The Occult Movement in the Nineteenth Century
GA 254
Lecture I
10 October 1915, Dornach
You will have realised from lectures given recently that in our times a materialistic view of the world, a materialistic way of thinking, is not the outcome of man's arbitrary volition but of a certain historical necessity.
Those who have some understanding of the spiritual process of human evolution know that, fundamentally speaking, in all earlier centuries and millennia man participated in spiritual life to a greater extent than has been the case during the last four or five hundred years. We know with what widespread phenomena this is connected. At the very beginning of Earth-evolution, the heritage of the Old Moon clairvoyance was working in mankind. We can envisage that in the earliest ages of Earth-evolution this faculty of ancient clairvoyance was very potent, very active, with the result that the range of man's spiritual vision in those times was exceedingly wide and comprehensive. This ancient clairvoyance then gradually diminished until times were reached when the great majority of human beings had lost the faculty of looking into the spiritual world, and the Mystery of Golgotha came in substitution. But a certain vestige of the old faculties of soul remained, and evidence of this is to be found, for example, in the nature-knowledge which was in existence until the fourteenth and fifteenth, and indeed until the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. This nature-knowledge was very different in character from modern natural science. It was a nature-knowledge able to some extent still to rely, not upon clear, Imaginative clairvoyance but nevertheless upon vestiges of the Inspirations and Intuitions which were then applied and elaborated by the so-called alchemists. If an alchemist of those times was honourable in his aims and not out for egotistic gain, he still worked, in a certain respect, with the old Inspirations and Intuitions. While he was engaged in his outer activities, vestiges of the old clairvoyance were still astir within him, although no longer accompanied by any reliable knowledge. But the number of people in whom these vestiges of ancient clairvoyance survived, steadily decreased. I have often said that these vestiges can very easily be drawn out of the human soul today in states of atavistic, visionary clairvoyance. We have shown in many different ways how this atavistic clairvoyance can manifest in our own time.
From all this you will realise that the nearer we come to our own period in evolution, the more we have to do with a decline of old soul-forces and a growth of tendencies in the human soul towards observation of the outer, material world. After slow and gradual preparation, this reached its peak in the nineteenth century, actually in the middle of that century. Little as this is realised today by those who do not concern themselves with such matters, it will be clear to men of the future that the materialistic tendencies of the second half of the nineteenth century had reached their peak in the middle of the century; it was then that these tendencies developed their greatest strength. But the consequence of every tendency is that certain talents develop and the really impressive greatness of the methods evolved by materialistic science stems from these tendencies of the soul to hold fast to the outer, material world of sense.
Now we must think of this phase in the evolution of humanity as being accompanied by another phenomenon. If we carry ourselves back in imagination to the primeval ages of humanity's spiritual development, we shall find that in respect of spiritual knowledge, men were in a comparatively fortunate position. Most human beings, in fact all of them, knew of the spiritual world through direct vision. Just as men of the modern age perceive minerals, plants and animals and are aware of tones and colours, so were the men of old aware of the spiritual world; it was concrete reality to them. So that in those olden times, when full waking consciousness of the outer, material world was dimmed during sleep or dream, there was really nobody who would not have been connected with the dead who had been near him during life. In the waking state a man could have intercourse with the living; during sleep or dream, with the dead. Teaching about the immortality of the soul would have been as superfluous in those primeval times as it would be nowadays to set out to prove that plants exist. Just imagine what would happen at the present time if anyone set out to prove that plants exist! Exactly the same attitude would have been adopted in primeval times if anyone had thought it necessary to prove that the soul also lives after death.
Humanity gradually lost this faculty of living in communion with the spiritual world. There were, of course, always individuals who used whatever opportunity was still available to develop seership. But even that became more and more difficult. How did men in olden times develop a particular gift of seership? If with insight today we study the philosophy of Plato, or what exists of that of Heraclitus, we must realise—and this applies especially to the still earlier Greek philosophies—that they are altogether different from later philosophies. Read the first chapter of my book Riddles of Philosophy, where I have shown how these ancient philosophers, Thales and Parmenides, Anaximenes and Heraclitus, are still influenced by their particular temperaments. This has not hitherto been pointed out; the first mention of it is in my book. Inevitably, therefore, some time must elapse before it is accepted—but that does not matter. Of Plato, we can still feel: this philosophy still lays hold of the whole man. When we come to Aristotle however, the feeling is that we have to do with an academic, learned philosophy. Therefore to understand Plato requires more insight than a modern philosopher usually has at his command. For the same reason there is a gulf between Plato and Aristotle. Aristotle is already a scholar in the modern sense. Plato is the last philosopher in the old Greek sense; he is a philosopher whose concepts are still imbued to some extent with life. As long as a philosophy of this kind exists, the link with the spiritual world is not broken, and indeed it continued for a long time, actually into the Middle Ages. The Middle Ages did not develop philosophy to further stages but simply took over Aristotelian philosophy; and up to a certain point of time this was all to the good. Platonic philosophy too was taken over in the same way.
