Education for Adolescents
GA 302
Lecture Two
13 June 1921, Stuttgart
In yesterday’s introduction I wanted to show the importance of the teacher’s understanding of the human being and of the school as organic unit. Everything else really depends on this understanding. Today I shall touch on several issues that may then be further developed.
If we wish to have a correct picture of the human being, what really matters is that we rid ourselves of all the prejudices in the current scientific world conceptions. Most people today—even those who are not materialists—are convinced that the processes in logical thinking are carried out by the soul, an inner organism, and that the brain is used as a kind of mechanism for carrying out these processes. All logical functions and processes, they say, are cerebral. The attempt is then made to explain these processes in three stages—the forming of mental images, judgments, and conclusions. It is true, is it not, that we must apply these processes in our lessons, that we must teach and practice them?
We have been so conditioned to this way of thinking that all logic is a function of the head that we have lost sight of the real, the actual nature of logic. When we draw people’s attention to the truth of the matter they demand proofs. The proof, however, lies in unprejudiced observation, in discovering the development of logic in the human being. Of the three stages—mental images, judgments, conclusions—only in the first is the head involved. We ought to be conscious of this: The head is concerned only with the forming of mental images, of ideas, and not with judgments or conclusions.
You may react by saying that spiritual science is gradually dismissing the head and diminishing its functions. But this is in accordance with the truth in its most profound meaning. The head really does not do all that much for us during our life between birth and death. True, in its outer appearance, its physical form, it is certainly the most perfect part of our body. But it is so because it is a copy of our spiritual organism between death and rebirth. It is, as it were, a seal, an impress of what we were before birth, before conception. Everything that was spirit and soul impressed itself on the head, so that it represents the picture of our prenatal life.
It is really only the etheric body—besides the physical—that is fully active in the head. The astral body and the I fill the head, but they merely reflect their activity in it; they are active for their own sake and the head merely reflects this. In the shape of the head we have a picture of the supersensible world. I indicated as much during last year’s lectures when I drew your attention to the fact that we are really carrying our heads as special entities on the top of our bodies. I compared the body to a coach or horse and the head to the passenger or rider. The head is indeed separated from the world outside. It sits, like a parasite, on the body; it even behaves like a parasite. We really must get away from the materialistic view of the head that attaches too much importance to it. We need our head as a reflecting apparatus, no more. We must learn to see the head as a picture of our prenatal spirit and soul organism.
The forming of mental images and ideas is indeed connected to the head. But not our judgments. These are actually connected to arms and hands. It is true—we judge with our arms and hands. Mental images, ideas we form in our heads. But the processes leading to judgments are carried out by the mechanism of arms and hands. The mental images of a judgment do, as its reflection, take place in the head.
You can develop a feeling for this distinction and then recognize its important didactic truth. You can tell yourselves that the task of our middle organism is to mediate the world of feelings. The rhythmical organism is essentially the basis for the mediation of feelings. Judgments are, you will agree, deeply related to feelings, even the most abstract of judgments. When we say “Carl is a good boy,” this is a judgment, and we have the feeling of confirmation. The feeling of confirmation or negation—any feeling actually that expresses the relation between predicate and subject—plays a major role in judgments. It is only because our judgments are already strongly anchored in our subconscious that we are not aware of our feelings’ participation in them.
There takes place for us as human beings, inasmuch as we judge, a phenomenon that we must understand. The arms, although in harmony with the rhythmic organism, are at the same time liberated from it. In this physical connection of the rhythmical organism with the liberated organism of the arms, we can see a physical, sense-perceptible expression of the relation between feelings and judgments.
In considering conclusions, the drawing of conclusions, we must understand the connection to legs and feet. Our contemporary psychologists will, of course, ridicule the idea that it is not the head that draws conclusions but the legs and feet. But it is true. Were we, as human beings, not oriented toward our legs and feet, we could never arrive at conclusions. What this means is that we form ideas and mental images with the etheric body, supported by the head organism; we make our judgments—in an elementary, original way—with our astral body, supported by our arms and hands; and we draw conclusions in our legs and feet—because we do this with our ego, and the ego, the I, is supported by legs and feet.
