The Bridge Between Universal Spirituality and the Physical Constitution of Man
GA 202
III. The Path to Freedom and Love and Their Significance in World-Events
19 December 1920, Dornach
Man stands in the world as thinking, contemplative being on the one hand, and as a doer, a being of action, on the other; with his feelings he lives within both these spheres. With his feeling he responds, on the one side, to what is presented to his observation; on the other side, feeling enters into his actions, his deeds. We need only consider how a man may be satisfied or dissatisfied with the success or lack of success of our deeds, how in truth all action is accompanied by impulses of feeling, and we shall see that feeling links the two poles of our being: the pole of thinking and the pole of deed, of action. Only through the fact that we are thinking beings are we Man in the truest sense. Consider too, how everything that gives us the consciousness of our essential manhood is connected with the fact that we can inwardly picture the world around us; we live in this world and can contemplate it. To imagine that we cannot contemplate the world would entail forfeiting our essential manhood. As doers, as men of action, we have our place in social life and fundamentally speaking, everything we accomplish between birth and death has a certain significance in this social life.
In so far as we are contemplative beings, thought operates in us; in so far as we are doers, that is to say, social beings, will operates in us. It is not the case in human nature, nor is it ever so, that things can simply be thought of intellectually side by side with one another; the truth is that whatever is an active factor in life can be characterized from one aspect or another; the forces of the world interpenetrate, flow into each other. Mentally, we can picture ourselves as beings of thought, also as beings of will. But even when we are entirely engrossed in contemplation, when the outer world is completely stilled, the will is continually active. And again, when we are performing deeds, thought is active in us. It is inconceivable that anything should proceed from us in the way of actions or deeds—which may also take effect in the realm of social life—without our identifying ourselves in thought with what thus takes place. In everything that is of the nature of will, the element of thought is contained; and in everything that is of the nature of thought, will is present. It is essential to be quite clear about what is involved here if we seriously want to build the bridge between the moral-spiritual world-order and natural-physical world-order.
Imagine that you are living for a time purely in reflection as usually understood, that you are engaging in no kind of outward activity at all, but are wholly engrossed in thought. You must realize, however, that in this life of thought, will is also active; will is then at work in your inner being, raying out its forces into the realm of thought. When we picture the thinking human being in this way, when we realize that the will is radiating all the time into his thoughts, something will certainly strike us concerning life and its realities. If we review all the thoughts we have formulated, we shall find in every case that they are linked with something in our environment, something that we ourselves have experienced. Between birth and death we have, in a certain respect, no thoughts other than those brought to us by life. If our life has been rich in experiences we have a rich thought-content; if our life experiences have been meagre, we have a meagre thought-content. The thought-content represents our inner destiny—to a certain extent. But within this life of thought there is something that is inherently our own; what is inherently our own is how we connect thoughts with one another and dissociate them again, how we elaborate them inwardly, how we arrive at judgments and draw conclusions, how we orientate ourselves in the life of thought—all this is inherently our own. The will in our life of thought is our own.
If we study this life of thought in careful self-examination we shall certainly realize that thoughts, as far as their actual content is concerned, come to us from outside, but that it is we ourselves who elaborate these thoughts.—Fundamentally speaking, therefore, in respect of our world of thought we are entirely dependent upon the experiences brought to us by our birth, by our destiny. But through the will, which rays out from the depths of the soul, we carry into what thus comes to us from the outer world, something that is inherently our own. For the fulfillment of what self-knowledge demands of us it is highly important to keep separate in our minds how, on the one side, the thought content comes to us from the surrounding world and how, on the other, the force of the will, coming from within our being, rays into the world of thought.
How, in reality, do we become inwardly more and more spiritual?—Not by taking in as many thoughts as possible from the surrounding world, for these thoughts merely reproduce in pictures this outer world, which is a physical, material world. Constantly to be running in pursuit of sensations does not make us more spiritual. We become more spiritual through the inner, will-permeated work we carry out in our thoughts. This is why meditation, too, consists in not indulging in haphazard thoughts but in holding certain easily envisaged thoughts in the very centre of our consciousness, drawing them there with a strong effort of will. And the greater the strength and intensity of this inner radiation of will into the sphere of thinking, the more spiritual we become. When we take in thoughts from the outer material world—and between birth and death we can take in only such thoughts—we become, as you can easily realize, unfree; for we are given over to the concatenations of things and events in the external world; as far as the actual content of the thoughts is concerned, we are obliged to think as the external world prescribes; only when we elaborate the thoughts do we become free in the real sense.