Now in days of antiquity, as long as at least the aptitude for clairvoyance of a certain kind was present, something very significant took place when men allowed this philosophy to work upon them. Today, philosophy works only upon the head, only upon the thinking. The reason why so many people avoid philosophy is because they do not like thinking. And especially because philosophy offers nothing in the way of sensationalism they have no desire to study it. Ancient philosophy, however, when received into the human soul, was still able, because of its greater life-giving power, to quicken still existing gifts of seership. Platonic philosophy, nay, even Aristotelian philosophy, still had this effect. Being less abstract than the philosophies of modern times, they were still able to quicken faculties of seership inherent in the human soul. And so it came to pass that in men who devoted themselves to philosophy, faculties that were otherwise sinking below the surface were quickened to life. That is how seers came into existence. But because what had now to be learnt about the physical world—and this also applies to philosophy—was of importance for the physical plane alone, and became increasingly important, man alienated himself more and more from the remnants of the old clairvoyance. He could no longer penetrate to the inner depths of existence and it was increasingly difficult to become a seer. Nor will this again be possible until the new methods indicated as a beginning in the book Knowledge of the Higher Worlds. How is it achieved? are accepted by mankind as plausible.
We have heard that a period of materialism reached its peak—one could also say, its deepest point—in the middle of the nineteenth century. It is certain that conditions will become more and more difficult but the threads of connection with the earlier impulses in the evolution of humanity must nevertheless not be broken. The following diagram indicates how seership has developed:
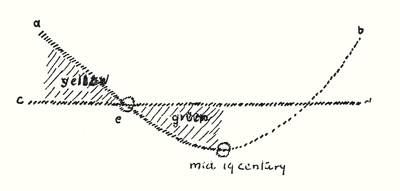
Here (yellow) seership is still present in full flower; it vanishes more and more completely until the lowest point is reached in the middle of the nineteenth century, and then there is again an ascent. But understanding of the spiritual world is not the same as seership. Just as in regard to the world, science is not the same thing as mere sensory perception, clairvoyance itself is a different matter from understanding what is seen. In the earliest epochs men were content, for the most part, with vision; they did not get to the point of thinking to any great extent about what was seen, for their seership sufficed. But now, thinking too came to the fore. The line a–b, therefore, indicates seership, vision; line c–d indicates thought or reflection about the spiritual worlds.
In ancient times man was occupied with his visions and thinking lay, as it were, in the subconscious region of the soul. The seers of old did not think, did not reflect; everything came to them directly through their vision. Thinking first began to affect seership about three or four thousand years B.C. There was a golden age in the old Indian, Persian, Egypto-Chaldean and also in very ancient Greek culture when thinking, still youthful and fresh, was wedded with vision in the human soul. In those times, thinking was not the laboured process it is in our day. Men had certain great, all-embracing notions, and, in addition, they had vision (e in diagram) . Something of the kind, although already in a weaker form, was present to a marked degree in the seers who founded the Samothracian Mysteries and there gave the monumental teaching of the four gods: Axieros, Axiokersos, Axiokersa and Kadmillos. In this great teaching which once had its home in the island of Samos, certain lofty concepts were imparted to those who were initiated in the Mysteries and they were able to unite with these concepts the still surviving fruits of ancient seership. It may be possible on some other occasion to speak of these things too in greater detail.1See Mystery Knowledge and Mystery Centres, Lecture XII. Fourteen lectures given in Dornach, 23rd November to 21st December, 1923. (Rudolf Steiner Press, 1973)
But then seership gradually sank below the threshold of consciousness and to call it up from the depths of the soul became more and more difficult. It was, of course, possible to retain some of the concepts, even to develop them further; and so finally a time came when there were initiates who were not necessarily seers—mark well, initiates who were not necessarily seers.
