progress of development up to the human being as an entity worked out of the spiritual-soul. Just as today's human being is the product of a father and a mother, so too was such a primeval human being, as I have now described him in the sense of spiritual science, joined together from two sides, from the substance of the earth and the spiritual-soul of the earth's surroundings. Thus we can say that the human being belonged to the spiritual environment. Through this primal element, the human being has lived more in the whole of the heavenly environment and felt his connection with cosmic conditions. But we could only receive our spiritual and soul germ at a certain point on the earth. Through this, the human being is individualized, through the fact that he came [to a certain place], through this he has become a special being, a being that has become native, that has become firmly bound to the locality of the earth. Thus in this primeval man we have at the same time: a general human and an individual, an earth-bound and a more heavenly, macrocosmic element. Strangely, we see the after-effects of what we have just characterized in today's man. If we carefully examine everything that comes to man through heredity, it shows that, despite all the other circumstances that have been specialized through heredity, we find a general human element at the basis of man, and that every human nature is individualized into a second. We still find both today: something universally human and something specialized. If we examine present-day humanity, we find that the universal human element is inherited from the female side, while the specific, individual character is essentially inherited from the male ancestors, regardless of whether the individual as an individuality is male or female. This means that we can still see the after-effects of what manifested itself in primeval man as a general heavenly element – if the expression is not taken pedantically – and what came from the general life substance of the earth. Therefore, we need only assume that in the primeval men, who were formed out of the spirit, in the one case the macrocosmic element predominated, which had a fertilizing effect from the surrounding area, while the element that came from the earth itself receded more. As a result, some of the primeval men specialized. Where the heavenly element was more active, specialization led to the female principle, while where the earthly element predominated, where the specific earthly destiny gained the upper hand, the more individual was formed, the tendency towards the male. Thus we see how, out of these general conditions, the tendencies were formed in the original human being, consisting of soul and spirit, and how these tendencies became more and more concentrated and took shape as man and woman. And this whole process, my esteemed audience, must be imagined in such a way that the conditions were always changing, that is to say, nothing else but that the conditions that had made it possible for the cosmic elements to fertilize from the spiritual environment were disappearing. The living earth substance released the purely mineral and chemical from itself and was therefore no longer able to release living substance. What had been brought into being through spiritual fertilization by the lower and the higher, and which could no longer shape the human being in this way, was replaced by something that emerged in a different way and became formative by being incorporated into the human being itself, so that reproduction occurred from generation to generation. We see that the forces that shape the human being lead back to each other in such a way that the female contribution leads back to a cosmic, heavenly element, and that which is given in reproduction by the male leads back to the original, organically living earth substance. We still see the general in the female and the individual in the male. No one will be able to shed light on the relationship of heredity and the contribution of male and female who does not take these things into account, even if only hypothetically. The forces that worked between the earth's environment and the earth itself had to be passed on to heredity. We must now consider how the development of animals relates to this development of man, to this view of the origin of man. For in a certain way, the origin of man is not properly understood without considering the development of animals. It shows that man, as he stands before us today in his duality - so that on the one hand there is still a certain scope for the spiritual and soul to work, and on the other hand he receives what he has inherited - could only develop as he is today , if he retained this spiritual-soul education until a certain point in time, until the conditions on earth were such that they could no longer provide the possibility for the human being to arise from the spiritual-soul. Only then did today's form of reproduction develop. As a being formed from the spiritual-soul, the human being had to wait. What would have happened if he had abandoned the origin of the spiritual and soul earlier and merely submitted to earthly conditions? Simple considerations can show us this. If the spiritual and soul had not remained in its original nature until the extreme moment of time, but had allowed earthly conditions to prevail, then the spiritual and soul would have become weak in the face of earthly conditions. If man had earlier adopted the mode of reproduction that is now his, his spiritual and soul forces would be weaker and that which comes from the earth would have gained the upper hand – because it was even more powerful when the earth still had organizing forces within it – and he would have descended to a lower level under the influence of the organizing forces of the earth. This is the case with animality. The spiritual soul of the animals united with the earth at different times, descending into the spheres of the earth before man. The animal preceded man. But man does not descend from the animal, but from its spiritual archetype. Those spiritual archetypes that have become animals descended earlier than man, who remained longest at the top in the spiritual regions. Thus the lines of development do not lead to the archetype of the animal kingdom and of man. We must think of the archetype of the animal kingdom as separate from the soul-spiritual of man. Thus we see how, in the sense of a logically developed theory of evolution, spiritual science places the human being in the context of the earth's overall development, and how this coincides with a properly considered scientific view. Spiritual science places man in such a line of development, in which the metamorphoses of the earth itself are taken into account, how then the animal forms arise and finally man arises, having waited so long in the spiritual surroundings of the earth, so that he could adapt to the conditions of the earth in such a way that the greatest scope was given for the spiritual and soul life. Dear attendees, I have already indicated that what has been said today, especially by people who have equipped themselves with all the knowledge of today, must often be regarded as unthinkable, as absurd. And if only a few people have the inclination and the will to recognize that these things [of spiritual science] that play into cultural life should be pursued with the same seriousness as [those of] natural science, then that will be enough to show how this influence on cultural life occurs. Spiritual science starts from a different point of view, and admittedly arrives at something to which the natural scientist must still relate negatively, but those who want to can see that true natural science, based on facts, comes straight to meet what spiritual science has to give. Spiritual science starts from a different point of view from natural science, but it does arrive at something to which the natural scientist must still be hostile. If we disregard the fantasies of natural science and consider only the facts, we shall see that these everywhere substantiate and prove what has been characterized today. But for man it is important to be aware that there is an independent spiritual element within him that is not the result of a material body, but that the physical is the result of a spiritual element that has its origin in the spiritual environment and has sunk its seeds into the now inanimate substance of the earth. The study of the external facts in the development of the earth [does not contradict the independent significance of the spiritual and soul in human nature, but rather, through every deeper reflection, every living in its essence – like a soliloquy, like a conversation that the soul has with itself, must form itself, which, from the depths of human nature, must repeatedly shape itself in such a way that we can summarize the relationship of the human being to himself and to life in the words:
|