Now it is possible to attain complete freedom of our inner life if we increasingly efface and exclude the actual thought content, in so far as this comes from outside, and kindle into greater activity the element of will which streams through our thoughts when we form judgments, draw conclusions and the like. Thereby, however, our thinking becomes what I have called in my Philosophy of Spiritual Activity: purethinking. We think, but in our thinking there is nothing but will. I have laid particular emphasis on this in the new edition of the book (1918). What is thus within us lies in the sphere of thinking. But pure thinking may equally be called pure will. Thus from the realm of thinking we reach the realm of will, when we become inwardly free; our thinking attains such maturity that it is entirely irradiated by will; it no longer takes anything in from outside, but its very life is of the nature of will. By progressively strengthening the impulse of will in our thinking we prepare ourselves for what I have called in the Philosophy of Spiritual Activity, "Moral Imagination." Moral Imagination rises to the Moral Intuitions which then pervade and illuminate our will that has now become thought, or our thinking that has now become will. In this way we raise ourselves above the sway of the ‘necessity’ prevailing in the material world, permeate ourselves with the force that is inherently our own, and prepare for Moral Intuition. And everything that can stream into man from the spiritual world has its foundation, primarily, in these Moral Intuitions. Therefore freedom dawns when we enable the will to become an ever mightier and mightier force in our thinking.
Now let us consider the human being from the opposite pole, that of the will. When does the will present itself with particular clarity through what we do?—When we sneeze, let us say, we are also doing something, but we cannot, surely, ascribe to ourselves any definite impulse of will when we sneeze! When we speak, we are doing something in which will is undoubtedly contained. But think how, in speaking, deliberate intent and absence of intent, volition and absence of volition, intermingle. You have to learn to speak, and in such a way that you are no longer obliged to formulate each single word by dint of an effort of will; an element of instinct enters into speech. In ordinary life at least, it is so, and it is emphatically so in the case of those who do not strive for spirituality. Garrulous people, who are always opening their mouths in order to say something or other in which very little thought is contained, give others an opportunity of noticing—they themselves, of course, do not notice—how much there is in speech that is instinctive and involuntary. But the more we go out beyond our organic life and pass over to activity that is liberated, as it were, from organic processes, the more do we carry thoughts into our actions and deeds. Sneezing is still entirely a matter of organic life; speaking is largely connected with organic life; walking really very little; what we do with the hands, also very little. And so we come by degrees to actions which are more and more emancipated from our organic life. We accompany such actions with our thoughts, although we do not know how the will streams into these thoughts. If we are not somnambulists and do not go about in this condition, our actions will always be accompanied by our thoughts. We carry our thoughts into our actions, and the more our actions evolve towards perfection, the more are our thoughts being carried into them.
Our inner life is constantly deepened when we send will—our own inherent force—into our thinking, when we permeate our thinking with will. We bring will into thinking and thereby attain freedom. As we gradually perfect our actions we finally succeed in sending thoughts into these actions; we irradiate our actions—which proceed from our will—with thoughts. On the one side (inwards) we live a life of thought; we permeate this with the will and thus find freedom. On the other side (outwards) our actions stream forth from our will, and we permeate them with our thoughts. (Diagram IX)

But by what means do our actions evolve to greater perfection? To use an invariably controversial expression—How do we achieve greater perfection in our actions? We achieve this by developing in ourselves the force which can only be designated by the words: devotion to the outer world.—The more our devotion to the outer world grows and intensifies, the more does this outer world stir us to action. But it is just through unfolding devotion to the outer world that we succeed in permeating our actions with thoughts. What, in reality, is devotion to the outer world? Devotion to the outer world, which pervades our actions with thoughts, is nothing else than love.