In different places where there were assemblies of these initiates, they simply adopted what was in part preserved from olden times, of which it could be affirmed that ancient seers revealed it—or what could be drawn forth from men who still possessed the faculties of atavistic clairvoyance. Conviction came partly through historical traditions, partly through experiments. Men convinced themselves that what their intellects thought was true. But as time went on the number of individuals in these assemblies who were still able to see into the spiritual world, steadily diminished, while the number of those who had theories about the spiritual world and expressed them in symbols and the like, steadily increased.
And now think of what inevitably resulted from this about the middle of the nineteenth century, when the materialistic tendencies of men had reached their deepest point. Naturally, there were people who knew that there is a spiritual world and also knew what is to be found in the spiritual world, but they had never seen that world. Indeed, the most outstanding savants in the nineteenth century were men who, although they had seen nothing whatever of the spiritual world, knew that it exists, could reflect about it, could even discover new truths with the help of certain methods and a certain symbolism that had been preserved in ancient tradition. To take one example only.—Nothing special is to be gained by looking at a drawing of a human being. But if a human form is drawn with a lion's head, or another with a bull's head, those who have learnt how these things are to be interpreted can glean a great deal from symbolical presentations of this kind—similarly, if a bull is depicted with the head of a man or a lion with the head of a man. Such symbols were in frequent use, and there were earnest assemblies in which the language of symbols could be learnt. I shall say no more about the matter than this, for the schools of Initiation guarded these symbols very strictly, communicating them to nobody who had not pledged himself to keep silence about them. To be a genuine knower a man needed only to have mastered this symbolic language—that is to say, a certain symbolic script.
And so the situation in the middle of the nineteenth century was that mankind in general, especially civilised mankind, possessed the faculty of spiritual vision deep down in the subconsciousness, yet had materialistic tendencies. There were, however, a great many people who knew that there is a spiritual world, who knew that just as we are surrounded by air, so we are surrounded by a spiritual world. But at the same time these men were burdened with a certain feeling of responsibility. They had no recourse to any actual faculties whereby the existence of a spiritual world could have been demonstrated, yet they were not willing to see the world outside succumbing altogether to materialism. And so in the nineteenth century a difficult situation confronted those who were initiated, a situation in face of which the question forced itself upon them: Ought we to continue to keep within restricted circles the knowledge that has come over to us from ancient times and merely look on while the whole of mankind, together with culture and philosophy, sinks down into materialism? Dare we simply look on while this is taking place? They dared not do so, especially those who were in real earnest about these things.
And so it came about that in the middle of the nineteenth century the words “esotericist” and “exotericist” which were used by the initiates among themselves, acquired a meaning deviating from what it had previously been. The occultists divided into exotericists and esotericists. If for purposes of analogy, expressions connected with modern parliaments are adopted—although naturally they are unsuitable here—the exotericists could be compared with the left-wing parties and the esotericists with the right-wing parties. The esotericists were those who wanted to continue to abide firmly by the principle of allowing nothing of what was sacred, traditional knowledge, nothing that might enable thinking men to gain insight into the symbolic language, to reach the public. The esotericists were, so to speak, the Conservatives among the occultists. Who, then—we may ask—were the exotericists ? They were and are those who want to make public some part of the esoteric knowledge. Fundamentally, the exotericists were not different from the esotericists, except that the former were inclined to follow the promptings of their feeling of responsibility, and to make part of the esoteric knowledge public.
There was widespread discussion at that time of which the outside world knows nothing but which was particularly heated in the middle of the nineteenth century. Indeed the clashes and discussions between the esotericists and the exotericists were far more heated than those between the Conservatives and Liberals in modern parliaments. The esotericists took the stand that only to those who had pledged themselves to strictest silence and were willing to belong to some particular society should anything be told concerning the spiritual world or any knowledge of it communicated. The exotericists said: If this principle is followed, people who do not attach themselves to some such society or league will sink altogether into materialism.
And now the exotericists proposed a way. I can tell you this today: the way proposed by the exotericists at that time is the way we ourselves are taking. Their proposal was that a certain part of the esoteric knowledge should be popularised. You see, too, how we ourselves have worked with the help of popular writings, in order that men may gradually be led to knowledge of the spiritual worlds.