As you can thus see, the whole of the human being participates in logic. It is important to understand this participation. Our conventional scientists and psychologists understand but little of the nature of the human being because they don’t know that the total human being is employed in the process of logic. They believe that only the head participates in it. We must now understand the way in which the human being, as a being of legs and feet, is placed on the earth—a way quite different from that of the human head being. We can illustrate this difference in a drawing.
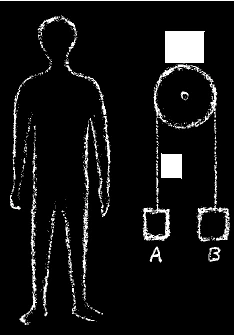
By imagining the outline of the human being we may arrive at the following concept. Let us assume that the person in the diagram is lifting a weight by hand, in our case a heavy object weighing one kilogram. The object is lifted by hand. Let us now ignore the person and, instead, tie the object (A) to a rope, pass the rope over a pulley, and tie another object of either identical or heavier weight to the other end (B). If B happens to be heavier, it will draw the original weight (A) up. We have here constructed a mechanical device the achievement of which is identical to that of hand and arm. I can replace hand and arm with a mechanical device—the result is the same. I unfold my will and, in so doing, I accomplish something that can equally be achieved by some mechanical device, as shown in the illustration.
What you can see in this diagram is a happening that is quite objective. The employment of my will does not alter the outer picture. With my will I am fully placed into the objective world. I impart myself into the objective world; unfolding my will, I no longer differentiate myself from it.
What I have demonstrated can be observed especially clearly when I take a few steps or use my legs for something else. What the will accomplishes during the use of my legs and feet is a process that is quite objective, something that takes place in the world outside. As seen from without, there is no difference between a mechanical process and my own personal effort of will. All my will does is to direct the course of events. This is most strongly the case when I employ functions that are connected with my legs and feet. I am then really outside myself, I flow together with the objective world, I become part of it.
The same cannot be said of the head. The functions of the head tear me away from the world. What I call seeing and hearing, what ultimately leads to the forming of ideas and mental images, cannot in this objective way impart itself to the world outside. My head is not part of that world; it is a foreign body on earth, a copy of what I was before I descended to earth.
Head and legs are extreme opposites and, between them, in the center—because there the will is already active, but in conjunction with feelings—between them we have the organization of arms and hands. I ask you to keep in your mind this picture of the human being—through the head, as it were, separated from the earth, having brought the head from the spiritual world as a witness, the proof of belonging to the spiritual world. One imparts oneself into the physical world by adapting the organs of will and the feelings to the outer laws, to environment and institutions. There is no sharp boundary between outer events and the accomplishments of the will. But a sharp boundary is always drawn between outer events and the ideas and mental pictures mediated to us through the head.
This distinction can give us an even better understanding of the human being. The head develops first in the embryo. It is utter nonsense to regard it as being merely inherited. Its spherical shape tells you that it is truly a copy of the cosmos, whose forces are active in it. What we inherit enters the organism of our arms and legs. There we are our parents’ children. They relate us to the terrestrial forces. But our heads have no access to the earth’s forces, not even to fertilization. The head is organized by the cosmos. Any hereditary likeness is caused by the fact that it develops with the help of the other organism, is nourished by the blood that is affected by the other organism. But it is the cosmos that gives the head its shape, that makes it autonomous and individual. Above all, the work of the cosmos—inasmuch as it is connected to the head—can be seen in those things that are part of the nerve-sense organism. We bring our nerve-sense organism with us from the cosmos, allowing it to impart itself into the other organism.