Just as we attain freedom by irradiating the life of thought with will, so do we attain love by permeating the life of will with thoughts. We unfold love in our actions by letting thoughts radiate into the realm of the will; we develop freedom in our thinking by letting what is of the nature of will radiate into our thoughts. And because, as man, we are a unified whole, when we reach the point where we find freedom in the life of thought and love in the life of will, there will be freedom in our actions and love in our thinking. Each irradiates the other: action filled with thought is wrought in love; thinking that is permeated with will gives rise to actions and deeds that are truly free.
Thus you see how in the human being the two great ideals, freedom and love, grow together. Freedom and love are also that which man, standing in the world, can bring to realization in himself in such a way that, through him, the one unites with the other for the good of the world.
We must now ask: How is the ideal, the highest ideal, to be attained in the will-permeated life of thought?—Now if the life of thought were something that represented material processes, the will could never penetrate fully into the realm of the thoughts and increasingly take root there. The will would at most be able to ray into these material processes as an organizing force. Will can take real effect only if the life of thought is something that has no outer, physical reality. What, then, must it be?
You will be able to envisage what it must be if you take a picture as a starting-point. If you have here a mirror and here an object, the object is reflected in the mirror; if you then go behind the mirror, you find nothing. In other words, you have a picture—nothing more. Our thoughts are pictures in this same sense. (Diagram X) How is this to be explained?—In a previous lecture I said that the life of thought as such is in truth not a reality of the immediate moment. The life of thought rays in from our existence before birth, or rather, before conception. The life of thought has its reality between death and a new birth. And just as here the object stands before the mirror and what it presents is a picture—only that and nothing more—so what we unfold as the life of thought is lived through in the real sense between death and a new birth, and merely rays into our life since birth. As thinking beings, we have within us a mirror-reality only. Because this is so, the other reality which, as you know, rays up from the metabolic process, can permeate the mirror-pictures of the life of thought. If, as is very rarely the case today, we make sincere endeavors to develop unbiased thinking, it will be clear to us that the life of thought consists of mirror-pictures if we turn to thinking in its purest form—in mathematics. Mathematical thinking streams up entirely from our inner being, but it has a mirror-existence only. Through mathematics the make-up of external objects can, it is true, be analyzed and determined; but the mathematical thoughts in themselves are only thoughts, they exist merely as pictures. They have not been acquired from any outer reality.
Abstract thinkers such as Kant also employ an abstract expression. They say: mathematical concepts are a priori.—A priori, apriority, means "from what is before." But why are mathematical concepts a priori? Because they stream in from the existence preceding birth, or rather, preceding conception. It is this that constitutes their ‘apriority.’ And the reason why they appear real to our consciousness is because they are irradiated by the will. This is what makes them real. Just think how abstract modern thinking has become when it uses abstract words for something which, in its reality, is not understood! Men such as Kant had a dim inkling that we bring mathematics with us from our existence before birth, and therefore they called the findings of mathematics ‘a priori.’ But the term ‘a priori’ really tells us nothing, for it points to no reality, it points to something merely formal.
In regard to the life of thought, which with its mirror-existence must be irradiated by the will in order to become reality, ancient traditions speak of Semblance. (Diagram XI, Schein.)
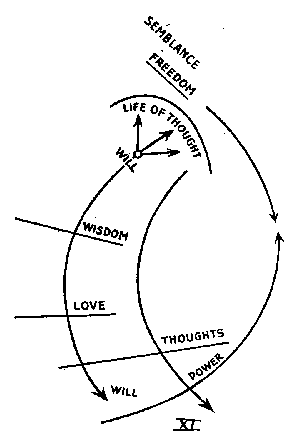
Let us now consider the other pole of man's nature, where the thoughts stream down towards the sphere of will, where deeds are performed in love. Here our consciousness is, so to speak, held at bay, it rebounds from reality. We cannot look into that realm of darkness—a realm of darkness for our consciousness—where the will unfolds whenever we raise an arm or turn the head, unless we take super-sensible conceptions to our aid. We move an arm; but the complicated process in operation there remains just as hidden from ordinary consciousness as what takes place in deep sleep, in dreamless sleep. We perceive our arm; we perceive how our hand grasps some object. This is because we permeate the action with thoughts. But the thoughts themselves that are in our consciousness are still only semblance. We live in what is real, but it does not ray into our ordinary consciousness. Ancient traditions spoke here of Power (Gewalt), because the reality in which we are living is indeed permeated by thought, but thought has nevertheless rebounded from it in a certain sense, during the life between birth and death. (Diagram XI.)
