Health and Illness II
GA 348
VI. Diphtheria and Influenza—Crossed Eyes
20 January 1922, Dornach
A question is raised concerning why, in one family, four mute children were born along with normal children. In his youth, the father of the children tore the tongues out of birds. Could the four mute children be his punishment?
Another question: Influenza, in which people suffer from double vision, is so frequent now. What is the cause of this?
Dr. Steiner: Were the children who cannot speak born one after the other in this family, or were the children who could speak born in-between?
The Questioner: The mute children were born one after the other.
Dr. Steiner: It is difficult to speak about such a case when one is not thoroughly familiar with it. We shall take up the question about influenza later. This first case, however, is difficult to judge when one is not familiar with the details. Much depends, for example, on whether a speaking child was born between the mute children; whether, after a certain moment in time, the speaking children were born and the mute children after, or whether the mute children were born first and the normal children after, or whether they were born alternately. Muteness in children naturally can be caused by any number of factors. If these children can hear and are only mute, not deaf—mute—something about which one can sometimes be in error of course—if they truly hear, and the problem therefore lies in the speech apparatus, then one must figure out how the father or mother could have influenced it.
Without thoroughly knowing this case, however, it is really risky to talk about it. One would have to know the age of both parents. Much depends on whether both parents were already old when they had the children or whether they are still young. Another factor is whether the mother or the father is the older. Much depends on all this.
Then, the character of both parents also plays a part. Whether or not it is important that the father tore out the tongues of birds in his youth, as you say, can be determined only after all the other questions have been answered. Such a consideration depends on whether the man was perhaps cruel in his youth. The characteristic of cruelty as such does come into consideration. To speak of a punishment, however, is out of the question here. First, punishments do not exist and second, if they did, this certainly would not be a punishment for the father! To say that the children were born mute to punish the father for his cruelty reminds me of the story of the boy whose hands froze and who said, “This serves my father right for not buying me gloves!” When somebody is as terribly afflicted as these four children, it is not a punishment for the father; he is much less affected than the four children, although his cruelty must be considered.
Again, certain other definite matters must be considered here. In relation to children's age you can see that if a person develops a quality as a youth—let us say one develops a quality of cruelty or something similar at age eleven, for example—the onset of such a tendency always recurs after about three and a half years. This individual would then express cruel tendencies again at fourteen and a half or fifteen, then again at eighteen, at twenty—one and a half, and so forth.
Imagine, if conception occurs during the period when such a tendency recurs, the conception itself can be a kind of cruelty and naturally can work harmfully. In this roundabout way, all such matters naturally can come under consideration. A connection can only be claimed, however, if all other factors have been excluded. I have told you what a difference there is between winter births and summer births. One would have to determine from the ages of these children whether the earlier births perhaps occurred in the summer or in the winter, and so forth.
This is why I say that to approach the problem conscientiously, one must know all the details. When you become acquainted with the whole case, we can talk about it. I would be glad to do so. You do not know, for example, whether the four mute children were the older or the younger ones. It must definitely be established whether or not this tendency to bring forth mute children was later cured or whether it appeared only after the four speaking children were born, in which case, the reason would have to be discovered somewhere after the birth of the fourth child. So, we would first have to be familiar with all the factors.
Regarding the question about the flu, it is related to all the diseases, such as bronchitis, that can afflict the human head or the organs of the upper chest, but I will refer particularly to illnesses such as diphtheria and influenza that are so widely prevalent just now. These diseases afflict the upper part of the human body, and they have a definite peculiarity. They can best be studied by examining diphtheria; here one really can learn the most.
You know well that those who study medicine in the ordinary sense today do not know much about the flu; therefore, the descriptions given by doctors of the symptoms that appear with the flu are quite inexact. When I see people suffering from influenza, I must always turn my attention to something other than the symptoms that the doctors pay heed to, because the flu is actually a kind of brain illness. The flu is really an illness of the brain! I shall say more about this later.
The following points especially must be taken into consideration regarding diphtheria. First, if you look at a child suffering from diphtheria—adults can also suffer from it, you know—you can see a membrane in the throat. This membrane, this formation of tissue, is usually what can cause suffocation in diphtheria. This formation of tissue is thus the first important factor. The second thing one notices in diphtheria is that the heart of a diphtheria patient is always assaulted. The heart does not function properly. The third aspect of diphtheria is that even if the patient is not strongly afflicted by the membrane in his throat, he nevertheless has a hard time swallowing because of a kind of paralysis of the throat that occurs in addition to the membrane. Finally, the same symptom that is nowadays observed in those suffering from influenza also appears in diphtheria patients: their eyes begin to cross and they see double. These are the most important symptoms of diphtheria that can be noted in the upper part of the body. A form of kidney ailment, unobserved in those who suffocate and die, appears as an aftereffect in the diphtheria patients who recover.