This knowledge is important because it helps us to avoid subscribing to the nonsensical idea that we are the more spiritual the more we ignore the physical and to avoid talking in abstractions about spirit and soul. We become truly spiritual when we learn to see the connection between the physical/corporeal and the soul and spirit, when we understand that our head is a product of the cosmos, is organized by it, makes us part of it. The organism of our legs is inherited; there we are our parents’ and grandparents’ descendants.
This knowledge, being true, will affect our feelings, while all the current concepts—be they about spirit or matter—are abstract, in no way related to reality. They leave us cold, cannot stir our feelings. I would therefore like to ask you to take to your hearts, to ponder deeply, and to develop for your educational work the fact that there is really no difference whether the human being is regarded as a physical/corporeal being or as a being of spirit and soul. Once we have learned to observe spirit and soul in the correct way we shall see them as creative elements from which flows the physical/corporeal. We shall recognize spirit and soul in their creative activity. And if, as artists, we reflect on this activity in the right way, we shall gradually lose sight of the material altogether as it becomes spirit all by itself. The physical/corporeal transforms into spirit in our correct imagination.
When one stands firmly on the ground of spiritual science, of anthroposophy, it no longer matters if one is a materialist or a spiritualist. It really doesn’t matter. The harm done by materialism is not the study of material phenomena. If this study were performed thoroughly, the phenomena would transform into spirit and all the materialistic concepts would be recognized as absurdities. The harm done is the feeble-mindedness that results when we do not complete thought processes, when we do not concentrate enough on what the senses perceive. We thus lose sight of reality. If we were to pursue thoughts about the material world to the end, we would arrive at the picture, the idea of the spirit.
As for spirit and soul, as long as we enter their reality when we reflect on them, they will not remain as the abstractions we are given by our current sciences but will assume form, will become visible. Abstract understanding becomes an artistic experience that will ultimately result in our seeing spirit and soul as material, tangible reality.
Be one a materialist or a spiritualist both perspectives will lead to the same result, provided the thought process is completed. Again, it is not the spirit that is the problem in spiritualism but rather this uncompleted thought process that so easily turns the spiritualist into an idiot, a nebulous mystic, a person who causes confusion and who can only vaguely come to grips with reality.
There is yet another essential and important task for you. Equipped with a sound understanding of the nature of the child, you must develop an eye for distinguishing the child with a predominant cosmic organism from the one with a predominant terrestrial/physical organism. The former will have a plastically formed head, the latter a plastically structured trunk and, especially, limbs.
What now matters is to find the appropriate treatment for each. In the more earthly child, the hereditary forces are playing a major role; they permeate the entire metabolic limb system in an extraordinarily strong way. Even when the child does not appear to be melancholic, there is, nonetheless, alongside the apparent temperament a nuance of melancholy. This is due to the child’s earth nature, the “earthiness” in the child’s being.
When we notice this trait in a child, we shall do well to try to interest him or her in music that passes from the minor to the major mood, from the melancholic strains of the minor to the major. The earthly child especially can be spiritualized by the movements demanded by music and eurythmy. A child with a distinct sanguine temperament and delicate melancholic features can easily be helped by painting. And even if such a child appears to have but little talent for music or eurythmy, we should still try our best to develop the disposition for it that is certainly there.
A child with a distinctly pronounced head organism will benefit from subjects such as history, geography, and the history of literature. But care must be taken not to remain in the contemplative element but, as I already pointed out yesterday in another context, to evoke moods, feelings, tension, curiosity that are again relaxed, satisfied, and so on.
Again, it is a matter of habitually seeing the harmony between spirit and body. The ancient Greeks had this knowledge, but it got lost. They really always saw in the effects of a work of art on human beings something they then also applied to the physical. They spoke of the crisis in an illness, of catharsis, and they spoke in the same way of the effects of a work of art and of education. The Greeks observed the processes that I described yesterday, and it is up to us to rediscover them, to learn to unite soul and spirit with the physical/corporeal in our thinking.