Between these two poles lies the balancing factor that unites the two—unites the will that rays towards the head with the thoughts which, as they flow into deeds wrought with love, are, so to say, felt with the heart. This means of union is the life of feeling, which is able to direct itself towards the will as well as towards the thoughts. In our ordinary consciousness we live in an element by means of which we grasp, on the one side, what comes to expression in our will-permeated thought with its predisposition to freedom, while on the other side, we try to ensure that what passes over into our deeds is filled more and more with thoughts. And what forms the bridge connecting both has since ancient times been called Wisdom. (Diagram XI.)
In his fairy-tale, The Green Snake and the Beautiful Lily, Goethe has given indications of these ancient traditions in the figures of the Golden King, the Silver King, and the Brazen King. We have already shown from other points of view how these three elements must come to life again, but in an entirely different form—these three elements to which ancient instinctive knowledge pointed and which can come to life again only if man acquires the knowledge yielded by Imagination, Inspiration, Intuition.
But what is it that is actually taking place as man unfolds his life of thought?—Reality is becoming semblance! It is very important to be clear about this. We carry about with us our head, which with its hard skull and tendency to ossification, presents, even outwardly, a picture of what is dead, in contrast to the rest of the living organism. Between birth and death we bear in our head that which, from an earlier time when it was reality, comes into us as semblance, and from the rest of our organism we pervade this semblance with the element issuing from our metabolic processes, we permeate it with the real element of the will. There we have within us a seed, a germinating entity which, first and foremost, is part of our manhood, but also means something in the cosmos. Think of it—a man is born in a particular year; before then he was in the spiritual world. When he passes out of the spiritual world, thought which there is reality, becomes semblance, and he leads over into this semblance the forces of his will which come from an entirely different direction, rising up from parts of his organism other than the head. That is how the past, dying away into semblance, is kindled again to become reality of the future.
Let us understand this rightly. What happens when man rises to pure thinking, to thinking that is irradiated by will?—On the foundation of the past that has dissolved into semblance, through fructification by the will which rises up from his egohood, there unfolds within him a new reality leading into the future. He is the bearer of the seed into the future. The thoughts of the past, as realities, are as it were the mother-soil; into this mother-soil is laid that which comes from the individual egohood, and the seed is sent on into the future for future life.
On the other side, man evolves by permeating his deeds and actions, his will-nature, with thoughts; deeds are performed in love. Such deeds detach themselves from him. Our deeds do not remain confined to ourselves. They become world-happenings; and if they are permeated by love, then love goes with them. As far as the cosmos is concerned, an egotistical action is different from an action permeated by love. When, out of semblance, through fructification by the will, we unfold that which proceeds from our inmost being, then what streams forth into the world from our head encounters our thought-permeated deeds. Just as when a plant unfolds it contains in its blossom the seed to which the light of the sun, the air outside, and so on, must come, to which something must be brought from the cosmos in order that it may grow, so what is unfolded through freedom must find an element in which to grow through the love that lives in our deeds.
Thus does man stand within the great process of world-evolution, and what takes place inside the boundary of his skin and flows out beyond his skin in the form of deeds, has significance not only for him but for the world, the universe. He has his place in the arena of cosmic happenings, world-happenings. In that what was reality in earlier times becomes semblance in man, reality is ever and again dissolved, and in that his semblance is quickened again by the will, new reality arises. Here we have—as if spiritually we could put our very finger upon it—what has also been spoken of from other points of view.—There is no eternal conservation of matter! Matter is transformed into semblance and semblance is transformed to reality by the will. The law of the conservation of matter and energy affirmed by physics is a delusion, because account is taken of the natural world only. The truth is that matter is continually passing away in that it is transformed into semblance; and a new creation takes place in that through Man, who stands before us as the supreme achievement of the cosmos, semblance is again transformed into Being (Sein.)