What does diphtheria really consist of? Diphtheria can be understood only when one knows that man is actually kept alive from two directions—from the outside in and from the inside out. Man lives first from within his skin. The skin is a tremendously important organ, and man really lives within the skin, within his surroundings. It is like this (sketching).
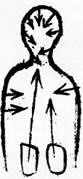
Diagram 1.
Here is the skin; I have already talked about it. The skin is constantly in contact with the outer air, with the external world, which causes it to become calloused. In humans it only becomes a little calloused and then sloughs off. The skin all over man's body constantly sloughs off. Man is continuously sloughing off his entire body. He is continuously exchanging his physical body because of outside influences. You can imagine what a tremendous influence the air has on the living body when you consider the following. Think of a being that lives entirely in water. The skin it forms will be quite soft. The water itself causes it to form skin that is quite soft. Particularly through the influence of sunlight, the soft skin is pulled forward, and the being in the water becomes a fish. You can hardly see the jaw of a fish, because it is entirely covered with skin. Now imagine that this creature does not live in water but in the air. If this being lives in the air, it cannot form the soft skin. If this being who has lived in the water could not form the soft skin, his jaw would no longer be inside; the whole inner jaw would lie outside, and he would be a bird. The jaw of the fish in the water is simply covered with soft skin. By virtue of living in the air, the bird is equipped with an exposed jaw, a jaw lying completely outside. Thus you see the influence exerted on a creature from outside. Man, however, can form soft skin with other organs, but this soft skin is always being sloughed off, worked off.

Diagram 2.
Aside from this life proceeding from the outside in, there is also a life going from inside out, particularly from the kidneys. Both must be active in the human being. Activity both from the skin inward and from the kidneys outward must be at work. The heart occupies a position in between and is highly sensitive to too much activity from outside or inside. The heart can sense when the kidneys begin to be overly active, and it also senses when the skin's activity begins to be too strong or too weak.
Now, what happens in the case of diphtheria? In diphtheria, the skin suddenly becomes weak and subdued. The activity of the skin is too weak, so a person with diphtheria suffers from too little exchange of air through the skin. Indeed, this is the main problem. The skin, including the skin of the nose exposed to the external surroundings, does not breathe enough, and it becomes too weak. The in-streaming activity, indicated in my sketch by the arrows, no longer functions properly, and the heart senses this. The heart also senses that the kidneys work upward. What is it that the kidneys are doing? The heart can no longer restrain the activity of the kidneys, which shoots upward. Long before inflammation of the kidneys, that is, nephritis, sets in, the activity of the kidneys is already shooting upward. Because the skin activity is no longer working effectively from outside, superfluous skin forms on the inside. Because the, skin's activity from the outside is not working properly, a superfluous skin is formed, filling everything out, because the kidneys' activity is too strong.
When a person becomes afflicted with shrunken kidneys, which can occur when the kidneys' activity is deficient, you can see an indentation here on the head. There is a connection between the kidneys and this section of the head. As soon as the kidneys' activity is not working properly, this indentation occurs. You can see in every person who has kidney disease this indentation in the head. Beneath it lie the optic nerves. When the indentation occurs, the optic nerves become inactive. In the case of ordinary kidney shrinkage, the patient begins to see unclearly. When shrinkage does not occur but nephritis sets in instead, the kidney activity shoots up into the head and exerts an influence on the optic nerves.
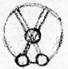
Diagram 3.
Now, you see, the optic nerves are such that when the head is viewed from above, they proceed back from the eyes. They cross in the brain, the two optic nerves, and continue on to the hindbrain. The optic nerves must be in good condition if we are to see well, because we see with both eyes. The moment these optic nerves that cross are not working properly, we see double. The optic nerves only need to be a little numbed and the crossing not made properly for us to see double. You know how a person who enjoys drinking can tell whether or not he is still functioning when he gets home: he places his hat at the foot of the bed, gets in bed, and if he sees one hat he is still all right, but if he sees two, he is not! This is easily done. So, because the blood circulates too fast, too much alcohol numbs the optic nerves, with the result that a person who has drunk too much has double vision.
The kidneys' activity also has a stimulating effect on the optic nerves. If the optic nerves do not interact properly at the point where they cross, man will see double. This is the case, for example, in diphtheria. You can see, therefore, that diphtheria is caused by a disorder in the skin's activity. Therefore, a future, more successful cure for diphtheria will consist above all of treating the patient in the right way with baths; he will have to be given such baths that will immediately stimulate vigorously the skin's activity. Then the formation of membranes will cease, and the patient's skin will begin to function properly again.