In the middle of the nineteenth century things had not reached the point at which anyone would have ventured to admit that this was their conviction. In such circles there is, of course, no voting, and to say the following is to speak in metaphor. Nevertheless it can be stated that at the first ballot the esotericists won the day and the exotericists were obliged to submit. The society or league was not opposed, because of the good old precept of holding together. Not until more modern times has the point been reached when members are expelled or resign. Such things used not to happen because people understood that they must hold together in brotherhood. So the exotericists could do no other than submit. But their responsibility to the whole of mankind weighed upon them. They felt themselves, so to speak, to be guardians of evolution. This weighed upon them, with the result that the first ballot—if I may again use this word—was not adhered to, and—once again I will use a word which as it is drawn from ordinary parlance must be taken metaphorically—a kind of compromise was reached. This led to the following situation.
It was said, and this was also admitted by the esotericists: it is urgently necessary for humanity in general to realise that the surrounding world is not devoid of the spiritual, does not consist only of matter nor is subject to purely material laws; humanity must come to know that just as we are surrounded by matter, so too we are surrounded by the spiritual, and that man is not only that being who confronts us when we look at him in the material sense, but also has within him something that is of the nature of spirit and soul. The possibility of knowing this must be saved for humanity. On this, agreement was reached—and that was the compromise.
But the esotericists of the nineteenth century were not prepared to surrender the esoteric knowledge, and a different method had therefore to be countenanced. How it came into being is a complicated story. Particularly on occasions of the founding of Groups I have often spoken of what happened then. The esotericists said: We do not wish the esoteric knowledge to be made public, but we realise that the materialism of the age must be tackled.—In a certain respect the esotericists were basing themselves on a well-founded principle, for when we see repeatedly the kind of attitude that is adopted today towards esoteric knowledge we can understand and sympathise with those who said at that time that they would not hear of it being made public. We must realise, however, that over and over again it can be seen that open communication of esoteric knowledge leads to calamity, and that those who get hold of such knowledge are themselves the cause of obstacles and hindrances in the way of its propagation. In recent weeks we have often spoken of the fact that far too little heed is paid to these obstacles and hindrances. Most unfortunate experiences are encountered when it is a matter of making esoteric knowledge public. Help rendered with the best will in the world to individuals—even there the most elementary matters lead to calamity! You would find it hard to believe how often it happens that advice is given to some individual—but it does not please him. When the outer world says that an occultist who works as we work here, exercises great authority—that is just a catchword. As long as the advice given is acceptable, the occultist, as a rule, is not grumbled at; but when the advice is not liked, it is not accepted. People even browbeat one by declaring: “If you do not give me different advice, I simply cannot get on.” This may come to the point of actual threats, yet it had simply been a matter of advising the person in question for his good. But as he wants something different, he says: “I have waited long enough; now tell me exactly what I ought to do.” He was told this long ago, but it went against the grain. Finally things come to the point where those who were once the most credulous believers in authority become the bitterest enemies. They expect to get the advice they themselves want and when it is not to their liking they become bitter enemies. In our own time, therefore, experience teaches us that we cannot simply condemn the esotericists who refused to have anything to do with popularising the esoteric truths.
And so in the middle of the nineteenth century this popularising did not take place; an attempt was, however, made to deal in some way with the materialistic tendencies of the age. It is difficult to express what has to be said and I can only put it in words which, as such, were never actually uttered but none the less give a true picture. At that time the esotericists said: What can be done about this humanity? We may talk at length about the esoteric teaching but people will simply laugh at us and at you. At most you will win over a few credulous people, a few credulous women, but you will not win over those who cling to the strictly scientific attitude, and you will be forced to reckon with the tendencies of the age.
The consequence was that endeavours were made to find a method by means of which attention could be drawn to the spiritual world, and indeed in exactly the same way as in the material world attention is called to the fact that in a criminal the occipital lobe does not or does not entirely cover the corresponding part of his brain.—And so it came about that mediumship was deliberately brought on the scene. In a sense, the mediums were the agents of those who wished, by this means, to convince men of the existence of a spiritual world, because through the mediums people could see with physical eyes that which originates in the spiritual world; the mediums produced phenomena that could be demonstrated on the physical plane. Mediumship was a means of demonstrating to humanity that there is a spiritual world. The exotericists and the esotericists had united in supporting mediumship, in order to deal with the tendency of the times.