We can also see this if we look at the other pole—only there it is not so easy to perceive. The processes which finally lead to freedom can certainly be grasped by unbiased thinking. But to see rightly in the case of this other pole needs a certain degree of spiritual-scientific development. For here, to begin with, ordinary consciousness rebounds when confronted by what ancient traditions called Power. What is living itself out as Power, as Force, is indeed permeated by thoughts; but the ordinary consciousness does not perceive that just as more and more will, a greater and greater faculty of judgment, comes into the world of thought, so, when we bring thoughts into the will-nature, when we overcome the element of Power more and more completely, we also pervade what is merely Power with the light of thought. At the one pole of man's being we see the overcoming of matter; at the other pole, the new birth of matter.
As I have indicated briefly in my book, Riddles of the Soul, man is a threefold being: as nerve-and-sense man he is the bearer of the life of thought, of perception; as rhythmic being (breathing, circulating blood), he is the bearer of the life of feeling; as metabolic being, he is the bearer of the life of will. But how, then, does the metabolic process operate in man when will is ever more and more unfolded in love? It operates in that, as man performs such deeds, matter is continually overcome.—And what is it that unfolds in man when, as a free being, he finds his way into pure thinking, which is, however, really of the nature of will?—Matter is born!—We behold the coming-into-being of matter! We bear in ourselves that which brings matter to birth: our head; and we bear in ourselves that which destroys matter, where we can see how matter is destroyed: our limb-and-metabolic organism.
This is the way in which to study the whole man. We see how what consciousness conceives of in abstractions is an actual factor in the process of World-Becoming; and we see how that which is contained in this process of World-Becoming and to which the ordinary consciousness clings so firmly that it can do no other than conceive it to be reality—we see how this is dissolved away to nullity. It is reality for the ordinary consciousness, and when it obviously does not tally with outer realities, then recourse has to be taken to the atoms, which are considered to be firmly fixed realities. And because man cannot free himself in his thoughts from these firmly fixed realities, one lets them mingle with each other, now in this way, now in that. At one time they mingle to form hydrogen, at another, oxygen; they are merely differently grouped. This is simply because people are incapable of any other belief than that what has once been firmly fixed in thought must also be as firmly fixed in reality.
It is nothing else than feebleness of thought into which one lapses when he accepts the existence of fixed, ever-enduring atoms. What reveals itself to us through thinking that is in accordance with reality is that matter is continually dissolved away to nullity and continually rebuilt out of nullity. It is only because whenever matter dies away, new matter comes into being, that people speak of the conservation of matter. They fall into the same error into which they would fall, let us say, if a number of documents were carried into a house, copied there, but the originals burned and the copies brought out again, and then they were to believe that what was carried in had been carried out—that it is the same thing. The reality is that the old documents have been burned and new ones written. It is the same with what comes into being in the world, and it is important for our knowledge to advance to this point. For in that realm of man's being, where matter dies away into semblance and new matter arises, there lies the possibility of freedom, and there lies the possibility of love. And freedom and love belong together, as I have already indicated in my Philosophy of Spiritual Activity.
Those who on the basis of some particular conception of the world speak of the imperishability of matter, annul freedom on the one side and the full development of love on the other. For only through the fact that in man the past dies away, becomes semblance, and the future is a new creation in the condition of a seed, does there arise in us the feeling of love—devotion to something to which we are not coerced by the past—and freedom—action that is not predetermined. Freedom and love are, in reality, comprehensible only to a spiritual-scientific conception of the world, not to any other. Those who are conversant with the picture of the world that has appeared in the course of the last few centuries will be able to assess the difficulties that will have to be overcome before the habits of thought prevailing in modern humanity can be induced to give way to this unbiased, spiritual-scientific thinking. For in the picture of the world existing in natural science there are really no points from which we can go forward to a true understanding of freedom and love.
How the natural-scientific picture of the world on the one side, and on the other, the ancient, traditional picture of the world, are related to a truly progressive, spiritual-scientific development of humanity—of this we will speak on some other occasion.