Treatment with modified virus vaccine is effective in the case of diphtheria, because the body is thus given a strong impulse to become active, but it has unfavorable aftereffects. Particularly if a child is treated with vaccine, it will later suffer a hardening of its organization. One therefore must strive actually to replace treatment with vaccine with that of bathing, especially in the case of diphtheria, which is based primarily on the defective activity of the skin. One can see how skin actually must receive special consideration. It is indeed true that diphtheria is more frequent now than in former times. Of course, one must consider centuries, not decades. According to all that is known of earlier ages, however—though many diseases naturally existed then that were much worse; people were afflicted with bubonic plague and cholera—diphtheria was more rare. This is connected with the fact that, in general, the European way of life increasingly leads in a direction in which the skin's activity is no longer supported. Certainly, people who have money bathe a lot, and so forth. The point, however, is what a person bathes in. Here you can see the ill effect of civilization in the fact that bald-headed people are much more numerous today than in former days. The growth of hair is also an outer activity. Just as plants grow from the soil, so the growth of hair is affected from outside. Not enough attention is paid today to the skin's activity. Do not assume that bathing with cold water, as practiced by Englishmen nowadays, has such good effects. What counts is what a person bathes in. Of course, it is also wrong for a person to cause too strong an activity of the skin by superfluous bathing. At any rate, in the case of diphtheria, one must try above all to bring about a proper activity of the skin.
This is also connected with a factor that affects people's offspring. Take a mother or father whose skin is too sluggish and doesn't slough off easily enough. This is most difficult to determine and takes a very sensitive insight into human peculiarities. The average layman cannot easily judge whether or not a person has callous skin, but some people do possess a much tougher skin than others. This is difficult to determine, because the skin is actually transparent. As it sloughs off, it appears to be colored differently because of what is underneath. Our skin is really transparent. If the father has a skin that is much tougher than it should be, the activity of the bones is also influenced thereby. As you know from what I have recently explained, the production of the blood depends on the activity of the bones. If the father has such callous skin that it reminds you of hippopotamus hide, he will produce white corpuscles that are too weak. This, in turn, influences his sperm, and his children will be weak from the beginning. So, one can say that if the father is a “hippopotamus,” it is possible for his children to be born with rickets—an English illness—for the children to be born weak and to be susceptible to tuberculosis. This is how these things are related.
If the father's skin is too soft, something that can be noted particularly when anxiety and so on easily cause blushing, then his bones become too hard, but this has little ill-effect.
If, however, the mother's skin is too soft, alternating between blushing and paling, her bones become too hard and she does not produce red corpuscles properly. Her child will acquire already at an early age, tendencies to all kinds of ailments such as rheumatism and particularly illnesses like measles, scarlet fever, and so on, diseases that are related to the metabolic system. These facts are all related.

Diagram 4.
Now, as for the flu, it really comes from a brain ailment. The lower part of the brain, located under the optic nerves, suffers a form of paralysis. The flu consists of a paralysis of that portion of the brain that lies quite near the optic nerves. Since this is a very significant part of the brain, an influence is actually exerted on the entire body. Proceeding from this paralysis in the brain, something in the human being becomes ill in the case of ordinary flu. Above all, the spinal cord is affected, since this part of the brain goes right into the spine, from which the nerves extend to all the limbs. The person thus gets aches and pains in his limbs, and so on.
Recently, an interesting case of flu occurred that is most instructive. I have told you that the brain not only consists of solid substances but that it is also surrounded by cranial fluid. Particularly in the vicinity of this part here (pointing to sketch), which is incapacitated during flu, much cranial fluid is present. This recent case of flu was extraordinarily interesting, because the patient had one illness after another as aftereffects: pneumonia with high fever, then a fall in temperature, followed by pleurisy with high fever, and then again a drop in temperature. This was followed by peritonitis with high fever that finally fell, then a kind of general paralysis, and so on. This case of flu took a different direction from that of the usual flu. What happened here? You see, when studying this with the ordinary means available to medicine, it is extraordinarily difficult to figure out. The patient, a seventeen-year-old girl, was asked when she recuperated to tell what went through her mind during the time of her illnesses. Quite strangely, the following was determined.