It is thus important that we use all our own temperamental energies, in order to teach history with a strong personal accent. Objectivity is something the children can develop later in life. To worry about objectivity, when we tell them about Brutus and Caesar, at the expense of expressing the feeling engendered in us during the dramatic presentation of their differences, their polarities—this would be bad teaching. As teachers, we must be involved. We do not need to wax passionate, to roar and rage, but we do need to express at least a delicate nuance of sympathy or antipathy toward Caesar and Brutus in our characterization. The children must be stimulated to participate.
History, geography, geology, and so on must be taught with real feeling. The latter subject is especially interesting—to feel deeply about the rocks beneath the earth. Goethe’s essay on the granite can here be of great help. I strongly recommend it to you. Read it with feeling, in order to see how a person could humanly relate—not merely in thinking, but in his whole being—to the primal father, the age-old, holy granite. This approach must, of course, then be extended to other subjects.
If we cultivate these responses in ourselves, we shall also make it possible for the children to experience and participate in them. This is naturally a more difficult approach, as it takes greater effort. But our teaching will be alive, a living experience. Believe me, everything we mediate to the children via feelings allows their inner life to grow, while an education that consists of mere thoughts and ideas is devoid of life, remains dead. Ideas and thoughts are no more than mirror images. With them we merely address the head, whose value lies in its connection with the past, its time in the spiritual world. When we give the children images and ideas that are made living through our strong feelings, we make a connection to what is significant for the earth, to the elements contained in the blood.
Let me give you an example. It is absolutely necessary for us to develop the appropriate feeling for the hostile, destructive forces in an airless space. The more graphically we show this—after the air has been pumped out—the more dramatically we can describe this terrible airless space, the more we shall achieve. In earlier times people referred to it as horror vacui. They experienced this horror streaming from it; their language contained it, and we must learn to discover this feeling again. We must learn to see a connection between an airless space and a thin, dried up person. Shakespeare indicated this in Julius Caesar:
Let me have men about me that are fat;
Sleek-headed men and such as sleep o’nights:
Yond Cassius has a lean and hungry look;
He thinks too much: such men are dangerous.
It is the well-padded whom we trust, rather than the lean, skinny, bald-headed person with cold intellect. We must feel this relation of a lean person or a spider to airless space. Then we shall be able to pass on to the children, through imponderables, the cosmic feeling that must be an integral part of the human being.
Again and again, when speaking of education, we must emphasize the necessity of connecting the totality of the human being to the objective world, because it is only then that we can bring a healthy element also to those aspects in education that are so harmfully influenced by materialistic thoughts. We cannot, my dear friends, be as outspoken as Herr Abderhalden who—after having been invited to a eurythmy performance where in my introduction I also mentioned the hygienic and other aspects of physical education—said: “As a physiologist I cannot see anything in physical education that is physiologically justified. On the contrary, physical education is, in my opinion, the most harmful activity imaginable; it has no educational value whatsoever. It is a barbarity.”
We cannot afford to be so direct. We would be attacked from every side, as happens today. It is so, isn’t it, when you really think about it, that all the exercises and activities of physical education, wherein the worst of materialistic concepts are applied to the physical body, have become idols, fetishes—be they systems concentrating on the strongly physical, the superphysical, or the subphysical; be it the Swedish method or the German. What the systems and methods have in common is the belief that the human being is no more than a physical organism—a belief resulting from the very worst ideas developed by the age of materialism, not in accord with the thoughts I have outlined.
The exercises are generally based on an assumption describing the ideal posture for the human being—the correct curvature of the spine, the form of the chest, the manner of moving the arms and hands. What we actually get from the exercises is certainly not a human being but merely the picture these people have made themselves of the human being. No wonder there are so many diagrams in the manuals. This picture of the human being lends itself to being modeled in a papier-mâché figure. Everything that is said of the human being in Swedish gymnastics can be found in such a papier-mâché doll. The living human being can then be used like a sack and made to imitate the lifeless dolls. The real human being is ignored, is lost sight of in such practices. All we have are papier-mâché figures.