Think only of men such as Zöllner, Wallace, du Prel, Crookes, Butlerow, Rochas, Oliver Lodge, Flammarion, Morselli, Schiaparelli, Ochorowicz, James, and others—how did they become convinced of the existence of a spiritual world? It was because they had witnessed manifestations from the spiritual world. But everything that can be done by the spiritual world and by the initiates must, to begin with, be in the nature of attempts in the world of men. The maturity of humanity must always be tested. This support of mediumship, of spiritualism, was therefore also, in a certain sense, an attempt. All that the exotericists and esotericists who had agreed to the compromise could say was: What will come of it remains to be seen.—And what did, in fact, come of it?
Most of the mediums gave accounts of a world in which the dead are living. Just read the literature on the subject! For those who were initiated, the result was distressing in the utmost degree, the very worst there could possibly have been. For you see, there were two possibilities. One was this.—Mediums were used and they made certain communications. They were only able to relate what they communicated to the ordinary environment—in the material elements of which spirit is, of course, present. It was expected, however, that the mediums would bring to light all kinds of hidden laws of nature, hidden laws of elemental nature. But what actually happened was inevitable, and for the following reason.—
Man, as we know, consists of physical body, etheric body, astral body and ego. From the time of going to sleep to waking, therefore, the real man is in his ego and astral body; but then he is at the same time in the realm of the dead. The medium sitting there, however, is not an ego and an astral body. The ego-consciousness and also the astral consciousness have been suppressed and as a result the physical and etheric bodies become particularly active. In this condition the medium may come into contact with a hypnotist, or an inspirer—that is to say, with some other human being. The ego of another human being, or also the environment, can then have an effect upon the medium. It is impossible for the medium to enter the realm of the dead because the very members of his being which belong to that realm have been made inoperative. The mediums went astray; they gave accounts allegedly of the realm of the dead. And so it was obvious that this attempt had achieved nothing except to promulgate a great fallacy. One fine day, therefore, it had to be admitted that a path had been followed which was leading men into fallacy—to purely Luciferic teachings bound up with purely Ahrimanic observations. Fallacy from which nothing good could result had been spread abroad. This was realised as time went on.
You see, therefore, how an attempt was made to deal with the materialistic tendencies of the age and yet to bring home to men's consciousness that there is a spiritual world around us. To begin with, this path led to fallacy, as we have heard. But you can gather from this how necessary it is to take the other path, namely, actually to begin to make public part of the esoteric knowledge. This is the path that must be taken even if it brings one calamity after another. The very fact that we pursue Spiritual Science is, so to say, an acknowledgment of the need to carry into effect the principle of the exotericists in the middle of the nineteenth century. And the aim of the Spiritual Science we wish to cultivate is nothing else than to carry this principle into effect, to carry it into effect honourably and sincerely.
From all this it will be clear to you that materialism is something about which we cannot merely speculate; we must understand the necessity of its appearance, especially of the peak—or lowest point—it reached about the middle of the nineteenth century. The whole trend had of course begun a long time before then—certainly three, four or five centuries before. Man's leanings to the spiritual passed more and more into his subconsciousness, and this state of things reached its climax in the middle of the nineteenth century. But that too was necessary, in order that the purely materialistic talents of men might develop unhindered by occult faculties. A materialistic philosopher such as Kant, a materialistic philosopher from the standpoint of the Idealists of the nineteenth century—you can easily read about this in my book Riddles of Philosophy—could not have appeared if the occult faculties had not drawn into the background. Certain faculties develop in man when others withdraw, but while the one kind of faculties and talents develops outwardly, the other kind takes its own inner path. These three, four or five centuries were not, therefore, a total loss for the spiritual evolution of mankind. The spiritual forces have continued to develop below the threshold of consciousness, and if you think about what I have indicated in connection with von Wrangell's pamphlet2Published in Leipzig in 1914, with the title, Wissenschaft and Theosophie. on the subject of what he there calls the “dreamlike”, you will be able to recognise the existence of occult faculties which are merely waiting to unfold. They are present in abundance in the souls of men; it is only a matter of drawing them out in the right way.
It was necessary to say these things by way of introduction, and tomorrow we will pass on to the question of the relation between the Living and the Dead, bearing in mind that in one respect the wrong path resulting from the compromise between the exotericists and the esotericists has actually been instructive. To understand the nature of this compromise we must study the questions of birth and death and then show what effect the materialistic methods have had in this connection.