Her parents and the doctor freely discussed her condition in the room in which she was resting, thinking it was all right to do so since she was constantly delirious. Indeed, during her delirium she did not appear to be aware of anything, but when she became well, she could repeat everything that had been discussed in her room. She knew and could relate it. This could be confirmed. Comprehension was therefore absent while she suffered from this severe case of flu and the subsequent illnesses; the conversations, however, remained in her memory. Much is retained in the memory after all, that at the moment may not be comprehended. This shows that it was not the solid part of the brain that was affected but the surrounding fluid. This influenced the rest of the body even more, because, when the solid part is partially numbed, the ensuing symptoms must be brought about through the working of the solid part of the brain on the spinal cord. The fluid, however, constantly flows up and down through the spinal canal here (see sketch on p. 103). Hence, if the fluid in the brain is afflicted, afflicted fluid also appears in the spinal canal, and from here it passes into all the limbs. It thereby gradually causes inflammation everywhere. Because it was the cranial fluid that was inflamed, and not the solid part of the brain, however, a more counteractive, healing force was present and—though in this case it was almost like a miracle—the girl recuperated in spite of having suffered from every possible illness.
Although various remedies must also be administered, in such illnesses it is essential that the body be given adequate rest and quiet. The patient must therefore lie in bed, and care should be taken to keep the room at a constant temperature and with even lighting, because rest is brought about not only by stretching out on a bed. One is also made restless by being hot one moment and frozen the next. But if the body is left totally to its own devices with steady warmth and light, it can itself endure even the worst attacks of pneumonia, pleurisy, and peritonitis. The human being is capable of that. Even with the worst illnesses that display the symptoms mentioned, it is more a matter of proper nursing care than of remedies. In general, proper care has great value.
You can recognize the significance of proper care from the following. When a limb is inflamed or injured, the best thing to do is simply to put a ligature on it somewhere above the affected area; it must be done correctly, however. In this way, the more delicate activity of the body, the etheric activity, is brought into play, and healing begins. So, when a hand or finger is ulcerated, a ligature is applied between it and the body, and then it heals quickly. The forces of healing must be summoned everywhere within the body itself. Naturally, cases vary. One must always consider the individual and know him well if one wishes to cure him; one must have insight into how a person is. In dealing with a patient suffering from diphtheria, for instance, it is under certain conditions best to place him in a rosemary bath so he can smell the rosemary. Repeated long rosemary baths will strengthen the activity of his skin. Sufficient rosemary must be added to the water, however, so that the patient constantly smells it during the bath. The activity of the skin is stimulated, and the patient will improve without being treated with vaccine. It really depends upon being able to arouse in the right way with the remedies the patient's own bodily resistance.
Of course, if a remedy isn't effective one time, people immediately consider it to be a bad remedy. You must realize, however, that with some people there is nothing to be done. Often, the remedy is used when it is too late to do anything, or else the dose would have to be increased so much that it would be enough for a horse; the patient wouldn't be able to tolerate it and would die of the remedy.
One must remember that the flu actually has its origin in an ailment of the brain. You will have perceived that a flu patient is always in a kind of doze, because the most important areas of the brain under the optic nerve are numbed. Thus he comes to doze. Now you can also grasp that when paralysis is located in the upper sections of the brain, the point of the intersection of the optic nerves is affected and the person sees double. All this shows you that double vision can come about quite naturally in influenza.
This should by no means be taken lightly. I once had a friend who at that time was thirty years old, ten years younger than me. He was cross-eyed, but here you have the opposite problem. In flu or diphtheria, a person becomes temporarily cross-eyed because something is internally out of order, but my friend was permanently cross-eyed and, of course, was unhappy about it because not everyone is totally without vanity. There was something in his body that caused his left and right sides to work inharmoniously. This is what caused his crossed eyes; his eyes were crossed, and he also stammered. Both afflictions had the same origin. On some occasions he overcame his crossed eyes and stammer quite well, but there are those who have little compassion for such people and complain about their afflictions. Once, for example, a person who was not too tactful said to my friend, “Tell me, Doctor, do you always stammer, or only occasionally?” The man could barely come out with, “N-n-not always, o-o-only w-when I m-meet a p-person, whom I find t-t-t-totally d-disagreeable!” This same man could recite long poems without stammering, and he didn't stammer when he was full of enthusiasm about something. The stammering is not the point, however; I only mention it because it is connected with this man's crossed eyes.
Now, my friend was a bit vain and wished to correct his condition. As you know, that leads to an operation, because crossed eyes are corrected by cutting one of the eye muscles. Crossed eyes are eliminated by this operation. Since, in my friend's case, his crossed eyes were so deeply rooted in his organism that he also stammered, I was terribly concerned when he decided to be operated on. I knew that when some brain ailment occurs a person can be temporarily cross-eyed, but when a person is permanently cross-eyed, as was my friend, his brain has become adjusted to this condition. If an eye muscle is cut when the problem is so deep-seated that a stammer is also present, then the opposite effect is brought about. By trying to correct the crossed eyes with an operation, a brain ailment is produced by that part of the brain being ruined where the optic nerves intersect.