In spite of the fact that they have become so popular and influential, these practices must be seen as infamous, really quite reprehensible, because of this exclusion of the real human being. The human being is theoretically excluded in the sciences; in modern gymnastics the human being is practically excluded, reduced to a papier-mâché figure. Such practices should never find their way into education. In good physical education, the students should only carry out movements and assume postures that they can also actually experience within. And they do experience them.
Let’s take a look at the breathing processes. We must know that we must bring the children to the point where the breathing- in bears a faint resemblance to tasting some favorite food. This experience should not go so far as to the actual perception of taste but merely to a faint resemblance of it; the freshness of the world ought to be experienced when breathing in. We should try to get the child to ask: “What is the intrinsic color of the air I am breathing in?” We shall indeed discover that as soon as breathing is correctly experienced, the child will have the feeling that “it is greenish, really actually green.” When we have brought a child to the point of experiencing inbreathing as greenish we have accomplished something. Then we shall also always notice something else: that the child will ask for a specific posture when breathing in. The inner experience stipulates the correct corresponding posture, and the right exercises will follow from it.
The same procedure will lead to the experience of the corresponding feeling in breathing out. As soon as the children, when breathing out, can feel that they really are fine, efficient boys and girls, as soon as they experience themselves as such, feel their strength, ask to apply their strength to the world outside, then they will also experience, in a way that is healthy and appropriate to their age, the corresponding abdominal movement, the movement of the limbs and the bearing of the head and arms. This rich feeling during breathing out will induce the children to move correctly.
Here the human being is employed. We can see the human being before us, no longer allowed to be a sack, imitating a papier-mâché figure. We are moving in accordance with the soul that then pulls the physical body after it. We adapt the physical movements to the children’s needs, to their inner, soul and spirit experience.
In the same way, we should encourage the inner experience the children’s physical nature asks for in other areas—in the movements of arms and legs, in running, and so forth. We can thus really connect physical education directly to eurythmy, as it should be connected. Eurythmy makes soul and spirit directly visible, ensouls and spiritualizes everything that moves in us. It makes use of everything human beings have developed for themselves during their evolution.
But—also—the physical can be spiritually experienced. We can experience our breathing and metabolism if we advance far enough in our efforts. It is possible to do this—to advance to the point that we can experience ourselves, including our physical organism. And then, what the children are—on a higher level, I would say—confronting in eurythmy can pass into physical education. It is certainly possible to connect the two activities, to build a bridge from the one to the other. But this kind of physical education should be based on the development of movements not from the mere experience of the physical/corporeal but rather from the experience of soul and spirit, by letting the children adapt the physical/corporeal to their experiences.
Of course, in order to achieve this we ourselves must learn a great deal. We must first work with these ideas before we apply them to both ourselves and especially before we apply them to our teaching. They don’t easily impress themselves on our memory. We are not unlike a mathematician who cannot remember formulae or theorems but who, at a given moment, is able to redevelop them. Our situation is the same. We must develop these ideas about the total human being—spirit, soul, and body—and we must always make them livingly present. Doing so will stand us in good stead. By working out of the totality of the human being we can have a stimulating effect on the children.
Again and again you will find that when you have spent long hours in preparing a lesson, when you have grappled with a subject and then enter the classroom, the children will learn differently than they would when taught by a “superior” lecturer or instructor who spent as little time as possible in preparation. I actually know people who on their way to school quickly read up the required material. Indeed, our education and teaching are deeply affected by the way we grapple not only with the immediate subject matter but also with all the other things connected to skills and methods. These things, too, should be worked and grappled with.
There are spiritual connections in life. If we have first heard a song in our mind, in the spirit, it will have a greater effect on the children when we teach it to them. These things are related. The spiritual world works in the physical. This activity, this work of the spiritual world, must be applied especially to education and didactics. If, for example, during the preparation for a religion lesson, the teacher experiences a naturally pious mood, the lesson will have a profound effect on the children. When such a mood is absent, the lesson will be of little value to them.