Well, my friend was not to be deterred, and so he underwent the operation. If I had expressed my reservations concerning such an operation, those who imagine themselves to be real medical authorities would have been ready to call me an idiot, since one who asserts something that is not found in their books is called an idiot. As you can imagine, I naturally tried in some way to deter my friend from having this operation, but I could not come right out and say, “If you go through with this operation, you may possibly suffer a brain ailment.” He would not have believed me since all the doctors had told him it was a simple operation. Since he knew that I was not really happy about his intention to have the operation, he told me nothing about it. One day, he visited me with a black patch on his eyes, which he removed and said, “Now look, aren't my eyes straight now?” They were, but I remained apprehensive. Well, two weeks hadn't passed before he fell ill with a brain ailment. Naturally, this brain ailment was not diagnosed as such by the doctor; what do ordinary doctors know of these relationships! How did the brain ailment manifest itself? There was some blood in his feces indicating that it made its appearance in the guise of an intestinal illness. The man became afflicted with an intestinal illness, but it was none other than the brain ailment because, as I have explained, the intestines and the brain are connected.
When this happened, I knew it was caused by the operation, and I lost hope for him. The most famous doctor in town was called. He diagnosed typhoid. What else could he say, when the contents of the intestines showed blood and had the peculiar consistency of pea soup? If he has blood in his feces and intestinal contents with the consistency of pea soup, he must have typhoid! It was not typhoid, however; it was the illness—really of the brain—that was the result of the inappropriate operation for his crossed eyes.
So here the opposite case occurred. This man died soon afterward. The doctor who had treated him for typhoid fever had admitted him to the hospital. I went there after his death and met his medical attendant. As such people are wont to do, he immediately greeted me with, “The Professor wrote `typhoid' on the chart. He is supposed to have had typhoid? Well, that's how much our doctors know!” After all, the attending personnel believe what the doctors proclaim least of all!
It really is quite upsetting to see the human organism treated in such a one-sided manner. If I were to tell a doctor what I have just told you concerning the appearance of an illness resembling typhoid that was a masked ailment of the brain and the result of an operation for crossed eyes, he would consider it pure nonsense. He wouldn't believe it, because he doesn't truly know the relationships within the body but is only familiar with theoretical relationships. As a result, such things will happen as in this anecdote I'll tell you. It is only an anecdote, but it has truth in it. A person is brought to the hospital. The doctor who is chief of staff examines him, assigns him to a certain ward, and gives an order concerning treatment to his assistants, saying, “When I return tomorrow, this patient will be dead.” He no longer concerns himself with this case until a few days later. Then he says, “There is still a patient in Room 15; he must be dead.” “No,” he is told, “that patient feels better and is getting well.” The doctor replies, “Then you've treated him the wrong way!”
Of course, this is a joke. But it is like this when theory is put in the place of true practice. Practice means learning to judge each case on an individual basis. The moment a question is raised concerning the connection between double vision, which is always a form of crossed eyes, and the flu, attention must be drawn to how, on the one hand, a form of double vision is caused by flu, which is a kind of brain ailment and, on the other, how the brain ailment can come about when a person is cross-eyed and the problem is so deeply rooted that left and right do not fit together.
All processes in the human being proceed outward from within and inward from without. If a person is crossed-eyed for internal reasons and this condition is externally corrected, he can become ill inwardly; in man, one never deals with a single activity but with two activities that meet in the heart. The heart is in-between and is affected when one does away with crossed eyes externally. The heart is also affected if something is not working properly inside. The heart is not a pump but a most delicate apparatus, which really perceives everything that is out of order, as it were.
Let us assume that I injure my knee externally or that by some circumstance, perhaps through drinking, I become afflicted with rheumatism. Then, internal activities are out of order, and inflammation results in that area. The processes that begin within are out of order. In such cases the heart is always influenced and doesn't work properly. Therefore, the heart's function can be influenced from within as well as from without. In all illnesses in which this is the case—that is, when something is wrong with a process that keeps it from running its course outward from within or inward from without—it will be noted that it comes to expression in the heart. One must know the correct relationship, however, between what is an outer process and what is an inner process when a person is cross-eyed or stammers, if one wishes to weigh the consequences of eliminating the condition. Operations for crossed eyes must always be weighed as to whether one should or should not do them. That is the important point.

